Question: QUESTION 2 (MATRIX MANIPULATION A matrix is an array of numbers of size m by n (i.e., mxn). When we multiply 2 matrices, we multiply


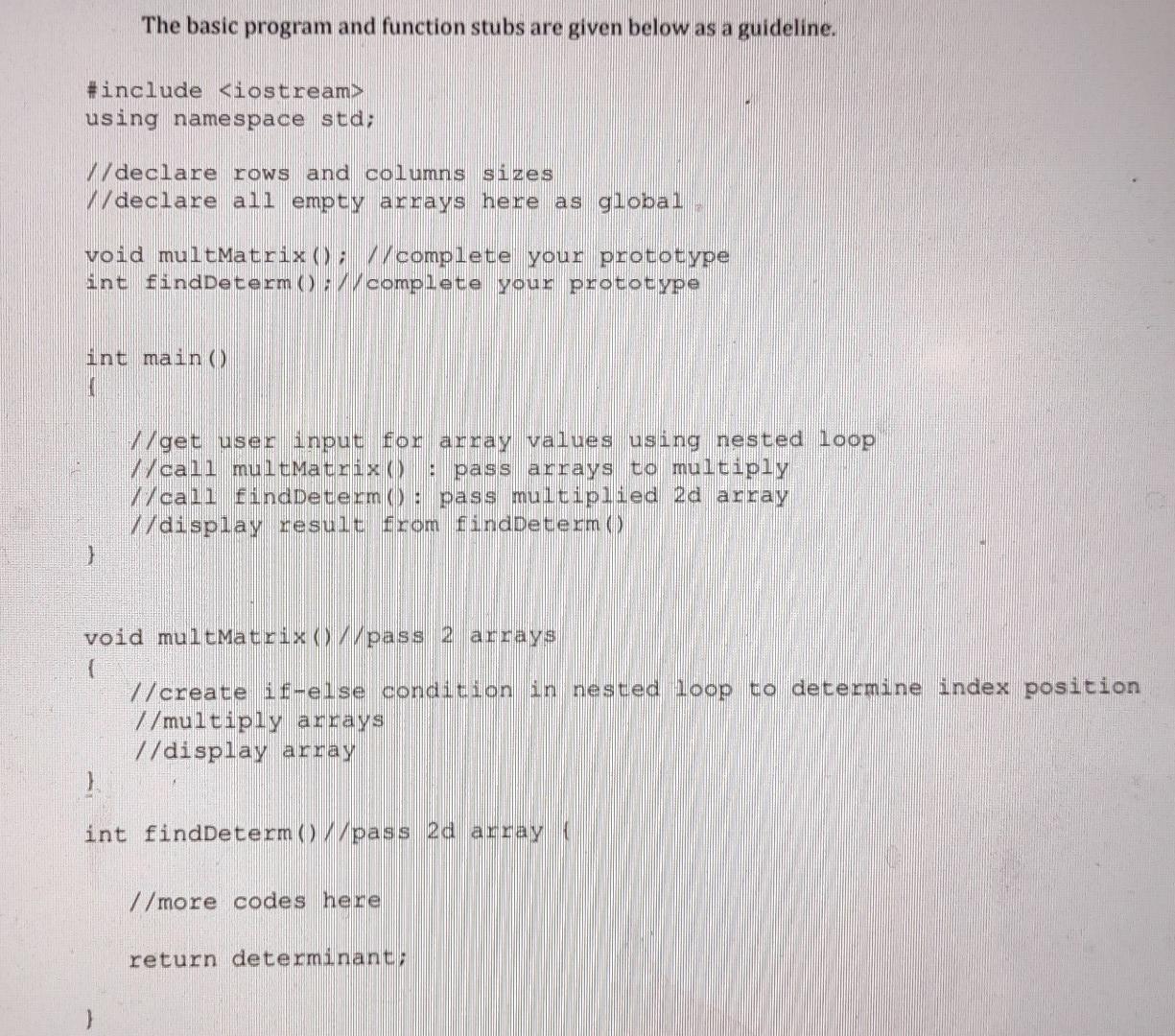
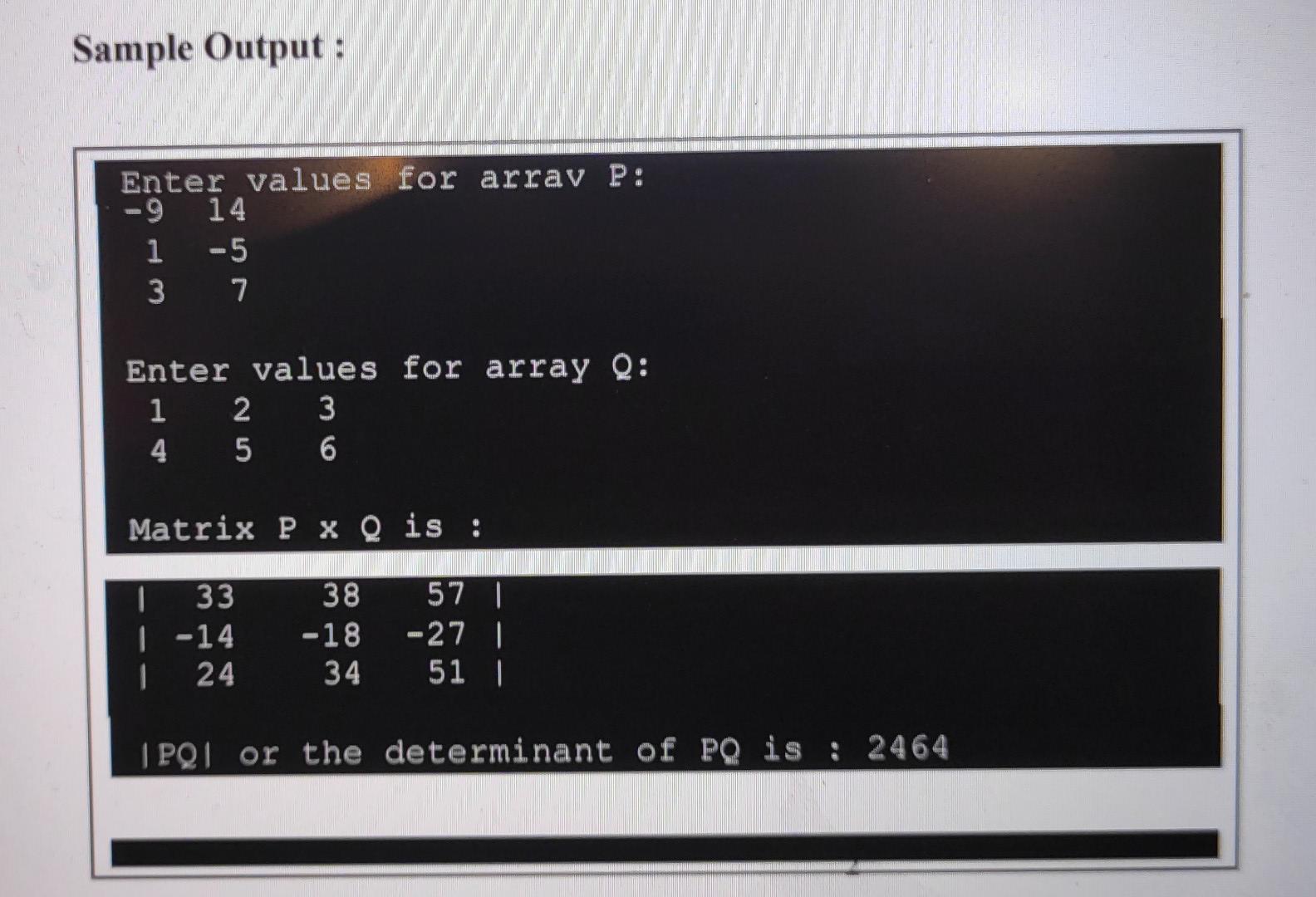
QUESTION 2 (MATRIX MANIPULATION A matrix is an array of numbers of size m by n (i.e., mxn). When we multiply 2 matrices, we multiply the matching numbers, then sum them up. Multiplying a matrix of size mxn with another matrix of size nxq will result in a matrix of size mxq. An example is shown in Figure 2: 18:11 S X pa + ad pb+ge pc +qf ra + sd rb + se ra + sf ta + ud tb + ue to + uf Matrix 3 x 2 Matrix 2 x 3 Matrix 3 x 3 Figure 1: Multiplication of Matrix 3 x 2 and 2 x 3 The determinant of a matrix represented by two vertical lines on either side |A is a special number that can be calculated from a square matrix. Figure 2 shows an example of how a determinant for matrix A is calculated: a la Matrix A la a 6 IA = ad - be a Matrix B ERI d B = a (ei - hf) - b (di - g) + c (dh - ge) Figure 2: Determinant of Matrix 2 x 2 and 3 X 3 Write a C++ program that multiplies 2 matrices and return the determinant of the multiplied matrix. Your program shall include the following: a) Define two 2 dimensional arrays, P and Q that each represents a matrix of size 3 x 2 and a matrix of size 2 x 3. Request the user to enter the values for the 2 arrays using advanced pointer notations (refer to your slides for the list of array pointer notations). b) Create a function named multMatrix( that passes as arguments, the values of array P and Q multiplies them and store the results in a new matrix PQ. Use pointer notations to multiply your arrays. Display your multiplied arrays. c) Create a function named find Determ( that passes as argument, the values of array PQ and return its determinant from the function. Use advanced pointer notations to perform your calculation. Display your result in main(). The basic program and function stubs are given below as a guideline. #include
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


