Question: Questions for part e: Which policy uses a constant-payout ratio?(Select the best answer below.) A. The policy described in part d is a constant-payout ratio
Questions for part e:
Which policy uses a constant-payout ratio?(Select the best answer below.)
A.
The policy described in part d is a constant-payout ratio which will yield low or no dividends if earnings decline or a loss occurs.
B.
The policy described in part b is a constant-payout ratio which will yield low or no dividends if earnings decline or a loss occurs.
C.
The policy described in part c is a constant-payout ratio which will yield low or no dividends if earnings decline or a loss occurs.
D.
The policy described in part a is a constant-payout ratio which will yield low or no dividends if earnings decline or a loss occurs.
Which policy uses a regular dividend?(Select the best answer below.)
A.
Policy described in part d uses a regular dividend policy which minimizes the owners' uncertainty of earnings.
B.
Policy described in part a uses a regular dividend policy which minimizes the owners' uncertainty of earnings.
C.
Policy described in part b uses a regular dividend policy which minimizes the owners' uncertainty of earnings.
D.
Policy described in part c uses a regular dividend policy which minimizes the owners' uncertainty of earnings.
Which policy uses a low-regular-and-extra dividend policy?(Select the best answer below.)
A.
Policy described in part a uses a low-regular-and-extra policy giving investors a stable income.
B.
Policy described in part c uses a low-regular-and-extra policy giving investors a stable income.
C.
Policy described in part b uses a low-regular-and-extra policy giving investors a stable income.
D.
Policy described in part d uses a low-regular-and-extra policy giving investors a stable income.
Which policy provides the stability of a regular dividend but allows for future dividend growth?(Select the best answer below.)
A.
Policy described in part d provides the stability of a regular dividend but allows for larger future growth of dividends.
B.
Policy described in part a provides the stability of a regular dividend but allows for larger future growth of dividends.
C.
Policy described in part c provides the stability of a regular dividend but allows for larger future growth of dividends.
D.
Policy described in part b provides the stability of a regular dividend but allows for larger future growth of dividends.
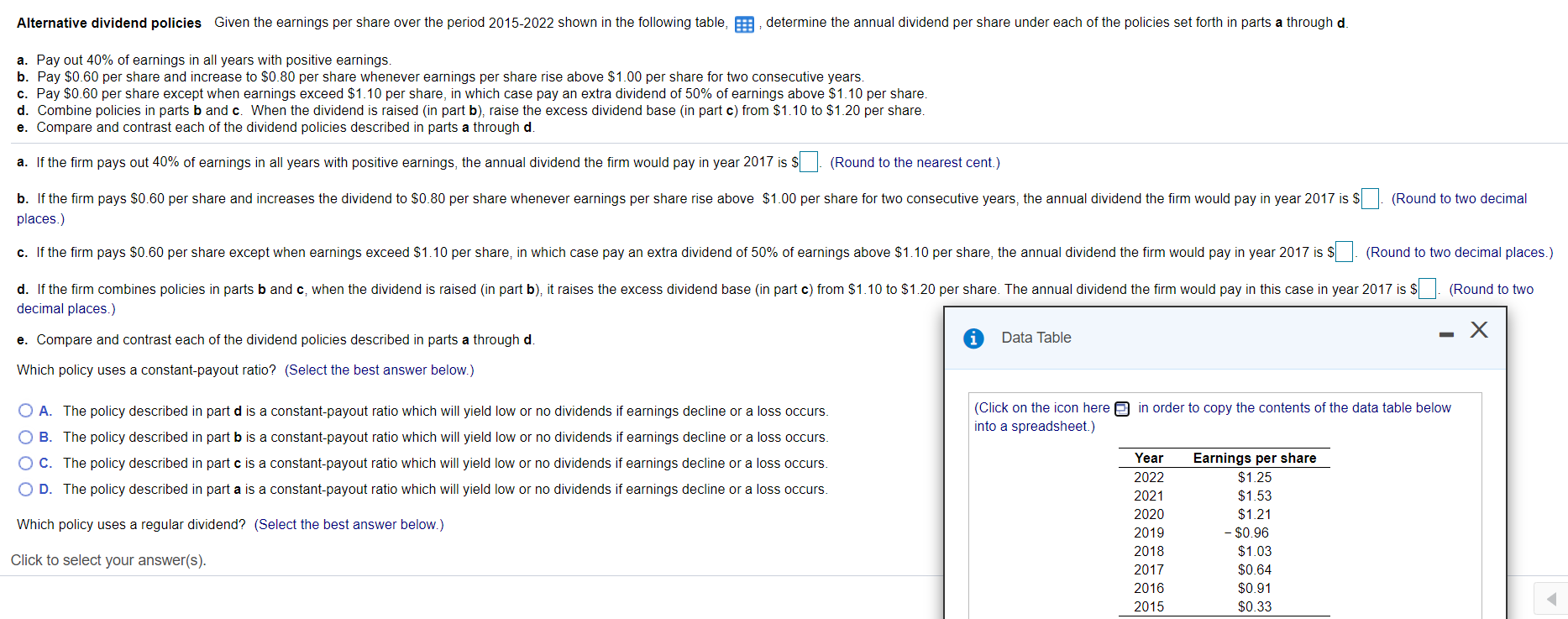
