Question: Question 4 (25 marks) (a) The network below gives the shipping routes from nodes 1 and 2 to nodes 5 and 6 by way of
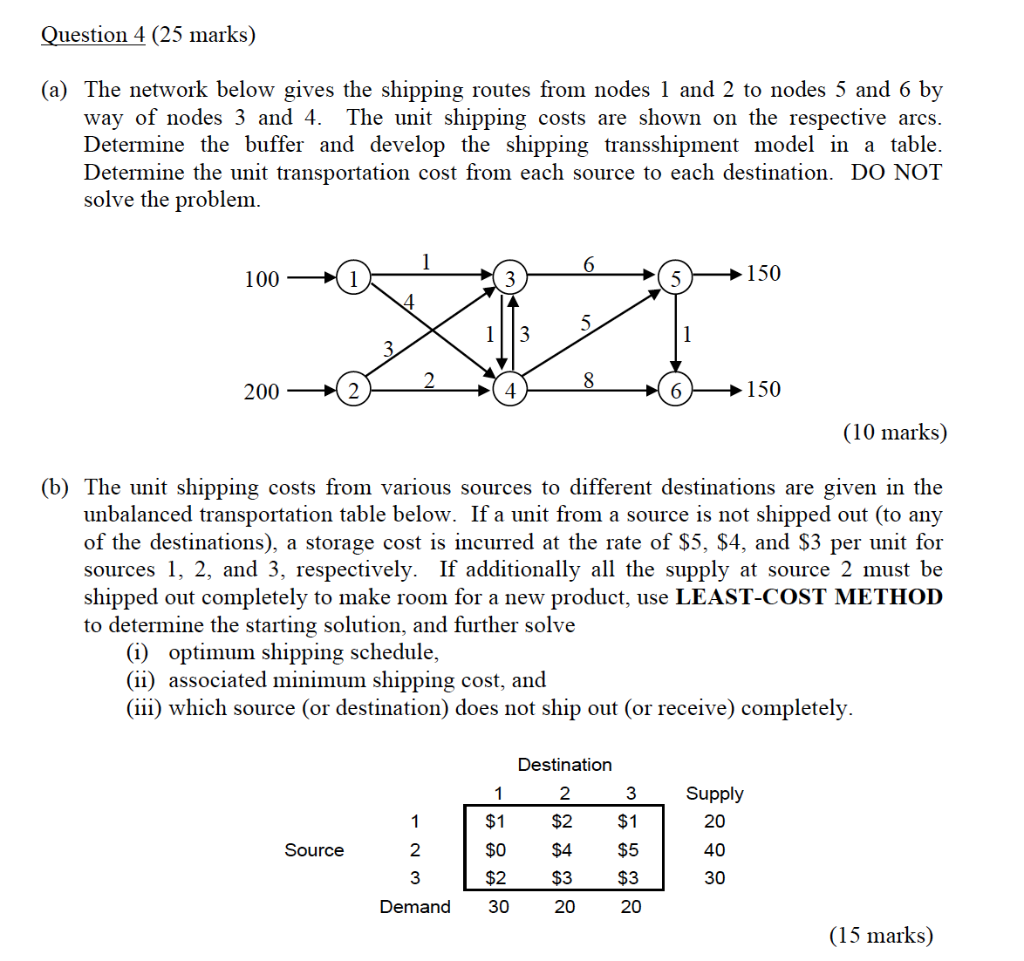
Question 4 (25 marks) (a) The network below gives the shipping routes from nodes 1 and 2 to nodes 5 and 6 by way of nodes 3 and 4. The unit shipping costs are shown on the respective arcs. Determine the buffer and develop the shipping transshipment model in a table. Determine the unit transportation cost from each source to each destination. DO NOT solve the problem. 100 (1) 150 200 2 4 8 5 150 (10 marks) (b) The unit shipping costs from various sources to different destinations are given in the unbalanced transportation table below. If a unit from a source is not shipped out (to any of the destinations), a storage cost is incurred at the rate of $5, $4, and $3 per unit for sources 1, 2, and 3, respectively. If additionally all the supply at source 2 must be shipped out completely to make room for a new product, use LEAST-COST METHOD to determine the starting solution, and further solve (i) optimum shipping schedule, (ii) associated minimum shipping cost, and (iii) which source (or destination) does not ship out (or receive) completely. Supply 20 1 2 Destination 1 2 3 $1 $2 $1 $0 $4 $5 $2 $3 $ 3 30 20 20 Source 40 30 Demand (15 marks) Question 4 (25 marks) (a) The network below gives the shipping routes from nodes 1 and 2 to nodes 5 and 6 by way of nodes 3 and 4. The unit shipping costs are shown on the respective arcs. Determine the buffer and develop the shipping transshipment model in a table. Determine the unit transportation cost from each source to each destination. DO NOT solve the problem. 100 (1) 150 200 2 4 8 5 150 (10 marks) (b) The unit shipping costs from various sources to different destinations are given in the unbalanced transportation table below. If a unit from a source is not shipped out (to any of the destinations), a storage cost is incurred at the rate of $5, $4, and $3 per unit for sources 1, 2, and 3, respectively. If additionally all the supply at source 2 must be shipped out completely to make room for a new product, use LEAST-COST METHOD to determine the starting solution, and further solve (i) optimum shipping schedule, (ii) associated minimum shipping cost, and (iii) which source (or destination) does not ship out (or receive) completely. Supply 20 1 2 Destination 1 2 3 $1 $2 $1 $0 $4 $5 $2 $3 $ 3 30 20 20 Source 40 30 Demand (15 marks)





