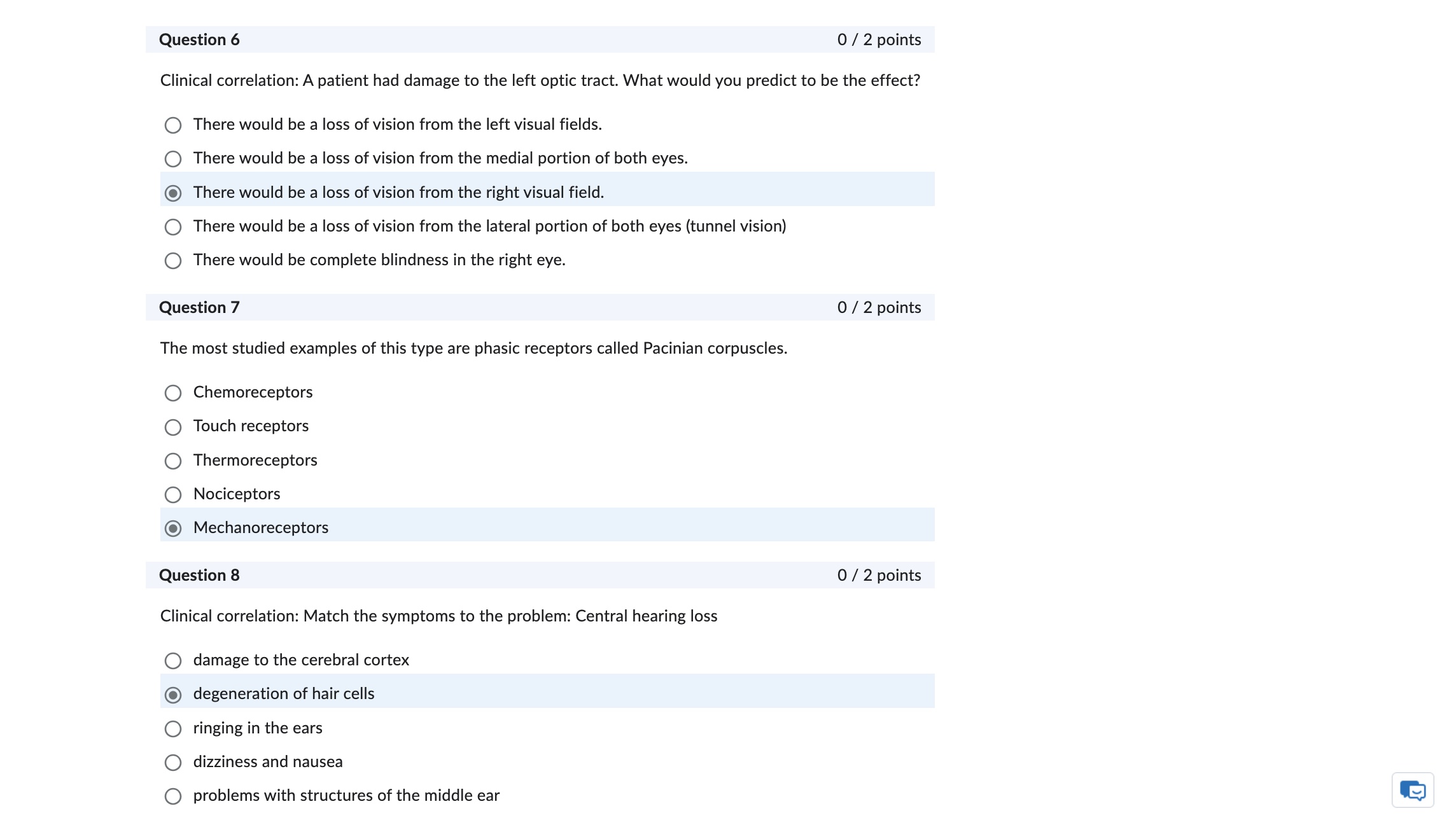
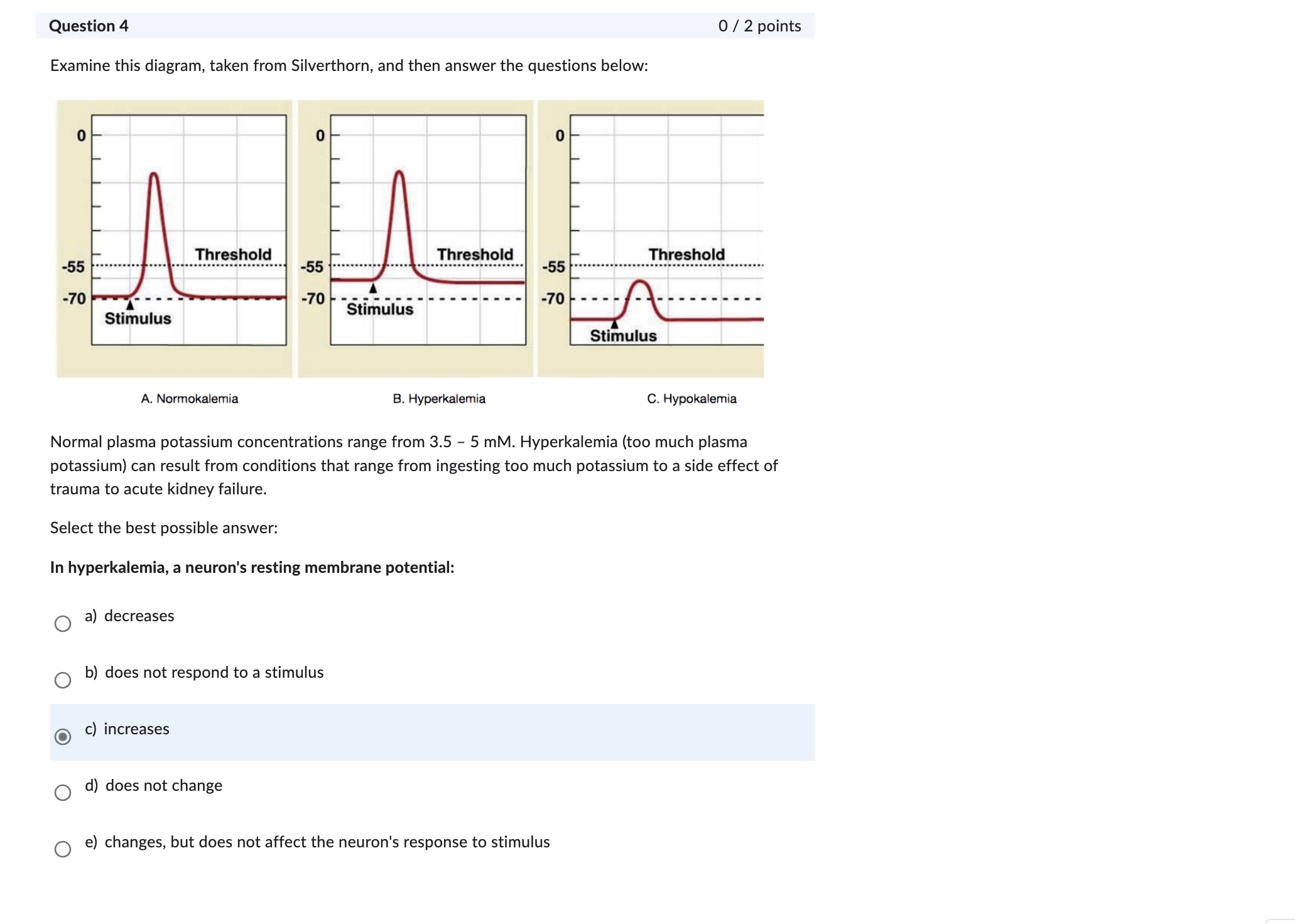
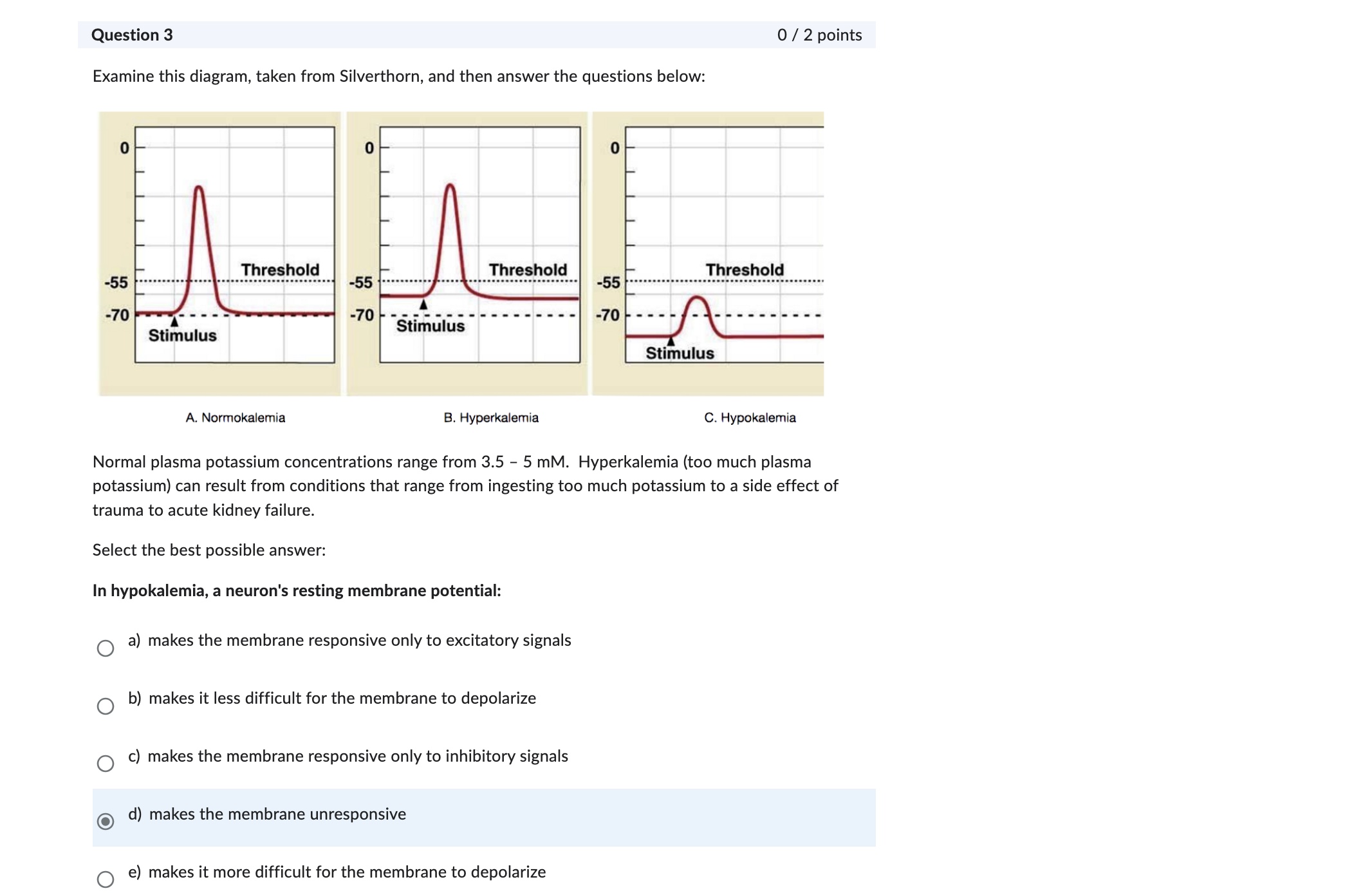
