Question: Question 3: Marginal versus Absorption Costing and Transfer Pricing Part A Bittern Ltd manufactures and sells a single product at a unit selling price of
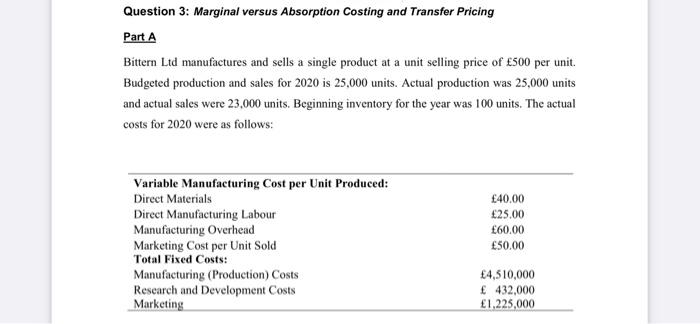



Question 3: Marginal versus Absorption Costing and Transfer Pricing Part A Bittern Ltd manufactures and sells a single product at a unit selling price of 500 per unit. Budgeted production and sales for 2020 is 25,000 units. Actual production was 25,000 units and actual sales were 23,000 units. Beginning inventory for the year was 100 units. The actual costs for 2020 were as follows: Variable Manufacturing Cost per Unit Produced: Direct Materials Direct Manufacturing Labour Manufacturing Overhead Marketing Cost per Unit Sold Total Fixed Costs: Manufacturing (Production) Costs Research and Development Costs Marketing 40.00 25.00 60.00 50,00 4,510,000 432,000 1,225,000 Required: a) Prepare the operating income statement under the Variable Costing Method for 2020. (4 Marks) b) If the budgeted fixed manufacturing overheads are 5,750,000, calculate the budgeted fixed cost per unit (i.c., the budgeted absorption rate). Also, calculate any over-/under overheads absorbed that must be written off to Cost of Goods Sold. (3 Marks) c) Using the information from (b), prepare the operating income statement under the Absorption costing Method for 2020. (4 Marks) d) Explain the differences in operating income obtained between the Variable and Absorption costing Methods calculated above. (3 Marks) Part B PL is an engineering company that specializes in providing engineering facilities that cannot justify operating their own facilities in-house. PL employs a number of engineers who are skilled in different engineering techniques that enable PL to provide a full range of engineering facilities to its customers. Most of the work undertaken by PL is unique to each of its customers, often requiring the manufacture of spare parts for its customers' equipment, or the building of new equipment from customer drawings. As a result, most of PL's work is short term, with some jobs being completed withing hours, while others may take a few days. To date, PL has adopted a cost-plus approach to setting its prices. This is based on absorption costing systems that uses machine hours as the basis of absorbing overheads into individual jobs. The managing director is concerned that over recent months PL has been unsuccessful when quoting for work with the consequence that there has been an increase in the level of unused capacity. It has been suggested that PL should adopt an alternative approach based on marginal costing. Required: With reference to the above scenario Question 3: Marginal versus Absorption Costing and Transfer Pricing Part A Bittern Ltd manufactures and sells a single product at a unit selling price of 500 per unit. Budgeted production and sales for 2020 is 25,000 units. Actual production was 25,000 units and actual sales were 23,000 units. Beginning inventory for the year was 100 units. The actual costs for 2020 were as follows: Variable Manufacturing Cost per Unit Produced: Direct Materials Direct Manufacturing Labour Manufacturing Overhead Marketing Cost per Unit Sold Total Fixed Costs: Manufacturing (Production) Costs Research and Development Costs Marketing 40.00 25.00 60.00 50,00 4,510,000 432,000 1,225,000 Required: a) Prepare the operating income statement under the Variable Costing Method for 2020. (4 Marks) b) If the budgeted fixed manufacturing overheads are 5,750,000, calculate the budgeted fixed cost per unit (i.c., the budgeted absorption rate). Also, calculate any over-/under overheads absorbed that must be written off to Cost of Goods Sold. (3 Marks) c) Using the information from (b), prepare the operating income statement under the Absorption costing Method for 2020. (4 Marks) d) Explain the differences in operating income obtained between the Variable and Absorption costing Methods calculated above. (3 Marks) Part B PL is an engineering company that specializes in providing engineering facilities that cannot justify operating their own facilities in-house. PL employs a number of engineers who are skilled in different engineering techniques that enable PL to provide a full range of engineering facilities to its customers. Most of the work undertaken by PL is unique to each of its customers, often requiring the manufacture of spare parts for its customers' equipment, or the building of new equipment from customer drawings. As a result, most of PL's work is short term, with some jobs being completed withing hours, while others may take a few days. To date, PL has adopted a cost-plus approach to setting its prices. This is based on absorption costing systems that uses machine hours as the basis of absorbing overheads into individual jobs. The managing director is concerned that over recent months PL has been unsuccessful when quoting for work with the consequence that there has been an increase in the level of unused capacity. It has been suggested that PL should adopt an alternative approach based on marginal costing. Required: With reference to the above scenario
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


