Question: question2 Question 6 (1 point) In order for a heuristic for A' search to be admissible, which of the following must be true ? The
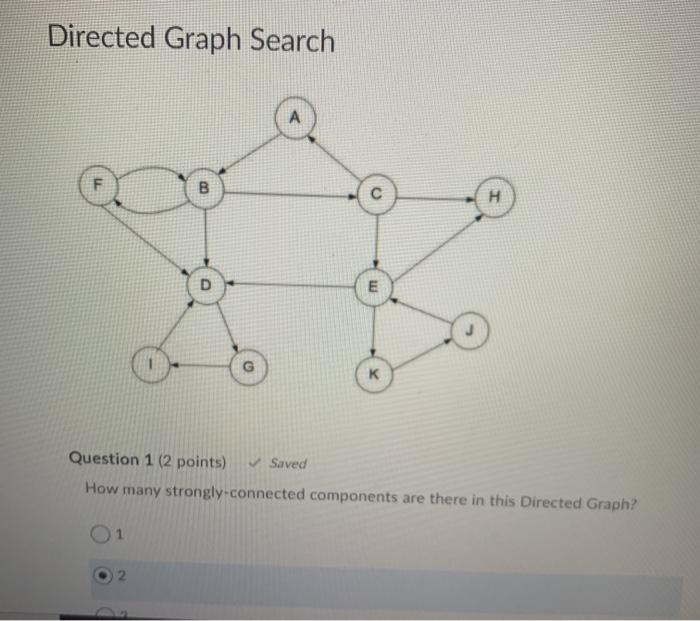
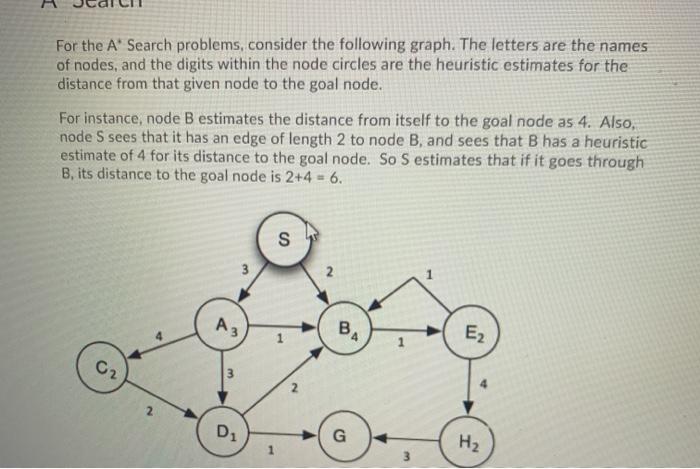
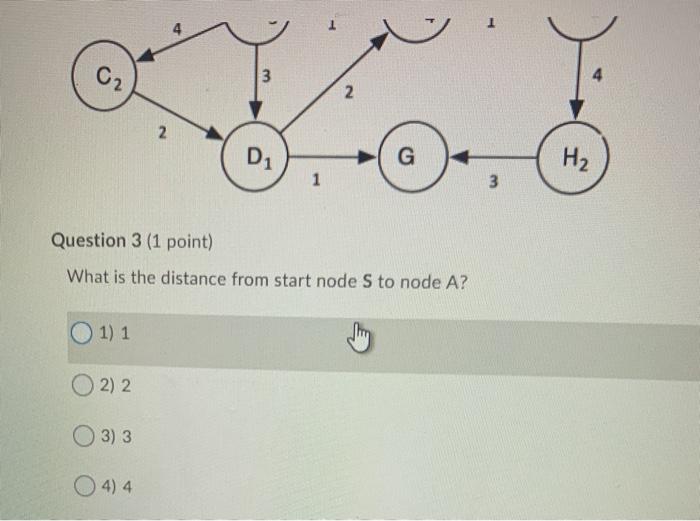
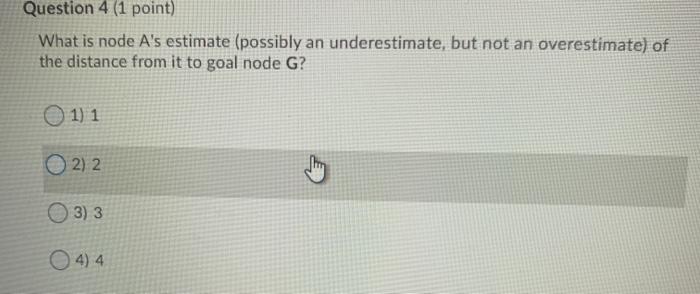
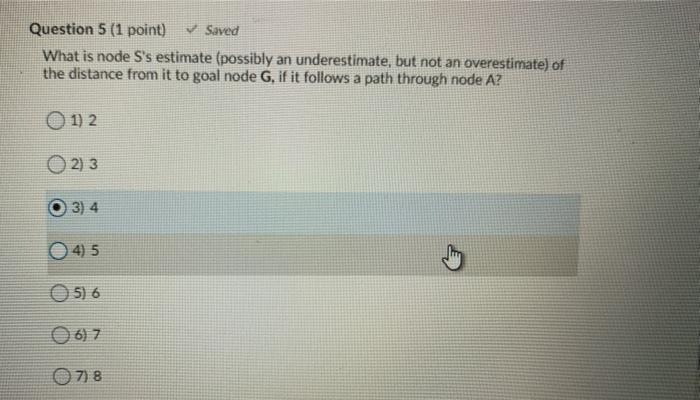
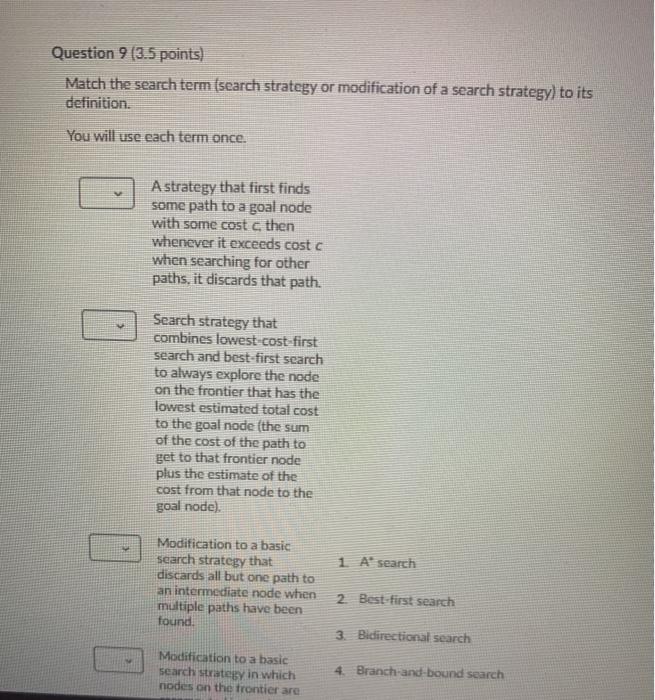
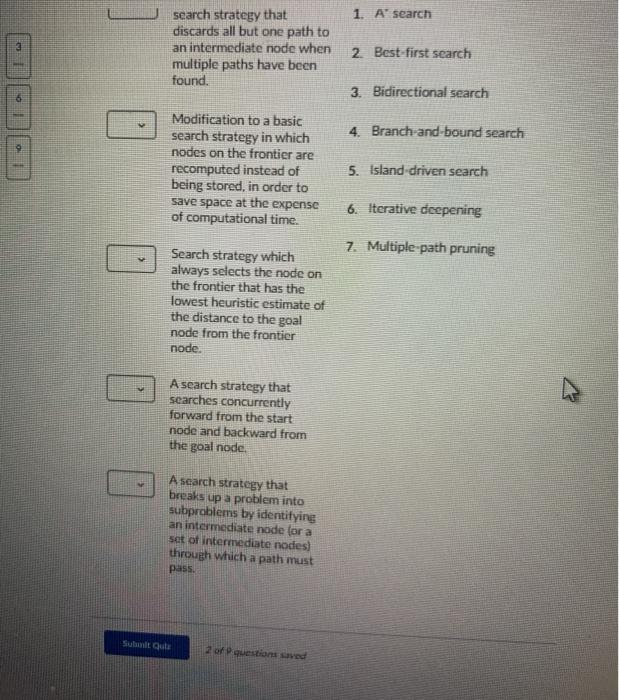
Directed Graph Search F B H E Question 1 (2 points) Saved How many strongly connected components are there in this Directed Graph? Question 2 (2 points) What is the size (in number of vertices) of the largest strongly connected component of the Directed Graph? 1) 1 0 2 2 3) 3 O 4) 4 5) 5 06) 6 7) 7 8) 8 99 010 For the A Search problems, consider the following graph. The letters are the names of nodes, and the digits within the node circles are the heuristic estimates for the distance from that given node to the goal node. For instance, node B estimates the distance from itself to the goal node as 4. Also, node S sees that it has an edge of length 2 to node B, and sees that B has a heuristic estimate of 4 for its distance to the goal node. So S estimates that if it goes through B, its distance to the goal node is 2+4 = 6. s 3 A3 BA E2 C2 N 2 D1 G H2 02 3 2. 2 D G H2 1 3 Question 3 (1 point) What is the distance from start node S to node A? 1) 1 0 2 2 O3)3 O 4) 4 Question 4 (1 point) What is node A's estimate (possibly an underestimate, but not an overestimate) of the distance from it to goal node G? 1) 1 0 2 2 3) 3 O 4) 4 Question 5 (1 point) Saved What is node S's estimate (possibly an underestimate, but not an overestimate) of the distance from it to goal node G, if it follows a path through node A? 0 1 2 O2) 3 3) 4 4) 5 5) 6 06) 7 07) 8 Question 9 (3.5 points) Match