Question: Questions 1 Using the information in the 'Background' section of Lian's proposal, what concerns may be raised about the proposed 'Research design', 'Title', 'Research question






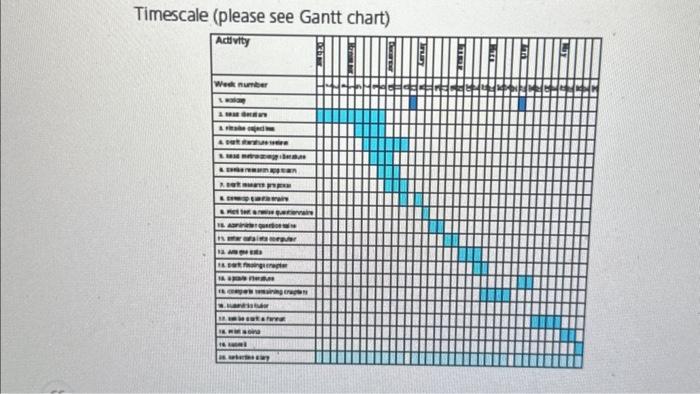
Questions 1 Using the information in the 'Background' section of Lian's proposal, what concerns may be raised about the proposed 'Research design', 'Title', 'Research question and research objectives'? 2 What further information would be helpful to know in the 'Participants' section? 3 Drawing on your responses to questions 2 and 3, how would you re-draft the 'Title', 'Research question and research objectives' and the 'Research design'? Method Research design This research is designed to test the applicability of these theories in a case study. Chinese organisation, The research will use a survey strategy incorporating existing scales from peer-reviewed, high-quality acadernic journab. The research will be cross-secticnal in nature. Participants The intended participants in this study work for [company namel in China. Its managernent have agreed to grant me access to a representative sample of employees drawn from the different grades and occupations and between males and fernaks employed within the organication [email attached], I am currently in correspondence with the manager of the human resource department to finalise a stratified random sample to mpresent the characteristics of the organtiation $ workdorce. it is envisaged that the sample size will be 200 employees. Timescale (please see Gantt chart) initiative. This new scale overlaps with some earier OCB dimensions but replaces cr eliminates outdated iterns related to willingly obeying rules or regimented working practices. Secondly, questions have been asked about the transferability of CB scales to other cultures. OCB studies may apply only to the cultural context within which they are conducted (Choi 2009). The applicablity of OCB to other cultural settings therefore requires further research. Hui et al. (2004) examined the relationships between psychobgical contract constructs and OCBs in China. They adopted the OCB scale developed by Podsakoff et al. (1990) (see earlier) and, in part, found that that more research is required to understand how culture affects the applicability of CB. Farh et al. (1997) examined the relationsh ps between organisational justice theory and OCBs in China, using a Chinese CCBB scale they develcoped. They found that the relationships between organisational justice and OCB were moderated by cultural (attitudes about either modernity or tradition) and gender factors. Some behaviour of Chinese employees may be due to socialisation or broader cultural norms and be more personally focused than organisationally related (Farh et al. 1997; Hui et al. 2004). This raises questions about the applicability of OCB in China and whether organisational justice and psychology contract constructs may be determinants or antecedents of OCB. In addition, Hui et al. (2004) point out that organisational type may affect OCB; for example, they cite research saying that Chinese employees may prefer working for a foreign-owned compary rather than a state-owned enterprise. Research question and research objectives The research question is: To what extent are organisational citizenship behaviour, organiational justice and psychological contract theories applicable to Chinese organisations and why? The research objectives are: 1. To identify suitable measurement scales for each theory, to use in the case study Chinese organisation. 2. To examine the relationsh p in the case study organisation between findings from the organisational justice scale and findings from the organisational citizenship behaviour scale. 3. To examine the relationship in the case study organisation between findings from the psychological contract scale and findings from the organisational citisenship behaviour scale. 4. To exarnine the relationship between findings in the case study organisation from the organisational citizenship behaviour scale and findings in other national contexts from organibational citizenship behaviour research. 5. To draw conclusions from the relationships observed in objectives 2,3 and 4 , to evaluate the applicability of these concepts in a Chinese organisation. Case 2 'Helpful but not required': A student research proposal Lan was a student from China tian was interested in the applcablity of organiational citiserehip behaviour thecry to Chinese worken. An abbreviated werion of tians mearch proposal follows. it has been delberately modicd to allow you to maluate and improve it by working through the case study questions Title The applicabisty of organiational cittenuhip behaviour theory to a Chinent organisation Background The early defrition of erganbationel citizenship behavour (OCB) vimed this as decivtionar behavour by employes that wew not recognised thiough the reward sytem iOrgan 19ef Organ et al. 2006). Party because woch behwours could sutrequenty be recogised through rward, OCB was redefinds as 'performance that wpports the soclal and psochoibokal weh as kolno et at. (2002) to indicate stuations where enployes work beyond contrictual requirements to support cne anochec, to subordinme ind widual interests bo organkational organisational performance and posentialy ofler a source of competitive advavege. Podsahot et at (2009) eppont finding over 650 puthahed artider on 0CB, mainly esamining 10 these other varlables. An early, infuential study bo identfy its dimensiona vaed inlewew wth marapen in a manutacturing conpany 10 'idently matances of helphe, but ret early studies led to the identicaton of five categores of OClis rorgan 1960 . Theie were the organisaton), conscentiousress (woring byond the minirum requivments for the jobl. courey fcorsidening how ones own behwiout might aflect othen and acting to facilike Background The early definition of organisational citizenship behaviour (CB) viewed this as discretionary behaviours by employees that were not recognised through the reward system (Organ 1988; Organ et al. 2006). Partly because such behaviours could subsequently be recognised through reward, B was redefined as 'performance that supports