Question: Question 2: Cost Estimation (7 marks) You have been asked to estimate the cost of manufacturing 100 extreme-weather tents that can be used by refugees
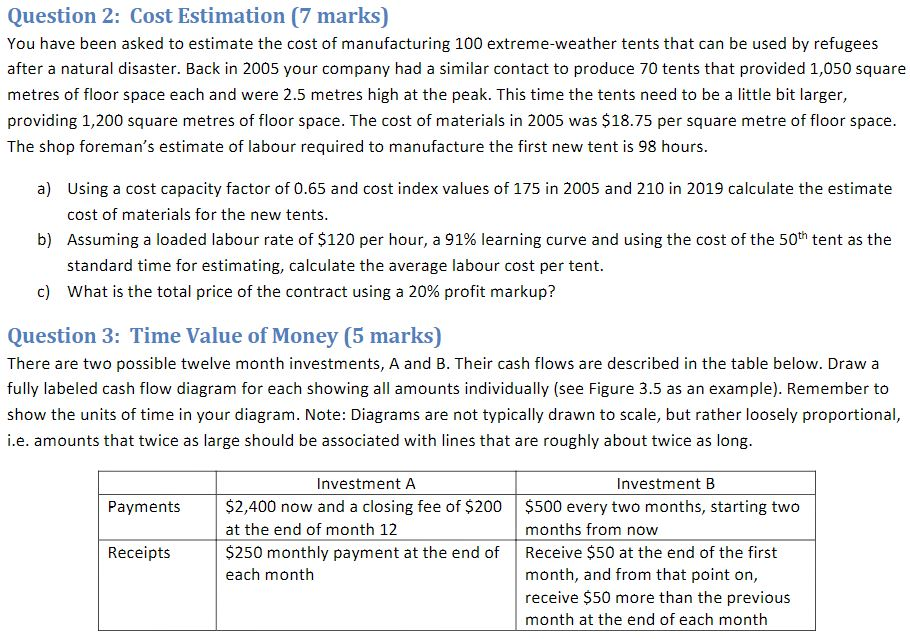
Question 2: Cost Estimation (7 marks) You have been asked to estimate the cost of manufacturing 100 extreme-weather tents that can be used by refugees after a natural disaster. Back in 2005 your company had a similar contact to produce 70 tents that provided 1,050 square metres of floor space each and were 2.5 metres high at the peak. This time the tents need to be a little bit larger, providing 1,200 square metres of floor space. The cost of materials in 2005 was $18.75 per square metre of floor space. The shop foreman's estimate of labour required to manufacture the first new tent is 98 hours. a) Using a cost capacity factor of 0.65 and cost index values of 175 in 2005 and 210 in 2019 calculate the estimate cost of materials for the new tents. b) Assuming a loaded labour rate of $120 per hour, a 91% learning curve and using the cost of the 50th tent as the standard time for estimating, calculate the average labour cost per tent. c) What is the total price of the contract using a 20% profit markup? Question 3: Time Value of Money (5 marks) There are two possible twelve month investments, A and B. Their cash flows are described in the table below. Draw a fully labeled cash flow diagram for each showing all amounts individually (see Figure 3.5 as an example). Remember to show the units of time in your diagram. Note: Diagrams are not typically drawn to scale, but rather loosely proportional, i.e. amounts that twice as large should be associated with lines that are roughly about twice as long. Payments Investment A $2,400 now and a closing fee of $200 at the end of month 12 $250 monthly payment at the end of each month Receipts Investment B $500 every two months, starting two months from now Receive $50 at the end of the first month, and from that point on, receive $50 more than the previous month at the end of each month Question 2: Cost Estimation (7 marks) You have been asked to estimate the cost of manufacturing 100 extreme-weather tents that can be used by refugees after a natural disaster. Back in 2005 your company had a similar contact to produce 70 tents that provided 1,050 square metres of floor space each and were 2.5 metres high at the peak. This time the tents need to be a little bit larger, providing 1,200 square metres of floor space. The cost of materials in 2005 was $18.75 per square metre of floor space. The shop foreman's estimate of labour required to manufacture the first new tent is 98 hours. a) Using a cost capacity factor of 0.65 and cost index values of 175 in 2005 and 210 in 2019 calculate the estimate cost of materials for the new tents. b) Assuming a loaded labour rate of $120 per hour, a 91% learning curve and using the cost of the 50th tent as the standard time for estimating, calculate the average labour cost per tent. c) What is the total price of the contract using a 20% profit markup? Question 3: Time Value of Money (5 marks) There are two possible twelve month investments, A and B. Their cash flows are described in the table below. Draw a fully labeled cash flow diagram for each showing all amounts individually (see Figure 3.5 as an example). Remember to show the units of time in your diagram. Note: Diagrams are not typically drawn to scale, but rather loosely proportional, i.e. amounts that twice as large should be associated with lines that are roughly about twice as long. Payments Investment A $2,400 now and a closing fee of $200 at the end of month 12 $250 monthly payment at the end of each month Receipts Investment B $500 every two months, starting two months from now Receive $50 at the end of the first month, and from that point on, receive $50 more than the previous month at the end of each month
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


