Question: Relevant data: Flyby velocity, V = 8.9 km/s Reaction wheel maximum torque, Tmax = 1.5 Nm Reaction wheel maximum rotation speed, max = 8,700

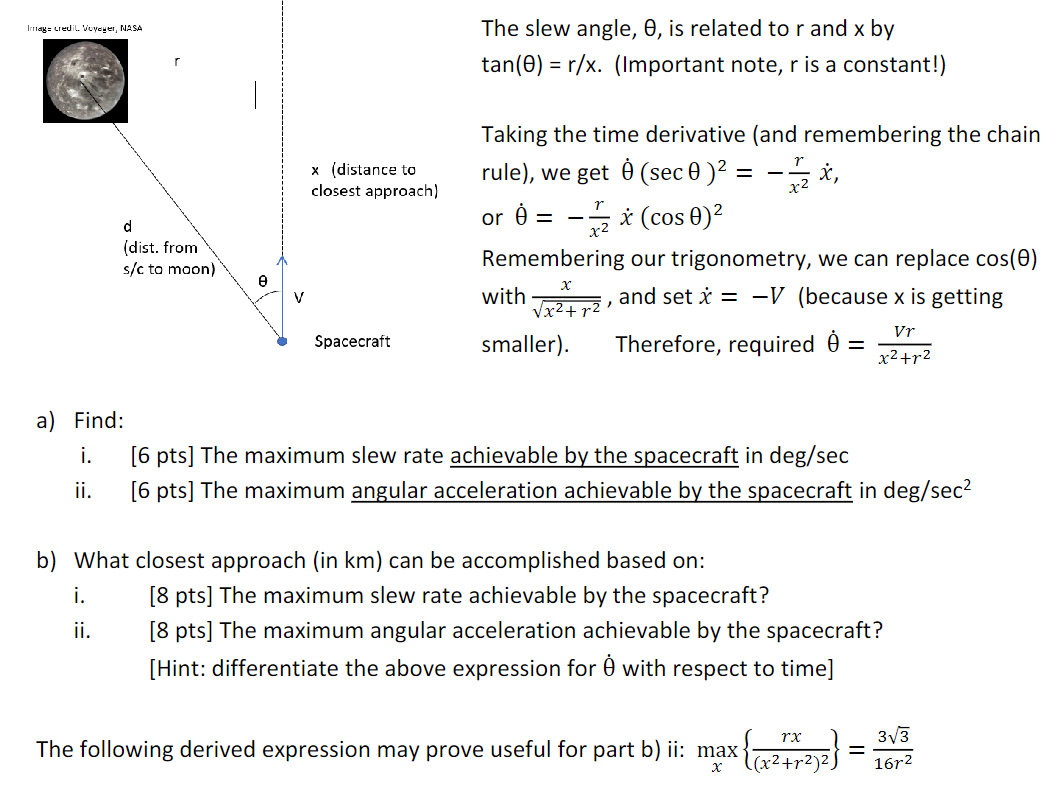
Relevant data: Flyby velocity, V = 8.9 km/s Reaction wheel maximum torque, Tmax = 1.5 Nm Reaction wheel maximum rotation speed, max = 8,700 RPM Reaction wheel moment of inertia, Irw = 1.0 kg m Slew axis moment of inertia, I = 16,500 kg m Image credit. Voyeyer, NASA d (dist. from s/c to moon) V x (distance to closest approach) Spacecraft The slew angle, e, is related to r and x by = tan(0) r/x. (Important note, r is a constant!) Taking the time derivative (and remembering the chain rule), we get (sec 0 ) = x, or = - x (cos 0) Remembering our trigonometry, we can replace cos(e) with 22, and set x = -V (because x is getting smaller). Therefore, required = Vr x+12 a) Find: i. [6 pts] The maximum slew rate achievable by the spacecraft in deg/sec ii. [6 pts] The maximum angular acceleration achievable by the spacecraft in deg/sec b) What closest approach (in km) can be accomplished based on: i. [8 pts] The maximum slew rate achievable by the spacecraft? ii. [8 pts] The maximum angular acceleration achievable by the spacecraft? [Hint: differentiate the above expression for with respect to time] The following derived expression may prove useful for part b) ii: max- X (x+r). rx 33 - 16r2
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


