Question: Question 4 (2 points) Two gliders on an air track collide in a perfectly elastic collision. Glider A has mass 1.1 kg and is initially

![is initially travelling at a velocity of 2.7 m/s [E]. It collides](https://s3.amazonaws.com/si.experts.images/answers/2024/07/668a432db6d6e_197668a432d9ef89.jpg)

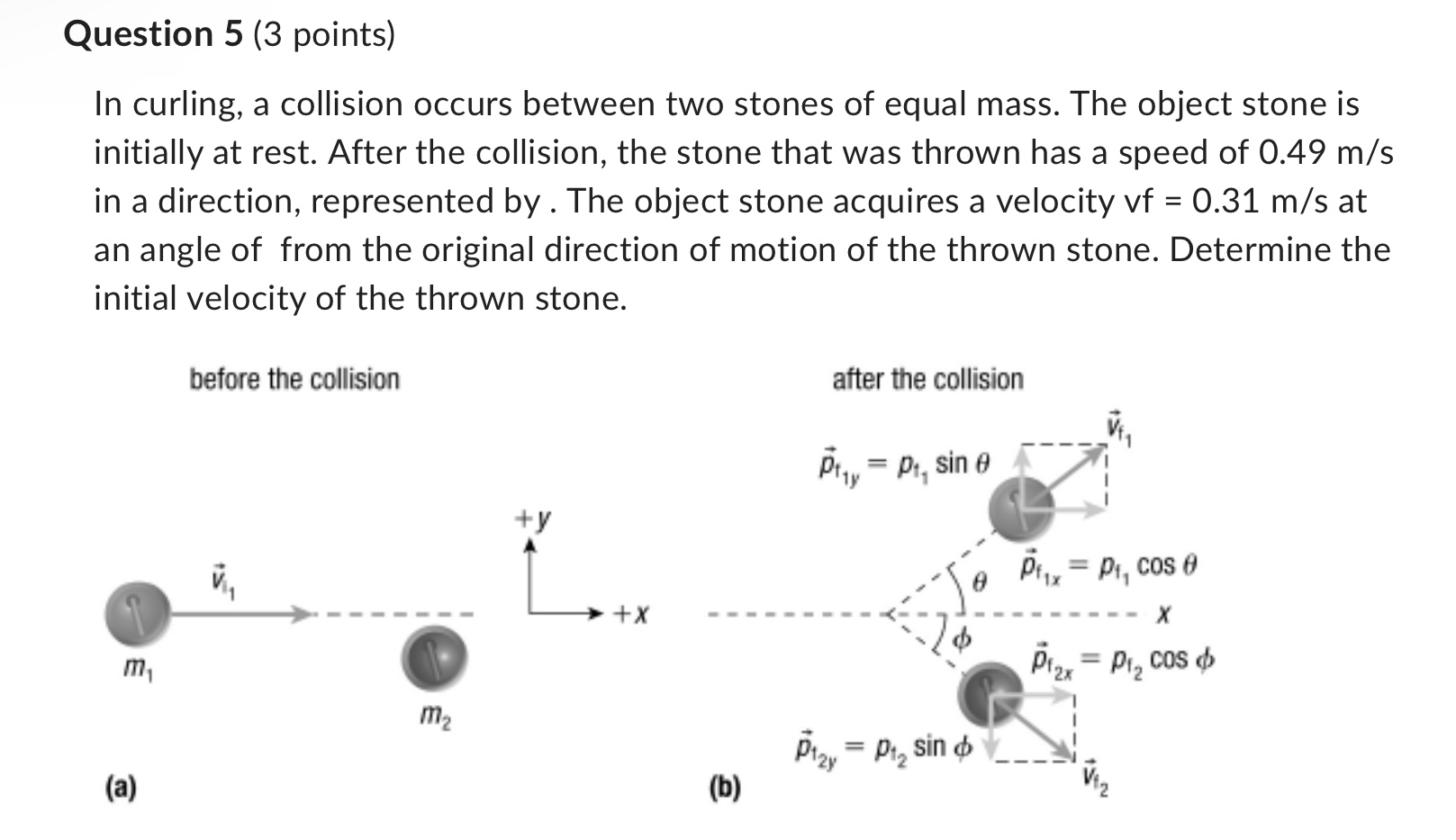
Question 4 (2 points) Two gliders on an air track collide in a perfectly elastic collision. Glider A has mass 1.1 kg and is initially travelling at a velocity of 2.7 m/s [E]. It collides head-on with glider B with mass 2.4 kg, travelling at a velocity of 1.9 m/s [W]. Determine the final velocity of glider B using elastic collision formulas. Provide your numerical results within the text box below and upload all of your problem solutions as PDF file. Question 5 (3 points) In curling, a collision occurs between two stones of equal mass. The object stone is initially at rest. After the collision, the stone that was thrown has a speed of 0.49 m/s in a direction, represented by . The object stone acquires a velocity vf = 0.31 m/s at an angle of from the original direction of motion of the thrown stone. Determine the initial velocity of the thrown stone. before the collision after the collision (a) (bi ,, "*2 Question 3 (1 point) Which of the following is (are) connected to the kinetic energy of an object? O displacement 0 all of the above Question 4 (2 points) Two gliders on an air track collide in a perfectly elastic collision. Glider A has mass 1.1 kg and is initially travelling at a velocity of 2.7 m/s [E]. It collides head-on with glider B with mass 2.4 kg, travelling at a velocity of 1.9 m/s [W]. Determine the final velocity of glider B using elastic collision formulas. Question 1 (1 point) Simple harmonic motion is periodic motion in which an object moves in response to a force that is inversely proportional and opposite in direction to its displacement. Question 2 (3 points) A 0.50 kg mass is attached to a spring with spring constant as shown. Suppose the mass is pushed upward, so that it rises past the spring's unstretched position, compressing the spring. Calculate the net force on the mass when the spring is compressed 3.7 cm. Include a free-body diagram
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


