Question: Question 2 The following table gives the expected returns and probabilities of various states of nature for securities A and B: State Boom Normal Recession
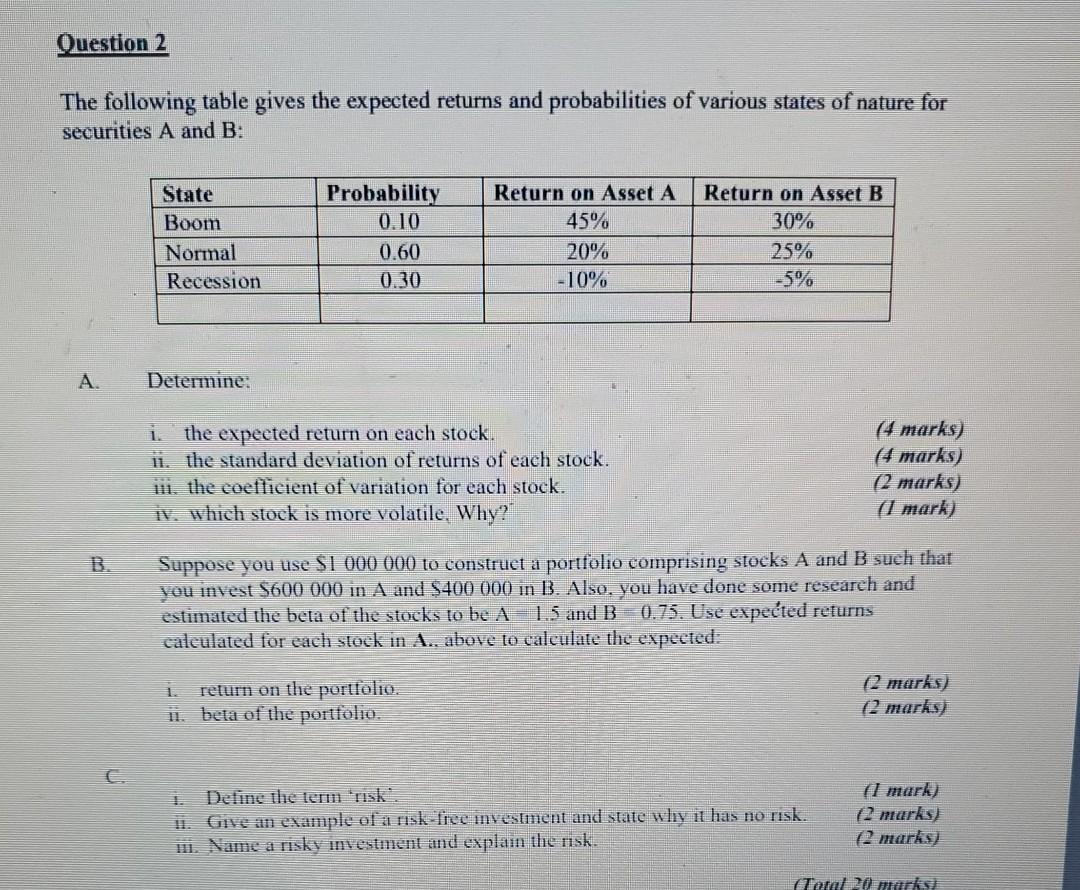



Question 2 The following table gives the expected returns and probabilities of various states of nature for securities A and B: State Boom Normal Recession Probability 0.10 0.60 0.30 Return on Asset A 45% 20% -10% Return on Asset B 30% 25% -5% A Determine: i the expected return on each stock. ii. the standard deviation of returns of each stock. iii. the coefficient of variation for each stock. it, which stock is more volatile. Why? (4 marks) (4 marks) (2 marks) (1 mark) B. Suppose you use $1 000 000 to construct a portfolio comprising stocks A and B such that you invest $600 000 in A and $400 000 in B. Also, you have done some research and estimated the beta of the stocks to be A 1.5 and B 0.75. Use expected returns calculated for each stock in A., above to calculate the expected: 11 return on the portfolio. ii. beta of the portfolio. (2 marks) (2 marks) Define the lemn risk. ii. Give an example of a risk-fiec investment and state why it has no risk. m. Name a risky investment and explain the risk. il mark) (2 marks) c marks) Tata 20 Faks A firm introduces a new product and must enter the market now to secure a niche but it will not know the demand for the product until after a year. There is a 75% chance that demand will be high and a 25% chance that it will be low. If demand is high, same firm will earn $4M in the first year, after which a decision must be made to keep the project as is and not expand. If it does not expand, PV of cash flow at the end of year one will be $16M. If it takes advantage of high demand to expand, the cost will be $2M and cash flow at year end will be $30M. If demand is low, said project will earn $0.8M in the first year and a decision must be made to keep project as is and not terminate. If the project is not terminated, PV of cash flow will be $3M in year one. If the company decides to terminate, cost of termination will be $0.5M and PV of cash flow from liquidation of project will be $6M at the end of year one. i Draw a decision tree for this project. il. Determine the value of the real options. (7 marks) (8 marks) B. i. Briefly explain what is meant by a real option in capital budgeting. Give TWO (2) examples. (3 marks) 11. Why is it important to consider real options in the capital budgeting process? (2 marks) al 27 Question 1 A Welders PLC, which currently has negligible cash holdings, expects to have to make a series of cash payments totalling $3 000 000 over the forthcoming year. These will become due at a steady rate and can be met by making periodic sales from existing holdings of short-term securities. According to the company's financial advisors, the most likely average percentage rate of return on these securities is 9% over the forthcoming