Question: Question 5 . 6 ) Consider an ordinary shower where hot water at ( 1 4 0 ^ { circ } mathrm
Question Consider an ordinary shower where hot water at circmathrmF is mixed with cold water at circmathrmF If it is desired that a steady stream of warm water at circmathrmF be supplied, determine the ratio of the mass flow rates of the hot to cold water. Assume the heat losses from the mixing chamber to be negligible and the mixing to take place at a pressure of psia
Answer to Q
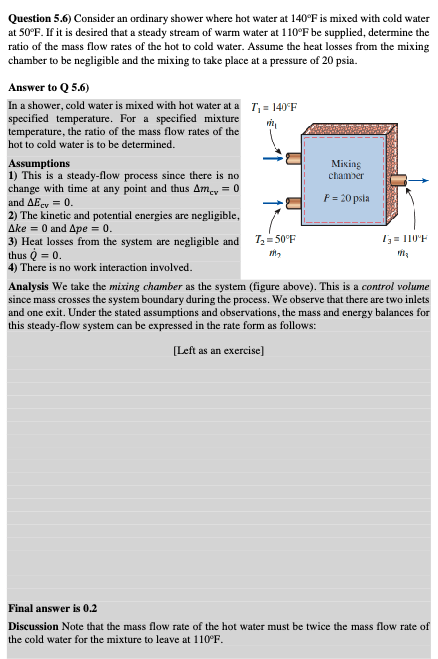
In a shower, cold water is mixed with hot water at a specified temperature. For a specified mixture temperature, the ratio of the mass flow rates of the hot to cold water is to be determined.
Assumptions
This is a steadyflow process since there is no change with time at any point and thus Delta mc v and Delta Emathrmcv
The kinetic and potential energies are negligible, Delta k e and Delta p e
Heat losses from the system are negligible and thus dotQ
There is no work interaction involved.
Analysis We take the mixing chamber as the system figure above This is a control volume since mass crosses the system boundary during the process. We observe that there are two inlets and one exit. Under the stated assumptions and observations, the mass and energy balances for this steadyflow system can be expressed in the rate form as follows:
Left as an exercise
Final answer is
Discussion Note that the mass flow rate of the hot water must be twice the mass flow rate of the cold water for the mixture to leave at circmathrmF
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


