Question: Question 6. The following experimental device is often used in dialysis membrane testing. The device comprises of a semi-permeable membrane which allows only small molecule
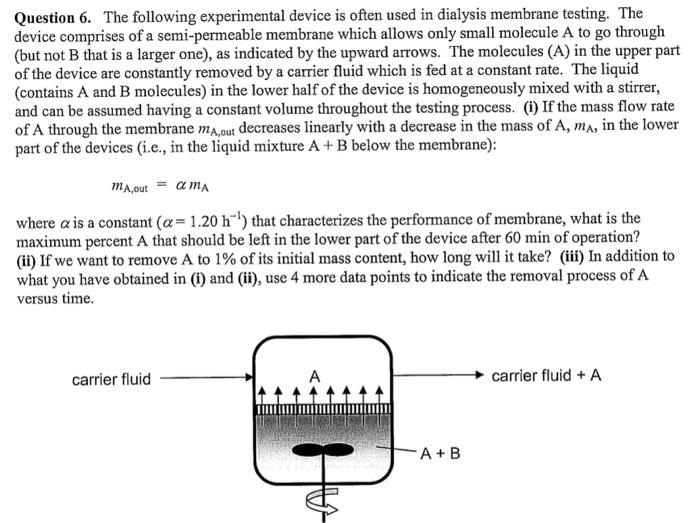
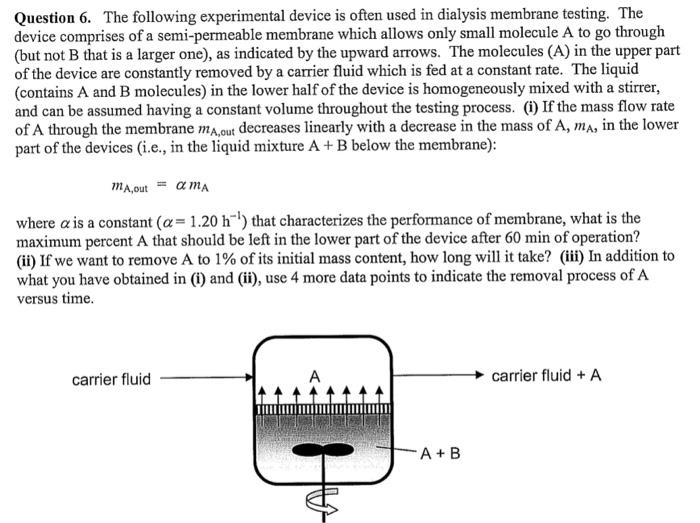
Question 6. The following experimental device is often used in dialysis membrane testing. The device comprises of a semi-permeable membrane which allows only small molecule A to go through (but not B that is a larger one), as indicated by the upward arrows. The molecules (A) in the upper part of the device are constantly removed by a carrier fluid which is fed at a constant rate. The liquid (contains A and B molecules) in the lower half of the device is homogeneously mixed with a stirrer, and can be assumed having a constant volume throughout the testing process. (i) If the mass flow rate of A through the membrane mA,out decreases linearly with a decrease in the mass of A,mA, in the lower part of the devices (i.e., in the liquid mixture A+B below the membrane): mA,out=mA where is a constant (=1.20h1) that characterizes the performance of membrane, what is the maximum percent A that should be left in the lower part of the device after 60min of operation? (ii) If we want to remove A to 1% of its initial mass content, how long will it take? (iii) In addition to what you have obtained in (i) and (ii), use 4 more data points to indicate the removal process of A versus time. Question 6. The following experimental device is often used in dialysis membrane testing. The device comprises of a semi-permeable membrane which allows only small molecule A to go through (but not B that is a larger one), as indicated by the upward arrows. The molecules (A) in the upper part of the device are constantly removed by a carrier fluid which is fed at a constant rate. The liquid (contains A and B molecules) in the lower half of the device is homogeneously mixed with a stirrer, and can be assumed having a constant volume throughout the testing process. (i) If the mass flow rate of A through the membrane mA,out decreases linearly with a decrease in the mass of A,mA, in the lower part of the devices (i.e., in the liquid mixture A+B below the membrane): mA,out=mA where is a constant (=1.20h1) that characterizes the performance of membrane, what is the maximum percent A that should be left in the lower part of the device after 60min of operation? (ii) If we want to remove A to 1% of its initial mass content, how long will it take? (iii) In addition to what you have obtained in (i) and (ii), use 4 more data points to indicate the removal process of A versus time
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