Alternative dividend policies Given the earnings per share over the period 2015-2022 shown in the following table, E, determine the annual dividend per share under each of the policies set forth in parts a through d. a. Pay out 40% of earnings in all years with positive earnings. b. Pay $0.60 per share and increase to $0.80 per share whenever earnings per share rise above $1.00 per share for two consecutive years. c. Pay $0.60 per share except when earnings exceed $1.10 per share, in which case pay an extra dividend of 50% of earnings above $1.10 per share. d. Combine policies in parts b and c. When the dividend is raised (in part b), raise the excess dividend base (in part c) from $1.10 to $1.20 per share. e. Compare and contrast each of the dividend policies described in parts a through d. a. If the firm pays out 40% of earnings in all years with positive earnings, the annual dividend the firm would pay in year 2017 is $ (Round to the nearest cent.) (Round to two decimal b. If the firm pays $0.60 per share and increases the dividend to $0.80 per share whenever earnings per share rise above $1.00 per share for two consecutive years, the annual dividend the firm would pay in year 2017 is S places.) c. If the firm pays $0.60 per share except when earnings exceed $1.10 per share, in which case pay an extra dividend of 50% of earnings above $1.10 per share, the annual dividend the firm would pay in year 2017 is $ (Round to two decimal places.) d. If the firm combines policies in parts b and c, when the dividend is raised (in part b), it raises the excess dividend base (in part c) from $1.10 to $1.20 per share. The annual dividend the firm would pay in this case in year 2017 is $. (Round to two decimal places.) e. Compare and contrast each of the dividend policies described in parts a through d. Data Table Which policy uses a constant-payout ratio? (Select the best answer below.) (Click on the icon here in order to copy the contents of the data table below into a spreadsheet.) O A. The policy described in part d is a constant-payout ratio which will yield low or no dividends if earnings decline or a loss occurs. OB. The policy described in part b is a constant-payout ratio which will yield low or no dividends if earnings decline or a loss occurs. O C. The policy described in part c is a constant-payout ratio which will yield low or no dividends if earnings decline or a loss occurs. OD. The policy described in part a is a constant-payout ratio which will yield low or no dividends if earnings decline or a loss occurs. Which policy uses a regular dividend? (Select the best answer below.) Year 2022 2021 2020 2019 2018 2017 2016 2015 Earnings per share $1.25 $1.53 $1.21 - $0.96 $1.03 $0.64 $0.91 $0.33 Click to select your answer(s)
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


