Question: Questions 1. M&A between firms from different countries link with some cultural differences, explain? 2. Illustrates how the countries culture fit with the attributes described


Questions
1. M&A between firms from different countries link with some cultural differences, explain?
2. Illustrates how the countries culture fit with the attributes described in this case?
3. Some culture conflicts could be ease by senior managers before and after the merger process, How? 4. Subsidiary and acquired firms enforce its own methods on another, why? Note: you might use the chart and the link above of GLOBE Project
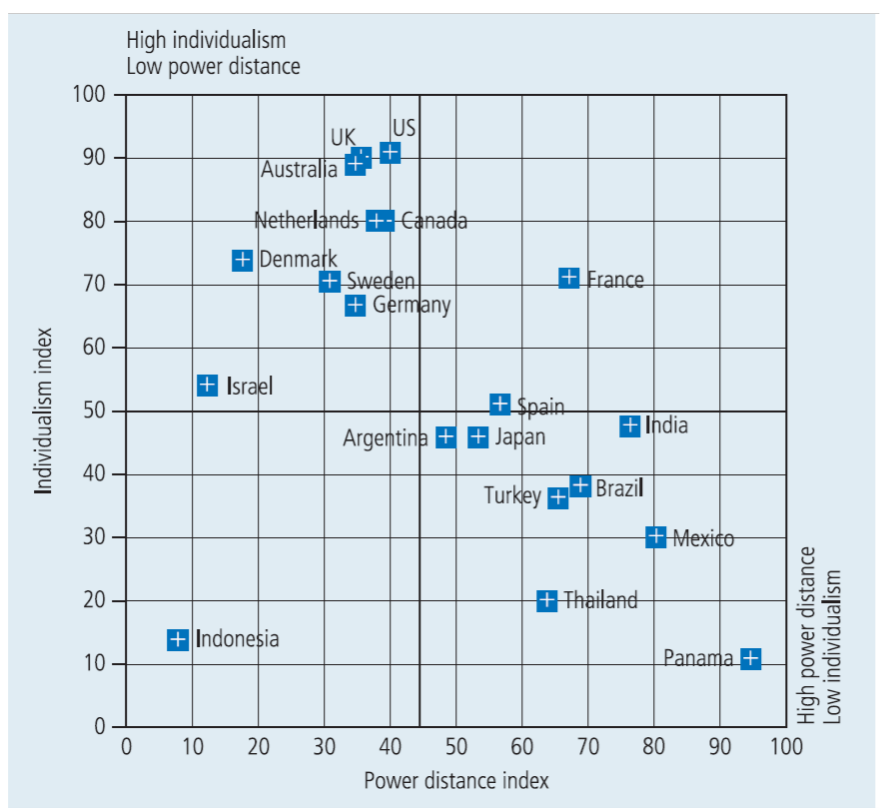
Despite all being part of the same advanced, industrialized world, Kalamazoo (Michigan, USA), Stockholm (Sweden), and Milan (Italy) are worlds apart in many important ways. Senior managers leading the merger between two pharma- ceutical firms, Upjohn Company of the United States and Pharmacia AB of Sweden (with operations in Italy), came to realize how significant these differences were after the merger took place in 1995. Swedes take off most of the month of July for their an- nual vacation, Italians take off most of August. Not knowing this, American executives scheduled meetings in the sum- mer only to have to cancel many because their European counterparts were at the beach. As the more dominant American firm began to impose its way of doing things on the newly-acquired European organizations, international relationships became increasingly strained. Neither the Swedes nor the Italians were happy with impositions such as the drug and alcohol testing policy brought in by Upjohn, or the office smoking ban. These clashed with local ways of doing things and the more infor- mal work environment that these cultures prefer. Although Upjohn later relaxed many of these work rules, allowing some local practices and preferences to prevail, ill-feeling and a degree of resistance had already developed among European colleagues. The additional bureaucracy and the command-and-control style imposed by the Americans created more significant problems for the 34,000 employees and managers in Pharmacia and Upjohn Company. The Swedes were used to an open, team-based style of management where responsi- bilities are devolved, managers are trusted and not strictly monitored or closely managed. Swedish executives also tend to build up a consensus behind big decisions, "getting everyone in the same boat" (alla aer i baten) rather than handing orders down the hierarchy. As a traditionally American multinational, however, Upjohn was more used to strong leadership and a centralized command-and-control structure. Its CEO, Dr. John Zabriskie, quickly created a strict reporting system, tight budget control, and frequent staffing updates, which clashed with the Swedish organization style. Swedish managers would leave meetings disgruntled, hav- ing been overruled by American executives keen to push their vision of the merged company. The Swedes own ways of doing things had already clashed with the Italian style of management, following the takeover of Farmitalia (part of Montedison) by Pharmacia in 1993. Italians are used to a distinctive division between workers (and their strong unions) and managers. Their steeper hierarchies contrast the more egalitarian Swedes. Italians also place a high value on families and will leave work to tend to sick relatives or help with childcare, which the Swedes frown upon. The addition of the Americans from Upjohn into this mix created further cultural confusion. Communication problems, beyond the obvious language