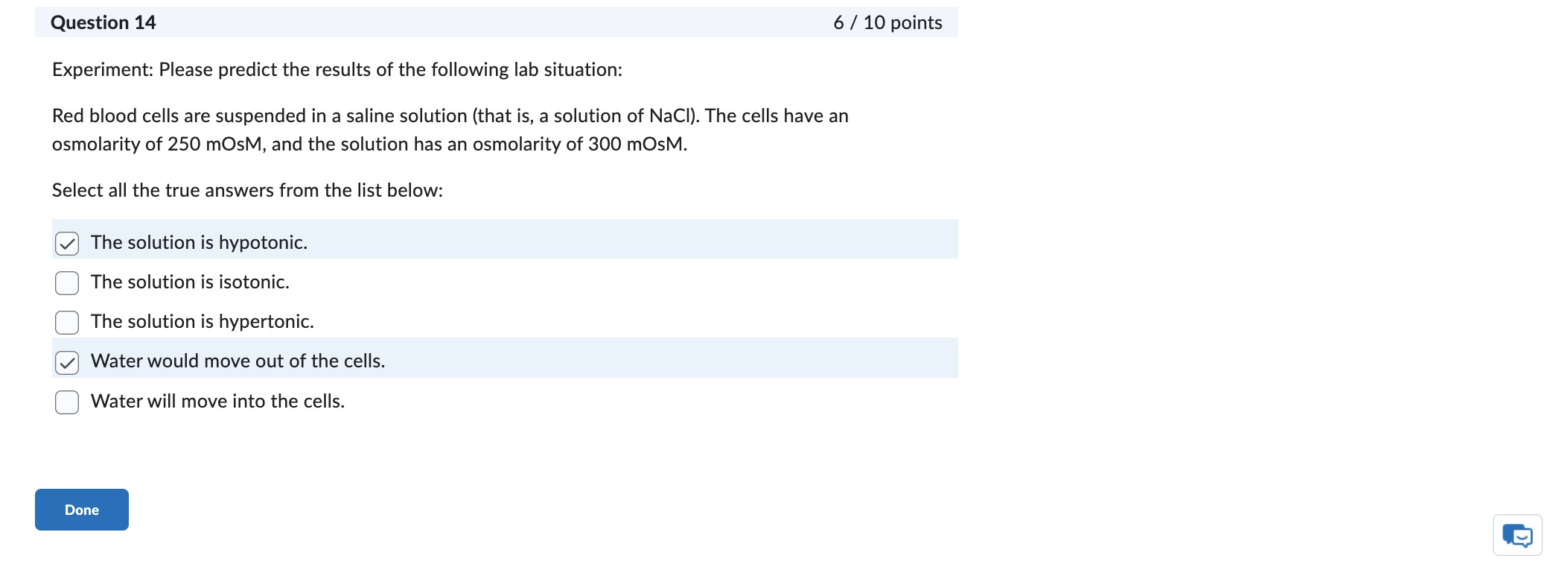
Question: Question 6 0/2 points Clinical correlation: A patient had damage to the left optic tract. What would you predict to be the effect? There would

Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