year, although this estimate is highly uncertain. Whenever the company sells securities, it incurs a transaction fee (T) of $50. i. Calculate the optimal cash balance for the company. ii. What is the optimal number of times Welders should sell securities? iii. Determine the cost of holding cash resulting from this policy. iv. How would you evaluate this approach to cash management? (2 marks) (1 mark) 13 marks) 3 marks) B A company has set a safety cash balance of $6 000. The standard deviation of the daily cash balance during the last year was $600 and the transaction cost was $&. The company also has an opportunity to invest idle cash in marketable securities at an annual interest rate of 12%. Assume a 360-day year. Determine: i. daily opportunity cost (interest rate) and the variance of daily cash flow. (2 marks) 11. the targeted cash balance (the return point) for the limm. (3 marks 111. the upper limit of cash balance (1 mark) iv. the number of short-term securities to be purchased or sold once the upper or lower limit is reached. (2 marks) V. how you would evaluate this approach to cash management. 3 marks) (Totul 20 marks) As an investment manager at H & L Securities, you are preparing for the next meeting of the investment committee which has requested you to assess the capital structure of Industrial Production Limited (IPL), a manufacturer of industrial products. The following information is available to assist your assessment: A. i. Preferred Stock: Industrial Production Limited issued a 10% preferred share which sold for $100 per share par value. The cost of issuing and selling the stock was $2 per share. Calculate the cost of this preferred share. (2 marks) ii. Common Stock: The company has a common share with a market price of $25 per share and an expected dividend of $2 per share at the coming year end. Growth rate in dividends has been 5%. Calculate the cost of IPL's common equity. (2 marks) ui. Debt Determine the after-tax cost of debt. Industrial Production Limited can borrow funds at an interest rate of 11% per year. Assume that the tax rate is 35%. (2 marks) iv. Use the information above to determine the organisation's WACC if the target capital structure comprises 40% debt, 10% preferred stock and 50% common stock. (3 marks) B. 1. The firm has a beta of 1.2. Markel retum equals 14% and a risk-free rate of return is 6. Determine IPL's cost of common equity. (3 marks) ii. If the company's capital structure is modified to 30% debt. 25% preferred stock and 45% common stock, what is its new WACC? 13 marks) in. Industrial Production Limited is expected to pay a year-end dividend of $2.50 per share and its flotation cost is 5%. Investors have projected a growth rate of 12% per annum. What is the cost of retained earnings, using the discounted cash flow approach? (2 marks) iv. Calculate the cost of issuing new common stock. (3 marks
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