differences, became a real barrier to honest dialogue. "You go there thinking you're going to streamline the place," said American Mark H. Corrigan, Pharmacia and Upjohn vice president for clinical development, and you leave just having added five pounds from some wonderful meals." These differences, many of them small but important at the local level, quickly began to have an impact on the over- all performance of the merged company. In the months and years following the merger unforeseen inefficiencies and added costs began to undermine the potential synergies of bringing together two such companies in the first place. At one level the problems amounted to things like canceled meetings, new organization demands (such as monthly report-writing), and a general decline in staff morale. There were also unexpected difficulties integrating the IT systems across the various parts of the merged organization. These and other changes added an estimated $200 million to the predicted costs of the restructuring, taking the total cost to $800 million. Even more seriously, for a pharmaceutical company heavily reliant on its new drugs pipeline to survive, delayed product launches and the loss of key staff (including the head of R&D at Pharmacia) had a longer-term impact. "There was probably an under-appreciation of these cul- tural differences," says Art Atkinson, former vice president for clinical research and development. Particular problems resulted from the restructuring of the firm's global R&D structure. Prior to the merger Upjohn owned well-known names such as Rogaine and Motrin and had annual sales of around $3.5 billion, but had a weak new product pipeline and slow sales growth compared to its larger competitors. Similar-sized Pharmacia had a more promising pipeline but weak distribution and sales in the US market, the world's largest. These amounted to a strong rationale for the merger. Together they could challenge the financial power and the larger R&D programs of their com- petitors. However, integrating and re-focusing the various parts of the new R&D structure became a major problem. Rather than place the R&D headquarters in the United States, Sweden, or Milan a decision was made to establish a new and neutral London-based center for the R&D function. This simply added a layer of management and a more com- plex matrix reporting structure, which further alienated key R&D personnel. In 1997, after the stock price of the merged corporation had fallen significantly, CEO John Zabriskie resigned. Swede Jan Ekberg, the former head of Pharmacia, took over tem- porarily and began to rebuild aspects of the merged organization. After acquiring a major part of Monsanto in 2000, Pharmacia and Upjohn became Pharmacia and was then itself acquired by the American giant Pfizer in April 2003. This made Pfizer, according to its own Annual Report, the "number one pharmaceutical company in every region of the World." All this proves is that going global is hard work. Not all of these problems could have been foreseen, but a real lack of awareness of cultural differences did lead to many of the organization difficulties and people problems with a real impact on the bottom line. High individualism Low power distance 100 US 90 UK # Australia 80 Netherlands +- Canada + Denmark + Sweden # Germany 70 + France 60 + Israel Individualism index 50 + $pain + India Argentina E + Japan 40 + Brazil Turkey + + Mexico 30 20 + Thailand + Indonesia High power distance Low individualism 10 Panama + 0 0 10 20 30 70 80 90 100 40 50 60 Power distance indexStep by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


