Question: QUESTION 5 (a) Principal component analysis shows that for the U.S. term structure of interest rates, three factors explain more than 99% of the variation
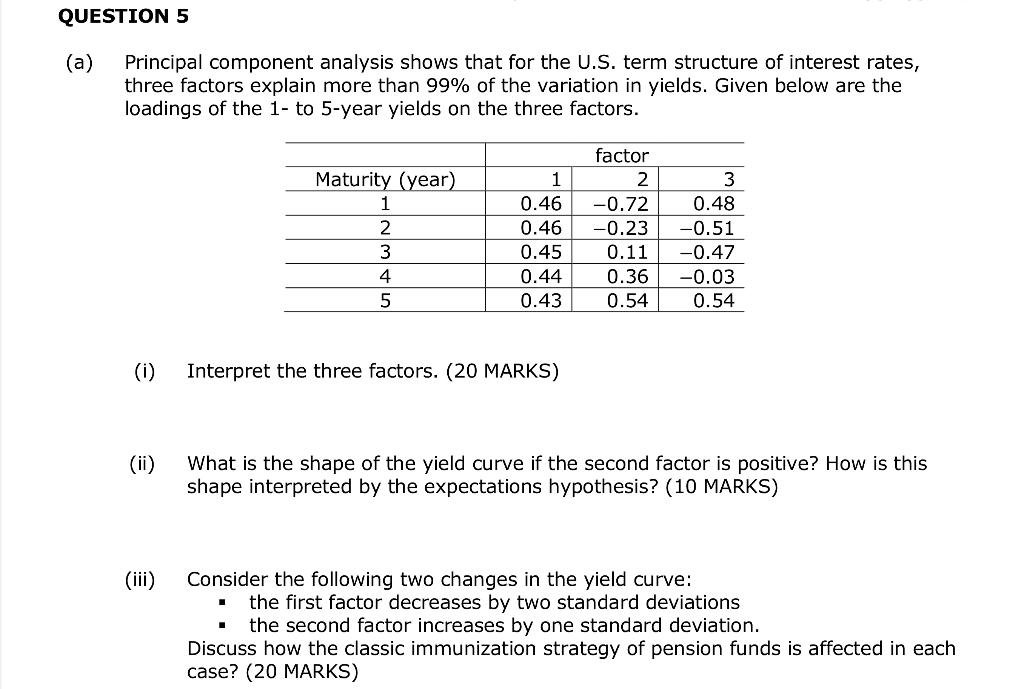

QUESTION 5 (a) Principal component analysis shows that for the U.S. term structure of interest rates, three factors explain more than 99% of the variation in yields. Given below are the loadings of the 1- to 5-year yields on the three factors. factor Maturity (year) 1 2 3 1 0.46 -0.72 0.48 2 0.46 -0.23 -0.51 3 0.45 0.11 -0.47 4 0.44 0.36 -0.03 5 0.43 0.54 0.54 (1) Interpret the three factors. (20 MARKS) (ii) What is the shape of the yield curve if the second factor is positive? How is shape interpreted by the expectations hypothesis? (10 MARKS) (iii) Consider the following two changes in the yield curve: the first factor decreases by two standard deviations the second factor increases by one standard deviation. Discuss how the classic immunization strategy of pension funds is affected in each case? (20 MARKS) (b) Financial Times wrote on 18 Jan 2021 that "Amid its pandemic firefighting, the European Central Bank is ploughing on with a strategic review of its monetary policy framework. One previously neglected idea is coming into the discussion. Pablo Hernndez de Cos, Spain's central bank governor, suggests that the ECB could explore 'yield curve control', or the policy of directly setting long-term interest rates. It is not a novel policy. Since 2016, the Bank of Japan has committed to keeping the market yield on 10-year Japanese government bonds near zero. The BoJ will buy or sell whatever quantity of bonds is needed to meet this goal." (i) How is yield curve control different from conventional monetary policies and quantitative easing purchases? (20 MARKS) (ii) Comment on the monetary policy of yield curve control. (30 MARKS) QUESTION 5 (a) Principal component analysis shows that for the U.S. term structure of interest rates, three factors explain more than 99% of the variation in yields. Given below are the loadings of the 1- to 5-year yields on the three factors. factor Maturity (year) 1 2 3 1 0.46 -0.72 0.48 2 0.46 -0.23 -0.51 3 0.45 0.11 -0.47 4 0.44 0.36 -0.03 5 0.43 0.54 0.54 (1) Interpret the three factors. (20 MARKS) (ii) What is the shape of the yield curve if the second factor is positive? How is shape interpreted by the expectations hypothesis? (10 MARKS) (iii) Consider the following two changes in the yield curve: the first factor decreases by two standard deviations the second factor increases by one standard deviation. Discuss how the classic immunization strategy of pension funds is affected in each case? (20 MARKS) (b) Financial Times wrote on 18 Jan 2021 that "Amid its pandemic firefighting, the European Central Bank is ploughing on with a strategic review of its monetary policy framework. One previously neglected idea is coming into the discussion. Pablo Hernndez de Cos, Spain's central bank governor, suggests that the ECB could explore 'yield curve control', or the policy of directly setting long-term interest rates. It is not a novel policy. Since 2016, the Bank of Japan has committed to keeping the market yield on 10-year Japanese government bonds near zero. The BoJ will buy or sell whatever quantity of bonds is needed to meet this goal." (i) How is yield curve control different from conventional monetary policies and quantitative easing purchases? (20 MARKS) (ii) Comment on the monetary policy of yield curve control. (30 MARKS)
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


