Question: Question 3 : Maximum flows and connectedness ( a ) A network is said to be k - edge - connected if it remains connected
Question : Maximum flows and connectedness
a A network is said to be edgeconnected if it remains connected after removing edges.
Here, we ask you to focus on a specific pair of nodes Then, the network is said to be
edgeconnected as far as are concerned if can send flow to upon removal of
edges. Formulate this problem as a maximum flow problem.
b A network is said to be nodeconnected if it remains connected after removing nodes.
Here, we ask you to focus on a specific pair of nodes Then, the network is said to be
nodeconnected as far as are concerned if can send flow to upon removal of nodes,
other than the source and the terminal themselves. Formulate this problem as a maximum flow
problem.
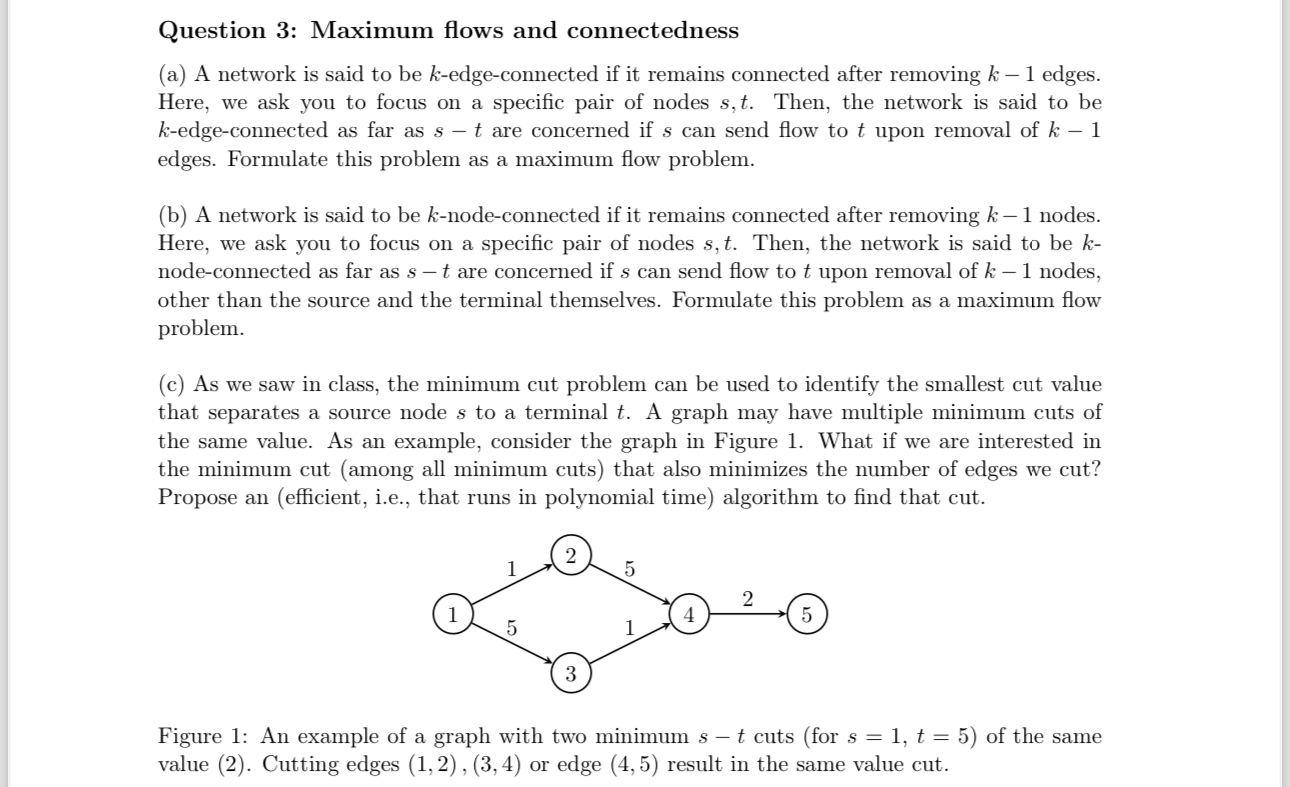
c As we saw in class, the minimum cut problem can be used to identify the smallest cut value
that separates a source node to a terminal A graph may have multiple minimum cuts of
the same value. As an example, consider the graph in Figure What if we are interested in
the minimum cut among all minimum cuts that also minimizes the number of edges we cut?
Propose an efficient ie that runs in polynomial time algorithm to find that cut.
Figure : An example of a graph with two minimum cuts for of the same
value Cutting edges or edge result in the same value cut.
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


