Question: Question 4 Next, consider again the bond in Question 1, but suppose that it now matures in three years. Settledate: 1-Jan-2019 Annual coupon rate: 8%

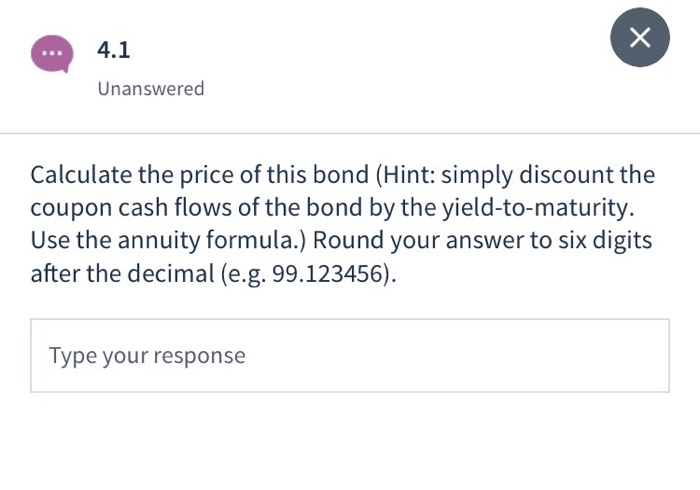
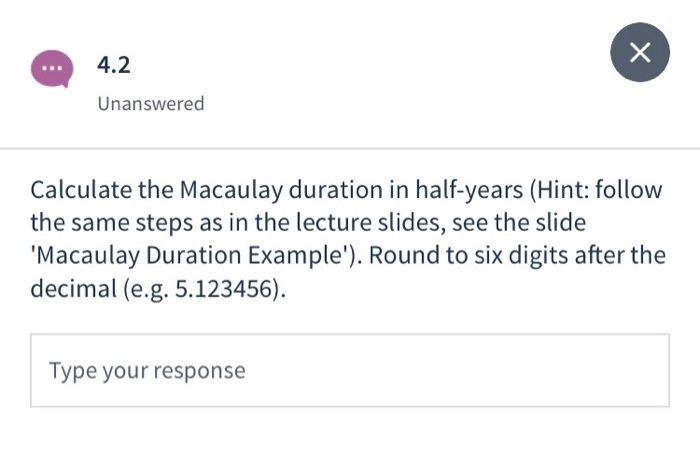

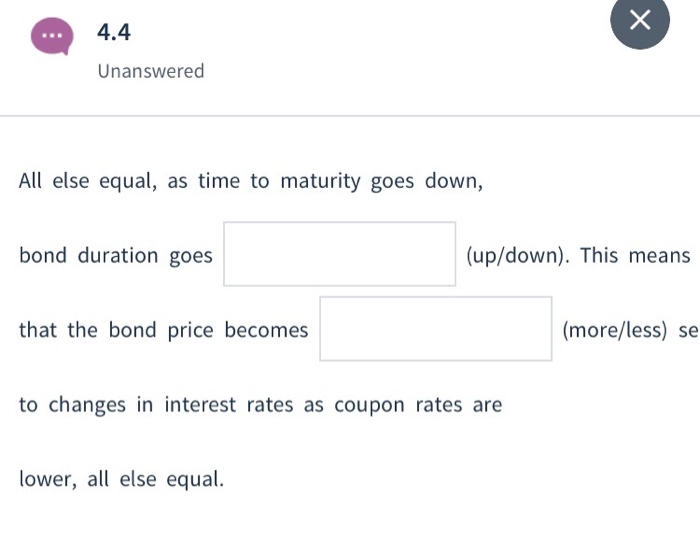
Question 4 Next, consider again the bond in Question 1, but suppose that it now matures in three years. Settledate: 1-Jan-2019 Annual coupon rate: 8% . Coupons paid semi-annually Yield to maturity: 6% Par value: $100 Time to maturity: T=3 years 4.1 Unanswered Calculate the price of this bond (Hint: simply discount the coupon cash flows of the bond by the yield-to-maturity. Use the annuity formula.) Round your answer to six digits after the decimal (e.g. 99.123456). Type your response 4.2 Unanswered Calculate the Macaulay duration in half-years (Hint: follow the same steps as in the lecture slides, see the slide 'Macaulay Duration Example'). Round to six digits after the decimal (e.g. 5.123456). Type your response 4.3 Unanswered Calculate the Macaulay duration in years (Hint: follow the same steps as in the lecture slides, see the slide 'Macaulay Duration Example'). Round to six digits after the decimal (e.g. 5.123456). Type your response x 4.4 Unanswered All else equal, as time to maturity goes down, bond duration goes (up/down). This means that the bond price becomes (more/less) se to changes in interest rates as coupon rates are lower, all else equal
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