the search term (search strategy or modification of a search strategy) to its definition You will use each term once. A strategy that first finds some path to a goal node with some cost then whenever it exceeds cost c when searching for other paths, it discards that path. Search strategy that combines lowest cost-first search and best first search to always explore the node on the frontier that has the lowest estimated total cost to the goal node (the sum of the cost of the path to get to that frontier node plus the estimate of the cost from that node to the goal node) 1 A' search Modification to a basic search strategy that discards all but one path to an intermediate node when multiple paths have been found 2 Best first search 3. Bidirectional search Modification to a basic search strategy in which nodes on the frontier are 4. Branch-and-bound search 1. A' search search strategy that discards all but one path to an intermediate node when multiple paths have been found. 2. Best first search 1 3. Bidirectional search 4. Branch-and-bound search 0 Modification to a basic search strategy in which nodes on the frontier are recomputed instead of being stored, in order to save space at the expense of computational time. 5. Island driven search 6. Iterative deepening 7. Multiple path pruning Search strategy which always selects the node on the frontier that has the lowest heuristic estimate of the distance to the goal node from the frontier node. A search strategy that searches concurrently forward from the start node and backward from the goal node. A search strategy that breaks up a problem into subproblems by identifying an intermediate node for a set of intermediate nodes) through which a path must pass. Sumu 2 of questions saved
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