the social and psychological environment' within which work occurs (Organ 1997: 95). It has been adopted by researchers such as Bolino et al. (2002) to indicate situations where employees work beyond contractual requirements to support one anothec, to subordinate ind widual interests to organisational ones and to demonstrate organisational commitment. In this way CBs may contrbute to organisational performance and potentially offer a source of competitive advantage. Podsakotf et al. (2009) report finding over 650 published articles on OCB, mainly examining the categories of behaviour that make up C B (its dimensions), what causes employees to engage in these behaviours (the determinants or antecedents of OCB ) and how OCB is related to these other variables. An early, influential study to identify its dimensions used interviews with managers in a manufacturing company to 'identify irstances of heipful, but not absolutely required job behaviour' to help to define OCB (Smith et al. 1983). This and other earty studies led to the identification of five categories of OCBs (Organ 1988). These were labelled as altruism (helping a co-worker with a workplace task); civic virtue (participating in the organisation); conscientiousness (working beyond the minimum requirernents for the job): courtesy (considering how one's own behaviour might affect others and acting to facilitate harmony: and sportsmansh p (not complaining even in less than ideal situations) (e.g. Organ 1988). Further research led to new dimensions of OCB being proposed (Organ et at. 2006, although these five original categories have remained the most commonly tested. However, continuing to use some of these dimereicns of OCB and the measurement scalen associated with them (Organ 1988; Podsakoff et al. 1990) han been questioned for two important mascons. Firstly, the nature of work has changed since the 1960s and 1990\%. Manufacturing and manual work is now less important in many economier while knowledge work a much moe important. Exed on research, Dekas et al (2013) deveioped an OCB scak for knowbdge worken that reflects the nature of knowledge-baved work, such as working flexbly and taking penonal Resources I will be responsible for producing and copying the questionnaire. I will pay for the cost of posting these to China. I abo have access to IBM SPSS Statistics and am competent in the analycical techniques required to analse the data and interpret this analysis. The corrpany has bindly agreed to pay the costs of returning the completed questionnaires to me. Once I have received these questionnaires I will be responsible for inputting the data into the software to analyse it. There should not be any other resource requirements in order to be able to undertake this research project. References Bolino, M.C., Turnley, W.H. and Bloodgood, LM. (2002) 'Otizenship behwwour and the creation of socul capital in organizations;, A cademy of Management Review, Vol. 27, No. 4, pp. 50522. Chol, JN. (2009) 'Collective dynamics of ctisenship behavour: What group charscierstua promote gouptevel helping?', buind of Menagement Studhes, vol. 46, No. 6, pp. 1396-420. Dekax, K.H., Saue, TN. Welle, B., Kurkosk, 1 and sullivan, 5. (2013) Organizational citbenship behavor, version 2.0: A renew and qualiasve investigason of OCBs for knowledge workess at Google and beyond", Acadeny of Management Perspectives, Vol, 27, No. 3. PP. 219-37. Faht, 1L, Eartey, P.C. and Un, S.C. (1997) Impetus for action: A cultural analyss of justoce and No. 3 , pp. 42144. Hul, C, Lee, C. and Roussesu, D.M. (2004) Pychological contract and organtzatconal otzenship Na. 2, pp. 311-21. MA. Lexington books. Avformarce, val, 10, No, 2, pp. 8597. Nature, Antecedents and Consequerces. Thourand ouks, CA: sage. Techniques The scales for organisational citizenship behaviour, organisational justice and the psychological contract will be incorporated into a questionnaire that will also collect data about respondents' demographic characteristics. This questionnaire will be administered in Chinese. It will be checked for accuracy of translation and pibt tested by some of my fellow students. Amendrnents will be made where necessary. It will then be adm histered in paper form. My data will be analysed quantitatively using IBM SPSS Statistics. A range of statistical techniques will be used to analyse these data and the results from these will be used to identify relationships between the concepts identified in the research objectives and to allow comparison with previously published research. Ethical considerations and procedures I will compose a letter to be sent to members of the sample that informs them about who I am and the purpose of my research project, and to assure them that their responses to each of the questionnaire items will be seen and used only by me. Respondents will not be asked for their narne on the questionnaire. The questionnaire will ask for only limited personal data about each participant [for example, whether they are male or fernale as previous research has found this to be a significant factor in the applicability of organisational justice and organisational citizenship behaviours in a Chinese context (fart et al, 1997)). Completed questionnaires will be posted into a sealed container that will be retumed to me to ensure respondent confidentiality and the anonymity of the data that they provide. These questionnaires will be given an ancnymous code and the data they contain entered into a spreadsheet by me. Once thave irput the data and it has been checked carefully to ensure accuracy the questionnaires will be shredded by me. Ensuring confidentiality and anonymity should mean that no harm should result from participating in this research. Part of my covering letter will state that participation is ensirely voluntary and if an intended participant does not wibh to take part they are not under any obligation to do so. Another matching employee will be sent a copy of my letter and acked if they would bike to receive a copy of my questionnaire, it he or she is willing to complete the questionnaire, he or she will be informed to post it personalyy into the sealed container
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


