Question: Question 4 Consider the basic pipelined CPU architecture. The CPU does not have any ad ditional circuitry to detect data dependency so it does not
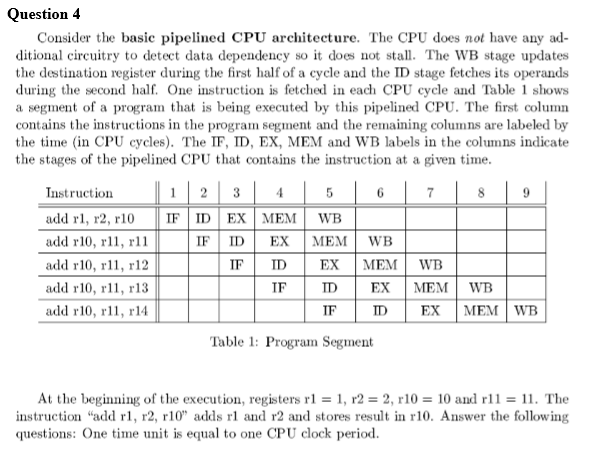

Question 4 Consider the basic pipelined CPU architecture. The CPU does not have any ad ditional circuitry to detect data dependency so it does not stall. The WB stage updates the destination register during the first half of a cycle and the ID stage fetches its operands during the second haf One instruction is fetched in each CPU cycle and Table 1 shows a segment of a program that is being executed by this pipelined CPU. The first column contains the instructions in the program segment and the remaining columns are labeled by the time (in CPU cycles). The IF, ID, EX, MEM and WB labels in the columns indicate the stages of the pipelined CPU that contains the instruction at a given time Instruction add r1, r2, r10 || IF | ID | EX | MEM | WB add r10, rl1, rll add r10, , r12 add r10, r11, r13 add r10, rl1, r14 IF? ID? EX | MEM | WB IF ID EX MEM WB IF ID EX MEM WB Table 1: Program Segment At the beginning of the execution, registers r1-1, r2 = 2, r10 = 10 and r11 = 11, The instruction "add r, r2, r10" adds and r2 and stores result in r10. Answer the following questions: One time unit is equal to one CPU clock period
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


