Question: Recall we define SXT = {(s, t): sS and t T}. For each of the following, prove it if it is always true, else
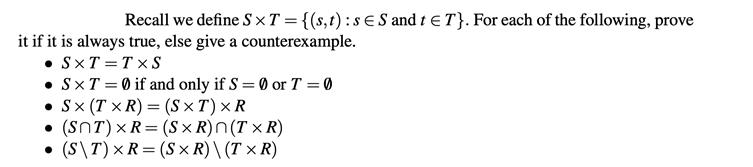
Recall we define SXT = {(s, t): sS and t T}. For each of the following, prove it if it is always true, else give a counterexample. SXT=TXS SXT = 0 if and only if S = 0 or T = 0 Sx (TxR) = (SxT) XR (SNT) XR=(SXR)n(TXR) (S\T) XR=(SXR)\ (TxR)
Step by Step Solution
3.41 Rating (151 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Answer To prove or disprove the statements lets define sets S T and R and examine each case separately 1 SXT TXS To prove this statement we need to show that for any sets S and T the set SXT is equal ... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


