Question: Question 3: Analyze the differences between static and flexible budgets. (36 points) What are the differences between the static and flexible budgets for Vroom-Vroom: what
 Question 3: Analyze the differences between static and flexible budgets. (36 points)
Question 3: Analyze the differences between static and flexible budgets. (36 points)
- What are the differences between the static and flexible budgets for Vroom-Vroom: what variances are different and by how much? What does this tell us?
- Write a letter to Vroom-Vrooms CFO. Explain the results in January and February. Provide your recommendation for either static or flexible budgets. Provide explanations and backup for your recommendation. Note: A letter to the CFO should have correct spelling and grammar, and is expected to be approximately 400 words. Thorough explanations with backup are required.
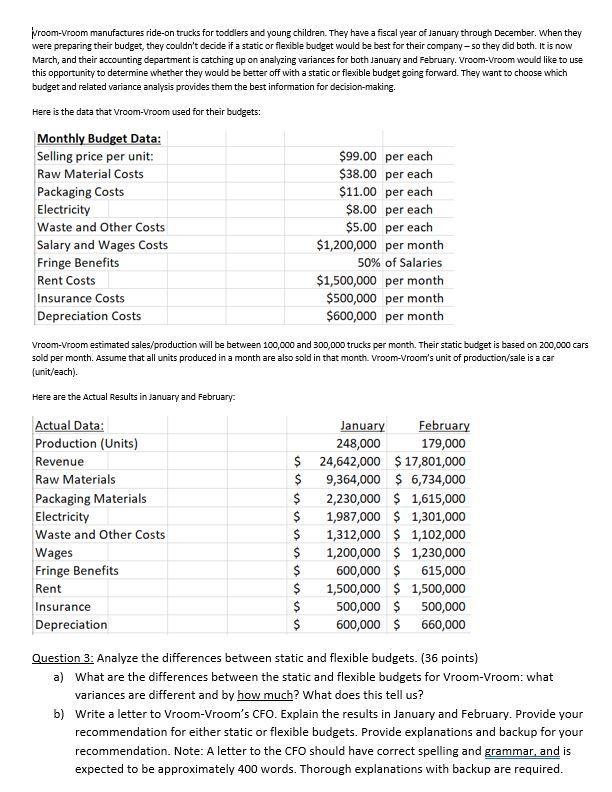
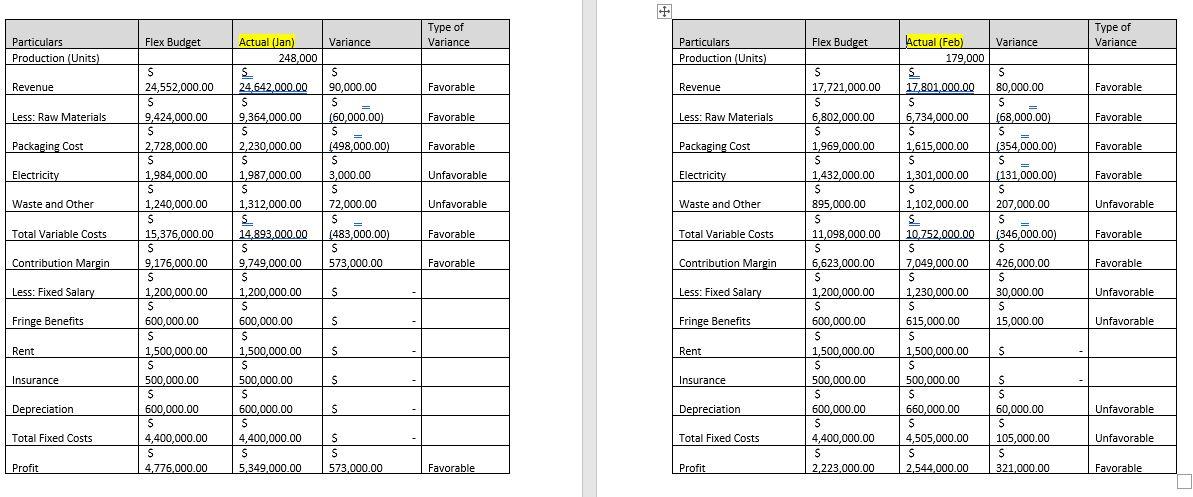
vroom-Vroom manufactures ride-on trucks for toddlers and young children. They have a fiscal year of January through December. When they were preparing their budget, they couldn't decide if a static or flexible budget would be best for their company - so they did both. It is now March, and their accounting department is catching up on analyzing variances for both January and February. Vroom-vroom would like to use this opportunity to determine whether they would be better off with a static or flexible budget going forward. They want to choose which budget and related variance analysis provides them the best information for decision-making. Here is the data that Vroom-Vroom used for their budgets: Monthly Budget Data: Selling price per unit: $99.00 per each Raw Material Costs $38.00 per each Packaging Costs $11.00 per each Electricity $8.00 per each Waste and Other Costs $5.00 per each Salary and Wages Costs $1,200,000 per month Fringe Benefits 50% of Salaries Rent Costs $1,500,000 per month Insurance Costs $500,000 per month Depreciation Costs $600,000 per month Vroom-Vroom estimated sales/production will be between 100,000 and 300,000 trucks per month. Their static budget is based on 200,000 cars sold per month. Assume that all units produced in a month are also sold in that month. Vroom-Vroom's unit of production/sale is a car (unit/each). Here are the Actual Results in January and February Actual Data: Production (Units) Revenue Raw Materials Packaging Materials Electricity Waste and Other Costs Wages Fringe Benefits Rent Insurance Depreciation January February 248,000 179,000 $ 24,642,000 $ 17,801,000 $ 9,364,000 $ 6,734,000 $ 2,230,000 $ 1,615,000 $ 1,987,000 $ 1,301,000 $ 1,312,000 $ 