Question: Refer to the following code, implement the method: Public NumStack join(NumStacks) GHT sa MumStack implements comparable public class NumStack public NumStack join(NumStack s) joins private
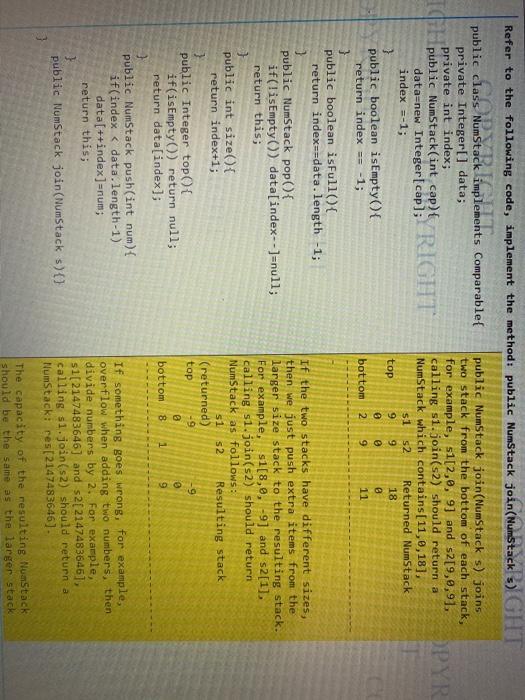
Refer to the following code, implement the method: Public NumStack join(NumStacks) GHT sa MumStack implements comparable public class NumStack public NumStack join(NumStack s) joins private Integer[] data; two stack from the bottom of each stack, private int index; for example, 51[2,0, 9] and s2[9,9,9]. calling s1.join(S2) should return a OPYR RIGHT data=new Integer[cap]; NumStack which contains[11,0,18]. index =-1; Returned NumStack } top public boolean isEmpty() { return index == -1; bottom 2 52 s1 9 0 9 18 B 9 11 public boolean isFull({ return index==data. length -1; 3 public NumStack pop(){ if(!isEmpty()) data[index--]=null; return this; 1 public int size({ return index+1; If the two stacks have different sizes, then we just push extra items from the larger size stack to the resulting stack. For example, $1[8,0, -9] and s2[1], calling s1.join(2) should return NumStack as follows: s1 s2 Resulting stack (returned) top -9 9 @ bottom 8 1 9 public Integer top { if(isEmpty) return null; return data[index]; public NumStack push(int num) { if(index
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


