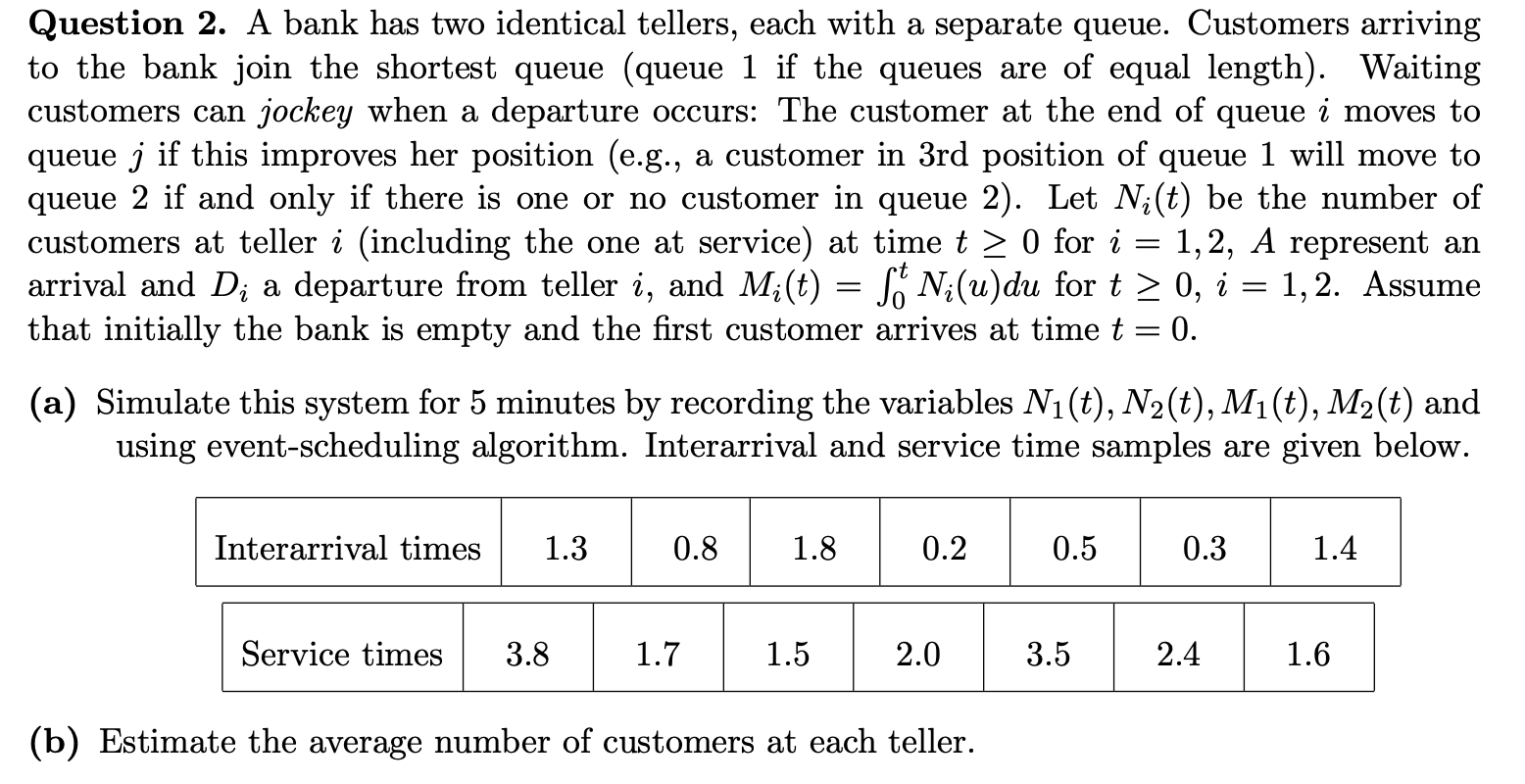
Question: Question 2. A bank has two identical tellers, each with a separate queue. Customers arriving to the bank join the shortest queue (queue 1 if
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


