Question: Question 18 only. Please provide Excel calculations. Week Demand 60 90 60 130 65 75 100 85 2. Suppose a customer cancels an order of
Question 18 only. Please provide Excel calculations.
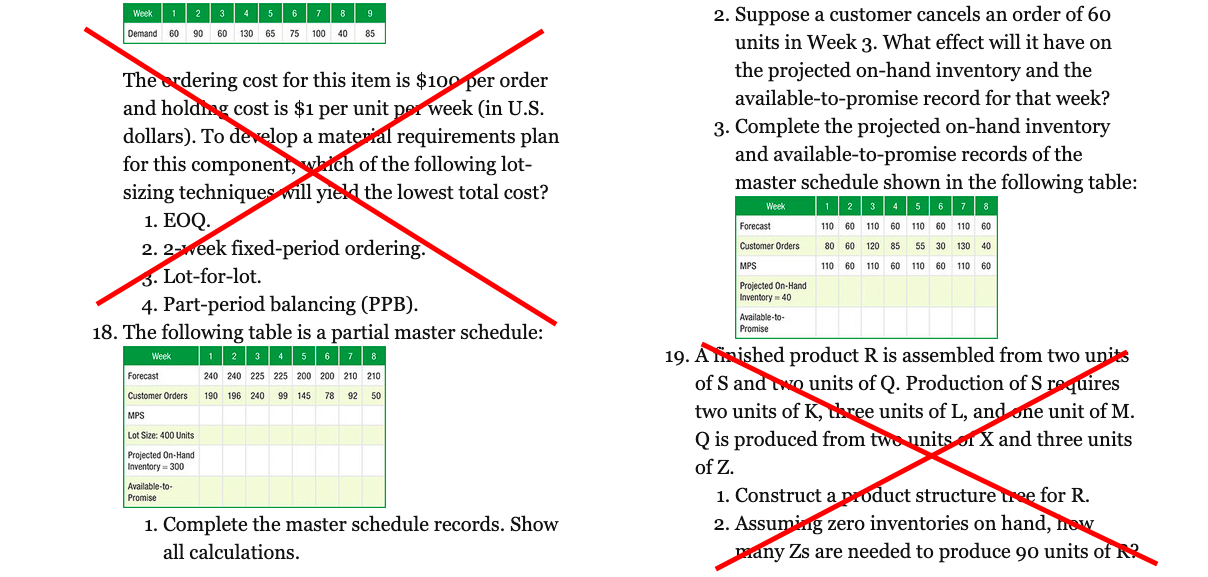
Week Demand 60 90 60 130 65 75 100 85 2. Suppose a customer cancels an order of 60 units in Week 3. What effect will it have on the projected on-hand inventory and the available-to-promise record for that week? 3. Complete the projected on-hand inventory and available-to-promise records of the master schedule shown in the following table: The ordering cost for this item is $10 per order and holding cost is $1 per unit per week (in U.S. dollars). To develop a material requirements plan for this component, which of the following lot- sizing techniques will yield the lowest total cost? 1. EOQ. 2. 2-week fixed-period ordering. 3. Lot-for-lot. 4. Part-period balancing (PPB). 18. The following table is a partial master schedule: Week Forecast 110 60 110 60 110 60 Customer Orders 80 60 120 85 55 30 130 40 MPS 110 60 110 60 110 60 110 60 Projected On-Hand Inventory - 40 Available-to- Promise Week Forecast Customer Orders MPS 240 240 225 225 200 200 210 210 190 196 24099 145 78 92 50 Lot Size: 400 Units Projected On-Hand Inventory - 300 Available to Promise 19. A finished product R is assembled from two units of S and two units of Q. Production of S requires two units of K, dree units of L, and one unit of M. Q is produced from two units X and three units of Z. 1. Construct a product structure tree for R. 2. Assuming zero inventories on hand, how many Zs are needed to produce 90 units of 1. Complete the master schedule records. Show all calculations. Week Demand 60 90 60 130 65 75 100 85 2. Suppose a customer cancels an order of 60 units in Week 3. What effect will it have on the projected on-hand inventory and the available-to-promise record for that week? 3. Complete the projected on-hand inventory and available-to-promise records of the master schedule shown in the following table: The ordering cost for this item is $10 per order and holding cost is $1 per unit per week (in U.S. dollars). To develop a material requirements plan for this component, which of the following lot- sizing techniques will yield the lowest total cost? 1. EOQ. 2. 2-week fixed-period ordering. 3. Lot-for-lot. 4. Part-period balancing (PPB). 18. The following table is a partial master schedule: Week Forecast 110 60 110 60 110 60 Customer Orders 80 60 120 85 55 30 130 40 MPS 110 60 110 60 110 60 110 60 Projected On-Hand Inventory - 40 Available-to- Promise Week Forecast Customer Orders MPS 240 240 225 225 200 200 210 210 190 196 24099 145 78 92 50 Lot Size: 400 Units Projected On-Hand Inventory - 300 Available to Promise 19. A finished product R is assembled from two units of S and two units of Q. Production of S requires two units of K, dree units of L, and one unit of M. Q is produced from two units X and three units of Z. 1. Construct a product structure tree for R. 2. Assuming zero inventories on hand, how many Zs are needed to produce 90 units of 1. Complete the master schedule records. Show all calculationsStep by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


