Question: Question 2: For the circuit presented in figure 2, determine: 1- Determine Ici, VCI, VE2 and IE2 2- Determine IB2, Icz, Vez Computer Engineering
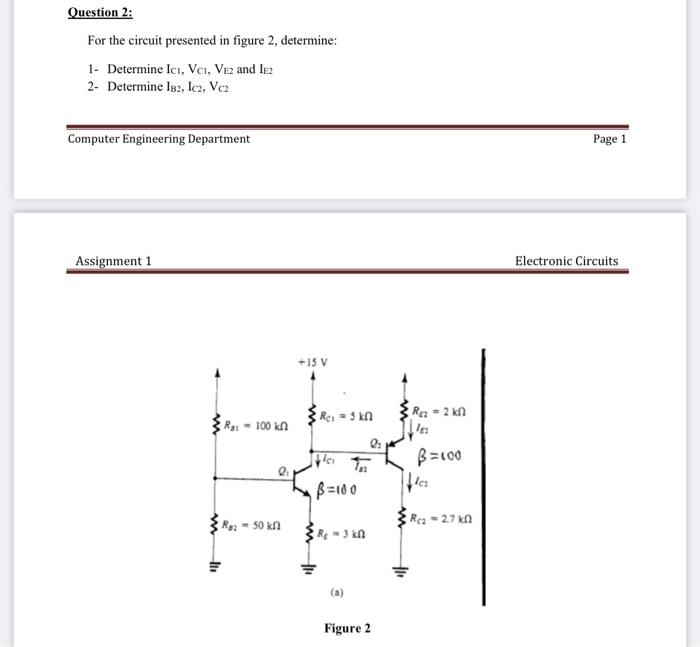

Question 2: For the circuit presented in figure 2, determine: 1- Determine Ici, VCI, VE2 and IE2 2- Determine IB2, Icz, Vez Computer Engineering Department Assignment 1 Ra: 100 kn +15 V Re = 5kn Q: R-2 kn In B=100 Raz-50 kn B=100 RE-3 kn Re: -2.7 kn J Figure 2 Page 1 Electronic Circuits 6. What is the output of this program? } import java.util.*; class Output public static void main(String args[]) ArrayList obj new ArrayList(); obj.add("A"); obj.add (0, "B"); System.out.println (obj.size()); a. 2 b. 3 c. 0 d. 4 e. I 7. Big-Theta notation is: a. A lower bound on the runtime complexity of an algorithm. b. A tight bound on the runtime complexity of an algorithm. c. An upper bound on the runtime complexity of an algorithm. d. A side bound on the runtime complexity of an algorithm. e. Has nothing to do with the algorithm's runtime complexity. 8. What is the tightest bound possible for f(N) N3(4 log N-log N) + (N2)? a. 0(N2) b. (Nlog N) c. (N) d. (log N) c. 8(N) 9. Big-Omega notation is: a. A lower bound on the runtime complexity of an algorithm. b. An upper bound on the runtime complexity of an algorithm. c. A tight bound on the runtime complexity of an algorithm. d. A side bound on the runtime complexity of an algorithm. e. Has nothing to do with the algorithm's runtime complexity. 10. What is the tightest bound possible for f(N) = N(N + 1)? a. (N2) b. 0(N) c. (N8) d. (N4) e. (N5)
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


