Question: Recall that the C++ vector data structure dynamically doubles its size if there is not an available slot to insert an item. (The vector::push_back operation
Recall that the C++ vector data structure dynamically doubles its size if there is not an available slot to insert an item. (The vector::push_back operation increases the number of elements by 1. It also doubles its capacity if there was an available slot to insert an item.) The load factor describes how full the data structure is. It is defined as the vector's size divided by it's capacity. (Empty vectors are given a load factor of 1.) Suppose we allow vector to also contract it's size by 2/3 when its load factor drops below 1/3. (The vector::pop_back operation reduces the number of elements by 1. It also reduces the capacity to 2/3 if the new load factor drops below 1/3. Using the potential function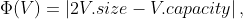 show that the amortized cost of vector::pop back that uses this strategy is bounded above by a constant.
show that the amortized cost of vector::pop back that uses this strategy is bounded above by a constant.
Remember that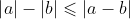 .
.
2V.size - V.capacity
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


