Question: Questions: 1) What kind of tree does the code below generate? 2) Modify it to do all 3 traversals (Pre-order traversal, In-order traversal, and Post-order
Questions:
1) What kind of tree does the code below generate?
2) Modify it to do all 3 traversals (Pre-order traversal, In-order traversal, and Post-order traversal).
3) Use rand() to generate data. Now what do you get? - I am unsure what was ment by this question so if anyone knows that would be great, if not I guess it is ok to just reply cannot answer 3.
4) How do you organize the input to produce the tree in the image? Prove this with your code
_____________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
Code:
#include
_____________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
Image of tree: I am unsure if 7 6 and 8 are part of the tree or not
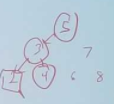
5
/ \
3 7
/ \ / \
2 4 6 8
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


