Question: Question one Data Case for Chapter 9: Valuing Stocks As a new analyst for a large brokerage firm, you are anxious to demonstrate the skills
Question one
Data Case for Chapter 9: Valuing Stocks
As a new analyst for a large brokerage firm, you are anxious to demonstrate the skills you learned in your MBA program and prove that you are worth your attractive salary. Your first assignment is to analyze the stock of the General Electric Corporation. Your boss recommends determining prices based on both the dividend-discount model and discounted free cash flow valuation methods. GE uses a cost of equity of 10.5% and an after-tax weighted average cost of capital of 7.5%. The expected return on new investments is 12%. However, you are a little concerned because your finance professor has told you that these two methods can result in widely differing estimates when applied to real data. You are really hoping that the two methods will reach similar prices. Good luck with that!
1. Go to Yahoo! Finance (http://finance.yahoo.com) and enter the symbol for General Electric (GE). From the main page for GE, gather the following information and enter it onto a spreadsheet:
a. The current stock price (last trade) at the top of the page.
b. The current dividend amount, which is in the bottom-right cell in the same box as the stock price.
2. Next, click "Key Statistics" from the left side of the page. From the Key Statistics page, gather the following information and enter it on the same spreadsheet:
a. The number of shares of stock outstanding.
b. The Payout ratio.
3. Next, click "Analyst Estimates" from the left side of the page. From the Analyst Estimates page, find the expected growth rate for the next five years and enter it onto your spreadsheet. It will be near the very bottom of the page.
4. Next, click "Income Statement" near the bottom of the menu on the left. Copy and paste the entire three years of income statements into a new worksheet in your existing Excel file. (Note : if you are using IE as your browser, you can place the cursor in the middle of the statement, rightclick, and select "Export to Microsoft Excel" to download an Excel version.) Repeat this process for both the balance sheet and cash flow statement for General Electric. Keep all the different statements in the same Excel worksheet.
5. To determine the stock value based on the dividend-discount model:
a. Create timeline in Excel for five years.
b. Use the dividend obtained from Yahoo! Finance as the current dividend to forecast the next five annual dividends based on the five-year growth rate.
c. Determine the long-term growth rate based on GE's payout ratio (which is one minus the retention ratio) using Eq. 9.12.
d. Use the long-term growth rate to determine the stock price for year five using Eq. 9.13. e. Determine the current stock price using Eq. 9.14.
6. To determine the stock value based on the discounted free cash flow method:
a. Forecast the free cash flows using the historic data from the financial statements downloaded from Yahoo! to compute the three-year average of the following ratios: i. EBIT/Sales ii. Tax Rate (Income Tax Expense/Income Before Tax) iii. Property Plant and Equipment/Sales iv. Depreciation/Property Plant and Equipment v. Net Working Capital/Sales
b. Create timeline for the next seven years.
c. Forecast future sales based on the most recent year's total revenue growing at the five-year growth rate from Yahoo! for the first five years and the long-term growth rate for years 6 and 7.
d. Use the average ratios computed in part (a) to forecast EBIT, property, plant and equipment, depreciation, and net working capital for the next seven years. e. Forecast the free cash flow for the next seven years using Eq. 9.18.
f. Determine the horizon enterprise value for year 5 using Eq. 9.24.
g. Determine the enterprise value of the firm as the present value of the free cash flows.
h. Determine the stock price using Eq. 9.22.
7. Compare the stock prices from the two methods to the actual stock price. What recommendations can you make as to whether clients should buy or sell GE stock based on your price estimates?
8. Explain to your boss why the estimates from the two valuation methods differ. Specifically, address the assumptions implicit in the models themselves as well as those you made in preparing your analysis. Why do these estimates differ from the actual stock price of GE?
The answers of Q 1-5 as below. I need step-by-step solutions of Q5 & Q6 and analysis of Q7 & Q8. Thanks very much indeed!
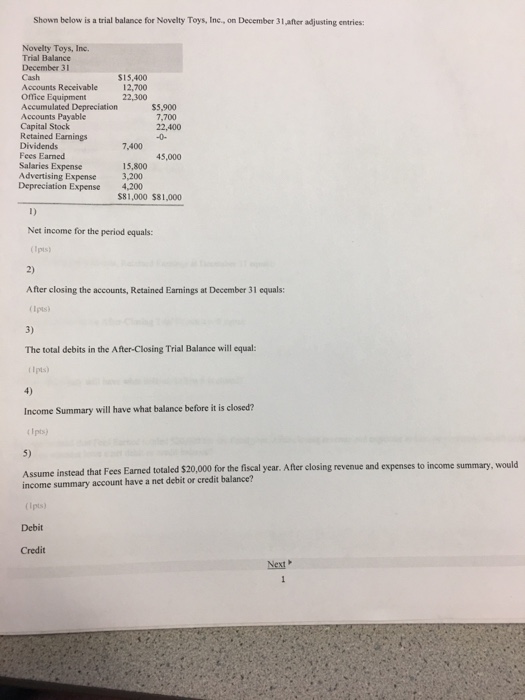
1)
General Electric (GE)
a. The current stock price (last trade) $30.19
b. current dividend amount $0.96
2)
a)number of shares of stock outstanding 8.72B
b) Payout Ratio 93.00%
3)
expected growth rate for the next five years 12.11%
5)
a)TimeLine 2017 - 2021
b) annual dividends based on the five-year growth rate
Year Growth rate Dividend
0 $0.96
1 12.11% $1.08
2 12.11% $1.21
3 12.11% $1.35
4 12.11% $1.52
5 12.11% $1.7
c)
g=retention rate x return on new investment
G = (1-93%) x 12%
Growth Rate 0.84%
d)
Stock Price = D5/(r-g) = $1.70/(12%-.84%) $15.23
e)
Current stock Price = $.96 x (1+.84%)/(12%-.84%) $8.67
ii.calculate npv of investment I and 2.
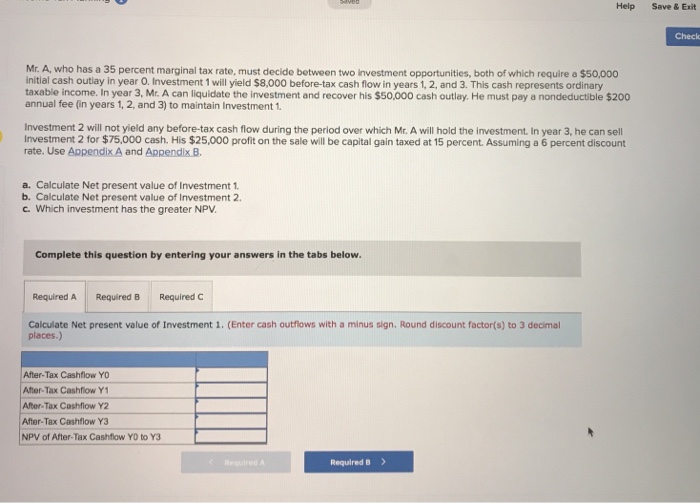
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