1,102,000 $ 1,200,000 $ 1,230,000 $ 600,000 $ 615,000 $ 1,500,000 $1,500,000 $ 500,000 $ 500,000 $ 600,000 $ 660,000 Question 3: Analyze the differences between static and flexible budgets. (36 points) a) What are the differences between the static and flexible budgets for Vroom-Vroom: what variances are different and by how much? What does this tell us? b) Write a letter to Vroom-Vroom's CFO. Explain the results in January and February. Provide your recommendation for either static or flexible budgets. Provide explanations and backup for your recommendation. Note: A letter to the CFO should have correct spelling and grammar, and is expected to be approximately 400 words. Thorough explanations with backup are required. Type of Variance Type of Variance Flex Budget Flex Budget Variance Particulars Production Units) Particulars Production (Units) Revenue Favorable Revenue Favorable Less: Raw Materials Favorable Less: Raw Materials Favorable Packaging Cost Favorable Packaging Cost Favorable Electricity Unfavorable Electricity Favorable Waste and Other Unfavorable Waste and Other S 80,000.00 S (68,000.00) SA (354,000.00) S = [131,000.00 S 207,000.00 S (346,000.00) S 426,000.00 S 30,000.00 S 15,000.00 Unfavorable Total Variable Costs Favorable Total Variable Costs Favorable Actual (Jan) Variance 248,000 S S 24.642,000.00 90,000.00 $ S 9,364,000.00 (60,000.00) S $ 2,230,000.00 1498,000.00) S S 1,987,000.00 3,000.00 S S 1,312,000.00 72,000.00 S SE 14.893,000.00 (483,000.00) $ $ S 9,749,000.00 573,000.00 S 1,200,000.00 S S 600,000.00 S S 1,500,000.00 S S 500,000.00 S s 600,000.00 S S 4,400,000.00 S S S 5,349,000.00 573,000.00 Actual (Feb) 179,000 S 17,801,000.00 S 6,734,000.00 S 1,615,000.00 S 1,301,000.00 S 1,102,000.00 S 10.752,000.00 S 7,049,000.00 S 1,230,000.00 S 615,000.00 S 1,500,000.00 S 500,000.00 S 660,000.00 S 4,505,000.00 S 2.544,000.00 Contribution Margin S 24,552,000.00 S 9,424,000.00 S 2,728,000.00 $ 1,984,000.00 S 1,240,000.00 S 15,376,000.00 S S 9,176,000.00 S 1,200,000.00 S 600,000.00 S 1,500,000.00 S 500,000.00 S 600,000.00 S 4,400,000.00 S 4,776,000.00 Favorable Contribution Margin S 17,721,000.00 S 6,802,000.00 S 1,969,000.00 S 1,432,000.00 S 895,000.00 $ 11,098,000.00 S 6,623,000.00 S 1,200,000.00 S 600,000.00 S 1,500,000.00 S 500,000.00 S 600,000.00 S 4,400,000.00 S 2,223,000.00 Favorable Less: Fixed Salary Less: Fixed Salary Unfavorable Fringe Benefits Fringe Benefits Unfavorable Rent Rent S Insurance Insurance Depreciation Depreciation Unfavorable S S 60,000.00 S 105,000.00 $ 321,000.00 Total Fixed Costs Total Fixed Costs Unfavorable Profit Favorable Profit Favorable
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


