Question: = Recall the least squares problem Xx = argmin|| Ax 6||2 and let f(3) = || Ax 6||2, so that the problem becomes X* argminf().
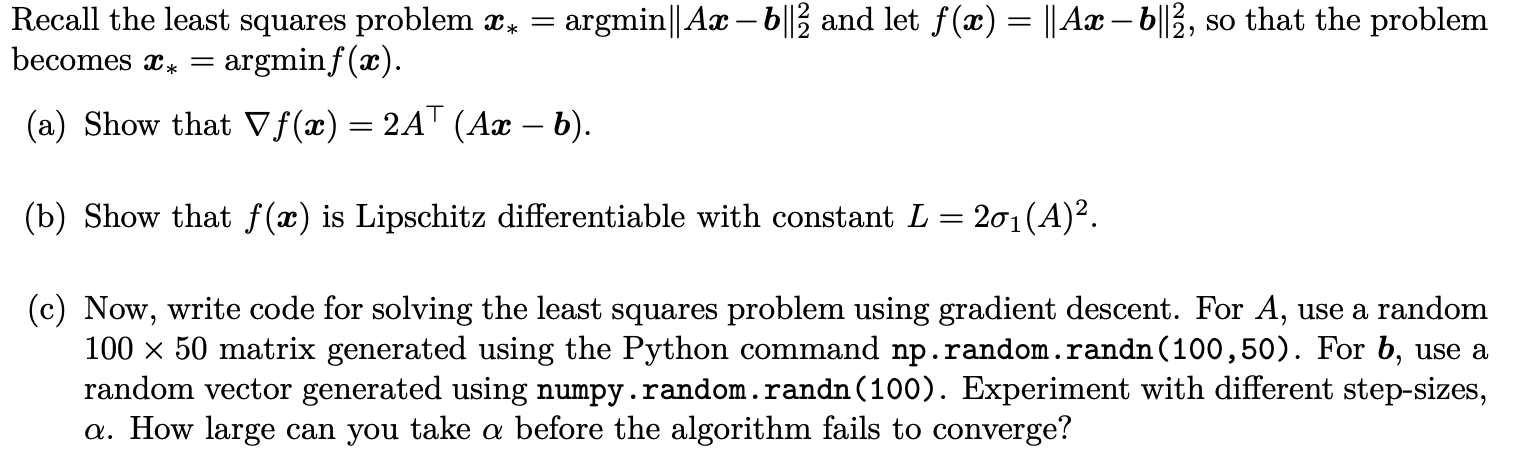
= Recall the least squares problem Xx = argmin|| Ax 6||2 and let f(3) = || Ax 6||2, so that the problem becomes X* argminf(). (a) Show that V f (x) = 2AT (Ax b). (b) Show that f(x) is Lipschitz differentiable with constant L = 201(A)2. (c) Now, write code for solving the least squares problem using gradient descent. For A, use a random 100 x 50 matrix generated using the Python command np.random.randn(100,50). For b, use a random vector generated using numpy.random.randn(100). Experiment with different step-sizes, a. How large can you take a before the algorithm fails to converge? = Recall the least squares problem Xx = argmin|| Ax 6||2 and let f(3) = || Ax 6||2, so that the problem becomes X* argminf(). (a) Show that V f (x) = 2AT (Ax b). (b) Show that f(x) is Lipschitz differentiable with constant L = 201(A)2. (c) Now, write code for solving the least squares problem using gradient descent. For A, use a random 100 x 50 matrix generated using the Python command np.random.randn(100,50). For b, use a random vector generated using numpy.random.randn(100). Experiment with different step-sizes, a. How large can you take a before the algorithm fails to converge
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


