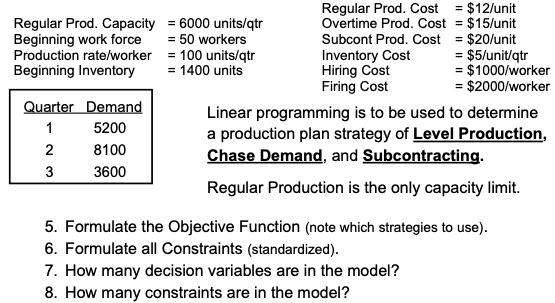
Question: Regular Prod. Cost = $12/unit Regular Prod. Capacity = 6000 units/qtr Overtime Prod. Cost = $15/unit Beginning work force = 50 workers Subcont Prod. Cost
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


