Question: Question 8 (2 points) Find the set An B. Don't worry about the subscripts, just enter an event like {E1) or sets of events like
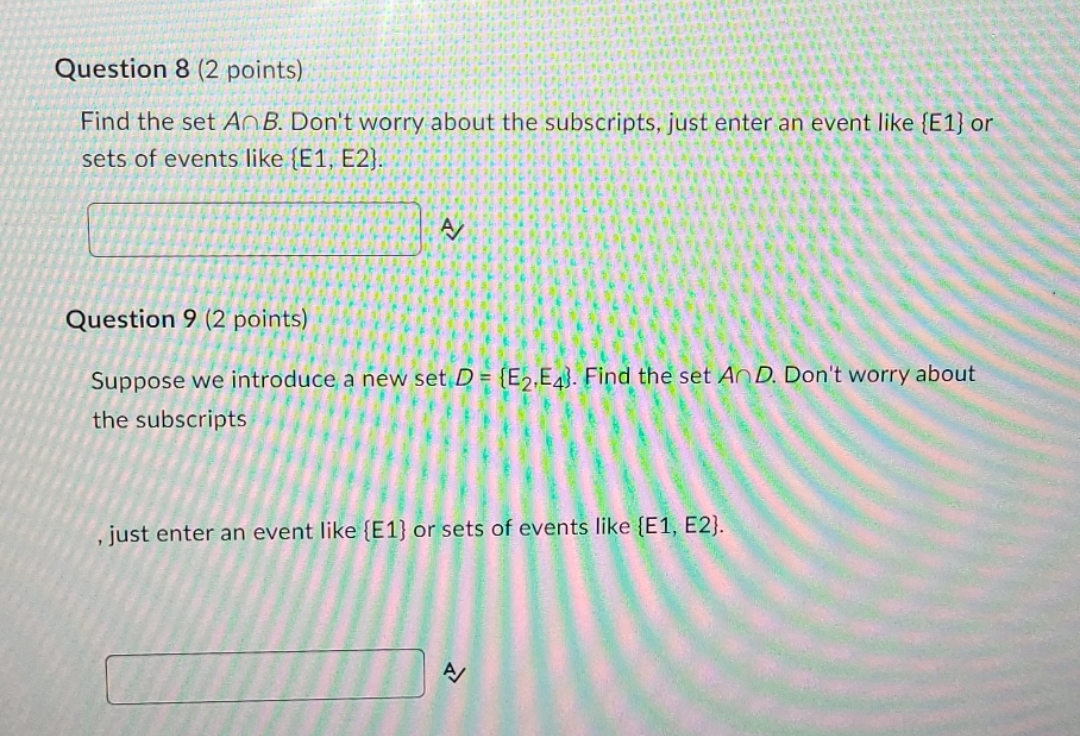
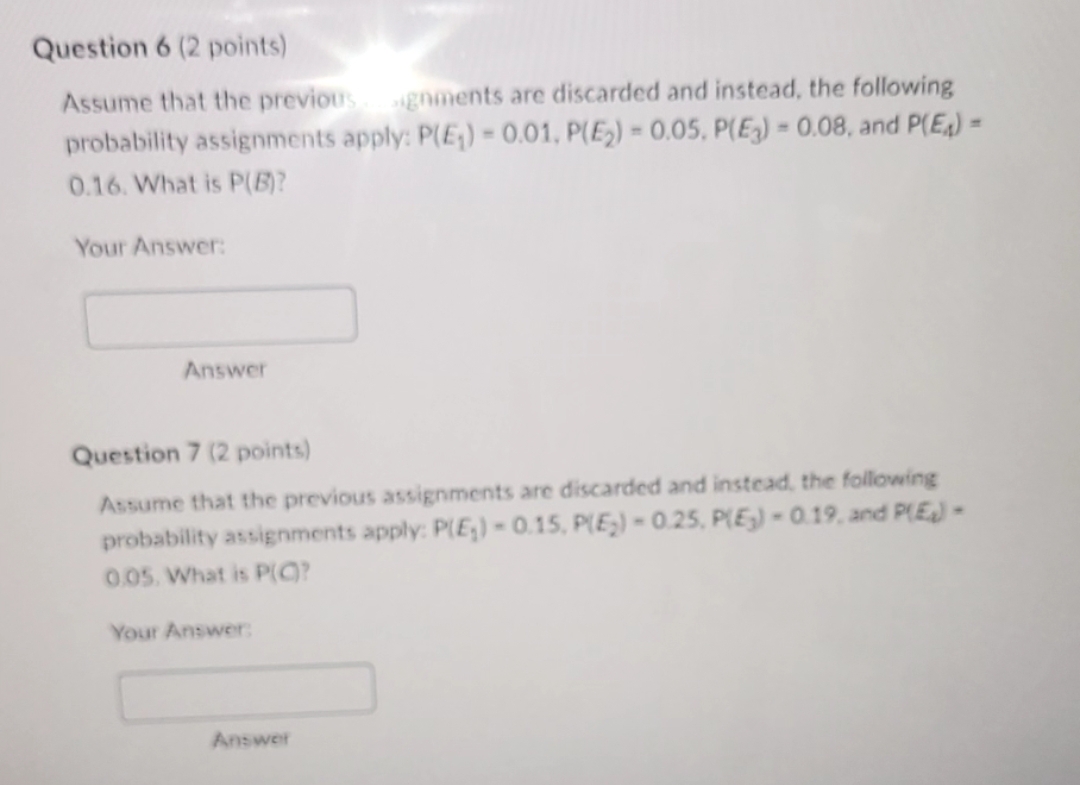
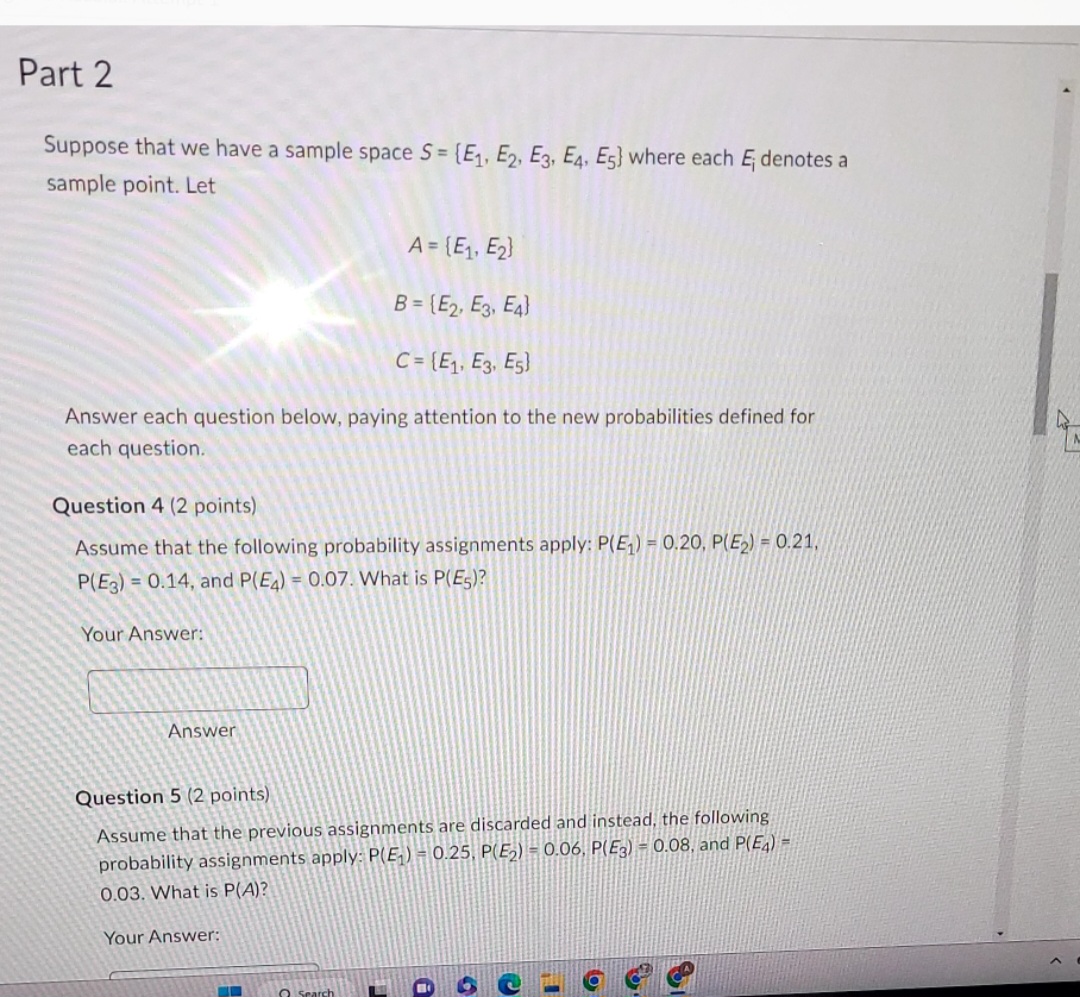
Question 8 (2 points) Find the set An B. Don't worry about the subscripts, just enter an event like {E1) or sets of events like {E1, E2}. Question 9 (2 points) Suppose we introduce a new set D= (E2,E). Find the set AnD. Don't worry about the subscripts just enter an event like {E1} or sets of events like {E1, E2]. A/Question 6 (2 points) Assume that the previous . .signments are discarded and instead, the following probability assignments apply: P(E,) - 0.01. P(E2) = 0.05. P(3) = 0.08, and P(E;) = 0.16. What is P(B)? Your Answer: Answer Question 7 (2 points) Assume that the previous assignments are discarded and instead, the following probability assignments apply: P(E,) - 0.15. P(E,) - 0.25. P(E;) - 0.19. and P(Ey) - 0.05. What is P(C)? Your Answer AnswerPart 2 Suppose that we have a sample space S = [E1, E2, E3, E4, Es] where each , denotes a sample point. Let A = {E1, E2) B = {E2, E3, E4] C = [E1, E3, Es] Answer each question below, paying attention to the new probabilities defined for each question. Question 4 (2 points) Assume that the following probability assignments apply: P(E,) - 0.20, P(E2) - 0.21, P(Eg) = 0.14, and P(E4) - 0.07. What is P(Es)? Your Answer: Answer Question 5 (2 points) Assume that the previous assignments are discarded and instead, the following probability assignments apply: P(E, ) - 0.25. P(E2) -0.06, P(Eg) - 0.08, and P(EA) 0.03. What is P(A)? Your
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


