Question: Question within image Consider the following initial value problem: xy' + 2y : 8302 y (1) : 3 We can solve algebraically to nd the
Question within image
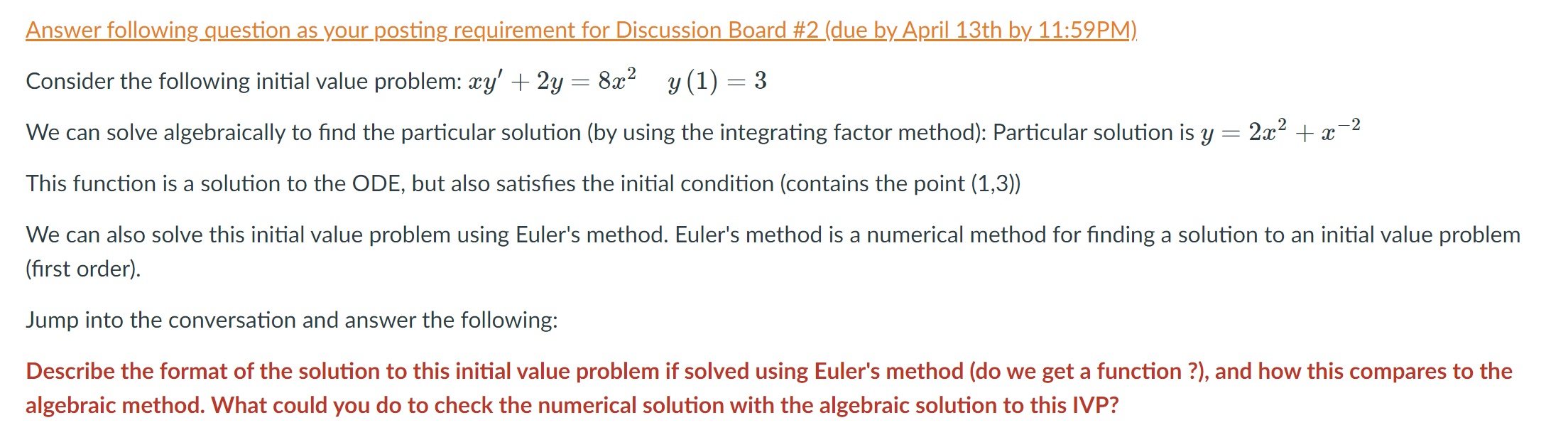

Consider the following initial value problem: xy' + 2y : 8302 y (1) : 3 We can solve algebraically to nd the particular solution (by using the integrating factor method): Particular solution is y : 2x2 + x72 This function is a solution to the ODE, but also satises the initial condition (contains the point (1,3)) We can also solve this initial value problem using Euler's method. Euler's method is a numerical method for nding a solution to an initial value problem (rst order). Jump into the conversation and answer the following: Describe the format of the solution to this initial value problem if solved using Euler's method (do we get a function ?), and how this compares to the algebraic method. What could you do to check the numerical solution with the algebraic solution to this IVP? Consider the second order equation y\" + By, 7 6y : 0, which can be solved using the characteristic equation. How can the discriminant ofa quadratic equation be used to determine the form of the general solution to y\" + 5y' 7 6y : 0
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


