Question: (Related to Checkpoint 6.4) (Present value of a perpetuity) What is the present value of a $230 perpetuity discounted back to the present at 15
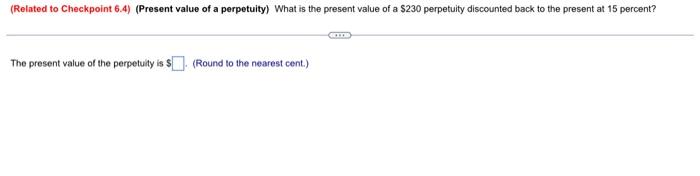


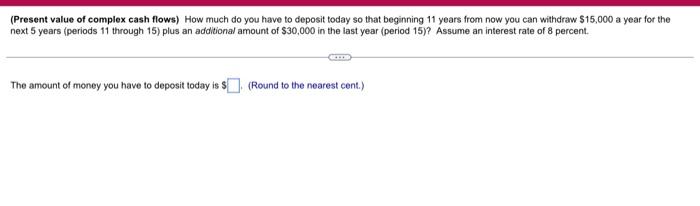
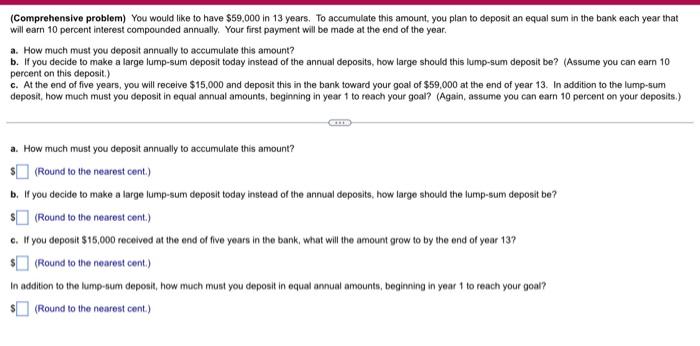
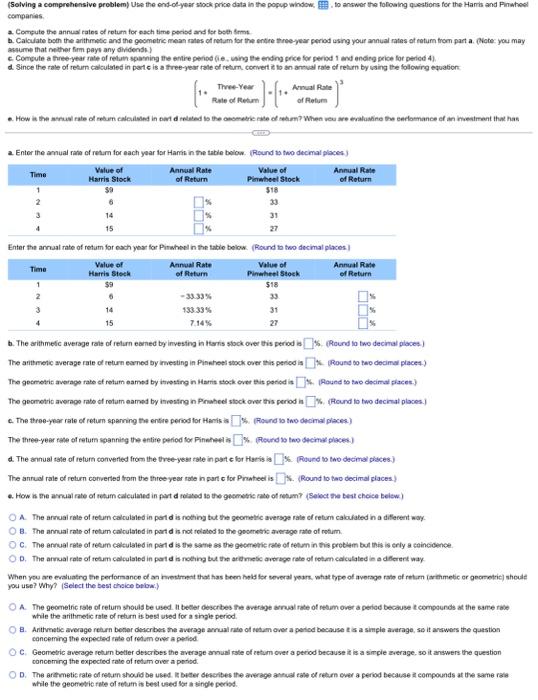
(Related to Checkpoint 6.4) (Present value of a perpetuity) What is the present value of a $230 perpetuity discounted back to the present at 15 percent? GE The present value of the perpetuity is $(Round to the nearest cent.) (Present value of a growing perpetuity) What is the present value of a perpetual stream of cash flows that pays $60,000 at the end of year one and then grows at a rate of 7% per year indefinitely? The rate of interest used to discount the cash flows is 12%. The present value of the growing perpetuity is S. (Round to the nearest cent.) (Related to Checkpoint 6.6) (Present value of annuities and complex cash flows) You are given three investment alternatives to analyze. The cash flows from these three investments are as follows: Investment Alternatives End of Year 1 $ 12,000 $ 12,000 2 12,000 3 12,000 4 12.000 5 12,000 $ 12,000 12,000 60,000 7 12,000 8 12,000 UAWN- 6 a. What is the present value of investment A at an annual discount rate of 19 percent? $(Round to the nearest cent.) b. What is the present value of investment B at an annual discount rate of 19 percent? $(Round to the nearest cent.) c. What is the present value of investment C at an annual discount rate of 19 percent? (Round to the nearest cent.) $ (Present value of complex cash flows) How much do you have to deposit today so that beginning 11 years from now you can withdraw $15,000 a year for the next 5 years (periods 11 through 15) plus an additional amount of $30,000 in the last year (period 15? Assume an interest rate of 8 percent. The amount of money you have to deposit today is $(Round to the nearest cent.) (Comprehensive problem) You would like to have $59.000 in 13 years. To accumulate this amount, you plan to deposit an equal sum in the bank each year that will earn 10 percent interest compounded annually. Your first payment will be made at the end of the year. a. How much must you deposit annually to accumulate this amount? b. If you decide to make a large lump-sum deposit today instead of the annual deposits, how large should this lump-sum deposit be? (Assume you can earn 10 percent on this deposit.) c. At the end of five years, you will receive $15,000 and deposit this in the bank toward your goal of $59,000 at the end of year 13. In addition to the lump-sum deposit, how much must you deposit in equal annual amounts, beginning in year 1 to reach your goal? (Again, assume you can earn 10 percent on your deposits.) a. How much must you deposit annually to accumulate this amount? (Round to the nearest cent.) b. If you decide to make a large lump-sum deposit today instead of the annual deposits, how large should the lump-sum deposit be? $(Round to the nearest cent.) c. If you deposit $15,000 received at the end of five years in the bank, what will the amount grow to by the end of year 13? (Round to the nearest cont.) In addition to the lump-sum deposit, how much must you deposit in equal annual amounts, beginning in year 1 to reach your goal? $(Round to the nearest cent.) (Solving a comprehensive problemUse the end-of-year stock price data in the popup window to answer the following questions for the Harris and Pinwheel companies a Computo the annual rates of return for each time period and for both Soms Calculate both the arithmetic and the geometric mean rates of retum for the entire three-year