Question: Question 3 This question will examine differentiation and integration as linear transformations. Recall that P. denotes the vector space of polynomials of degree less than
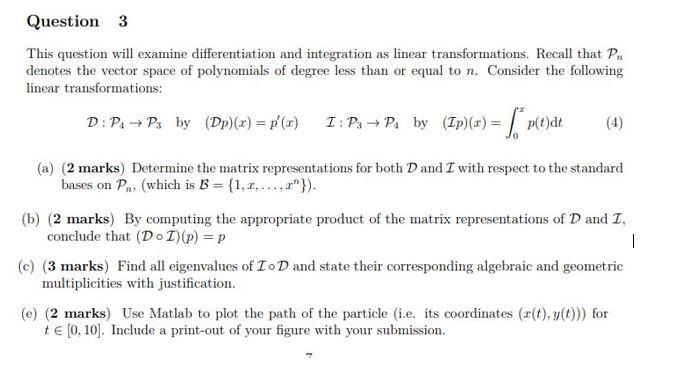
Question 3 This question will examine differentiation and integration as linear transformations. Recall that P. denotes the vector space of polynomials of degree less than or equal to n. Consider the following linear transformations: D:P. + P3 by (Dp)(x) = p' (r) L:Ps+P by (TP)(a) = [*peyat (a) (2 marks) Determine the matrix representations for both D and I with respect to the standard bases on Pn, (which is B = {1, 2,...,2"}). (b) (2 marks) By computing the appropriate product of the matrix representations of D and I, conclude that (DOL)(p) =p (e) (3 marks) Find all eigenvalues of ID and state their corresponding algebraic and geometric multiplicities with justification. (e) (2 marks) Use Matlab to plot the path of the particle (i.e. its coordinates (x(t).y(t))) for + 0,10). Include a print-out of your figure with your submission. | Question 3 This question will examine differentiation and integration as linear transformations. Recall that P. denotes the vector space of polynomials of degree less than or equal to n. Consider the following linear transformations: D:P. + P3 by (Dp)(x) = p' (r) L:Ps+P by (TP)(a) = [*peyat (a) (2 marks) Determine the matrix representations for both D and I with respect to the standard bases on Pn, (which is B = {1, 2,...,2"}). (b) (2 marks) By computing the appropriate product of the matrix representations of D and I, conclude that (DOL)(p) =p (e) (3 marks) Find all eigenvalues of ID and state their corresponding algebraic and geometric multiplicities with justification. (e) (2 marks) Use Matlab to plot the path of the particle (i.e. its coordinates (x(t).y(t))) for + 0,10). Include a print-out of your figure with your submission. |
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