period using your annual rates of rotum from part a. (Note: you may assume that the firm pays any dividende) Compute a three-year rate of return spanning the entire periode.ing the ending price for period 1 and ending price for period 4) d. Since the rate of return calculated in parte is a free-year rate of return convert a 10 annual rate of return by using the following equation Annual Rate Role of Retum of Retum . How is the ul rate of return calculated in part delated to the onometric rate of setem? When you are evaluating the cartomance of an investment that hon J-C a Enter the annual rate of return for each year for Hart in the table below. Round to two decimal places) Time Value of Annus Rate Value of Annual Rate Harris Stock of Return Pinwheel Stock of Return 1 $18 2 6 33 14 31 15 27 Enter the annual rate of retum for each year for Pinwheel in the table below. Round in two decimal places Time Value of Annual Rate Value of Annual Rate Harris Stock of Return Pinwheel Stock of Return 1 $9 $18 2 6 -33.33% 33 14 933 33% 31 4 15 7.14% 27 b. The arithmetic average rate of return earned by investing in Harris stock over this period Round to two decimal places The anthmetic average rate of return corned by investing in Pinshoe stock over this period is. Round to wo decimal places) The gecmeie average rate of rotum eamed by vesting in Haris stock over dit period is Round to two decimal placer) The geometrio average ratio of retum aated by investing in Puheel stock over this period u % (Round to two decimal places c. The three-year rate of retum sparring the entire perod for Hamisa Pound to two decimal places) The three-year rate of ratum spanning the entire period for Pintesi Round 0 two decimal places) 4. The sonul este of return converted from the tree-year rate in parte for Haeis a ) Round 1 two decimal places.) The annual rate of return converted from the three year rate in partc for Prsteel is. (Round to two decimal places) .. How is me anual rate of retum calculated in part droited to the geometric rate of retum Select the best choice below) O A The annual rate of totum calculated in parte is nothing but the geometric verage rate of retum calculated in a different way OB. The annual rate of retum calculated in partid is not related to the geometric average rate of retum OC. The annual rate of retum calculated in part is the same as the geometric rate of tetun in this problem but this is only a coincidence OD The annual rate of retum calculated in part d is nothing but the arthmec average rate of the calculated in a different way When you are entustro the performance of an investment that has been hold for several years, what type of average rate of return thmetic or geometric) shoult you use? Why? (Select the best choice below) O A The geometric rate of return should be used. It beder describes the average rual rate of retum over a period because compounds at the same se while the arithmetic rate of return is best used for a single period 8. Arttatic average return beter describes the average annual rate of retum over a period because is a simple average, soit answer the question concering the expected rate of retomover a period OC Geometric average retum better describes the average annual rate of tetum over a period because it is a simple average so it answer the question concoming the expected rate of retum over a period OD. The aritmetic rate of return should be used beter describes the average annual rate of retur over a period because a compounds at the same as while the geometric rate of return is best used for a single period
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


