Question: Replace X by the estimated value. X=32 1. The demand manager of Maverick Jeans is responsible for ensuring sufficient warehouse space for the finished jeans

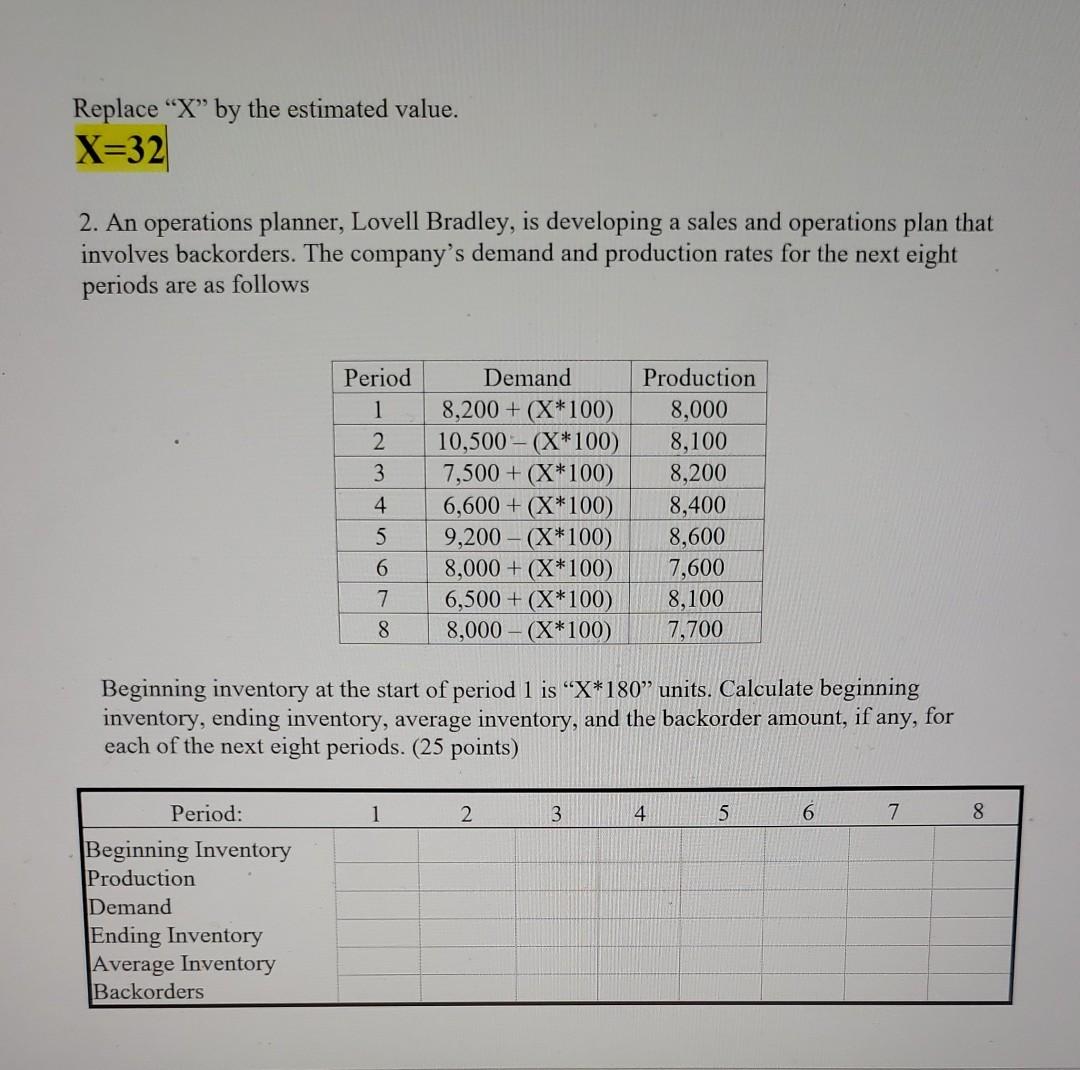
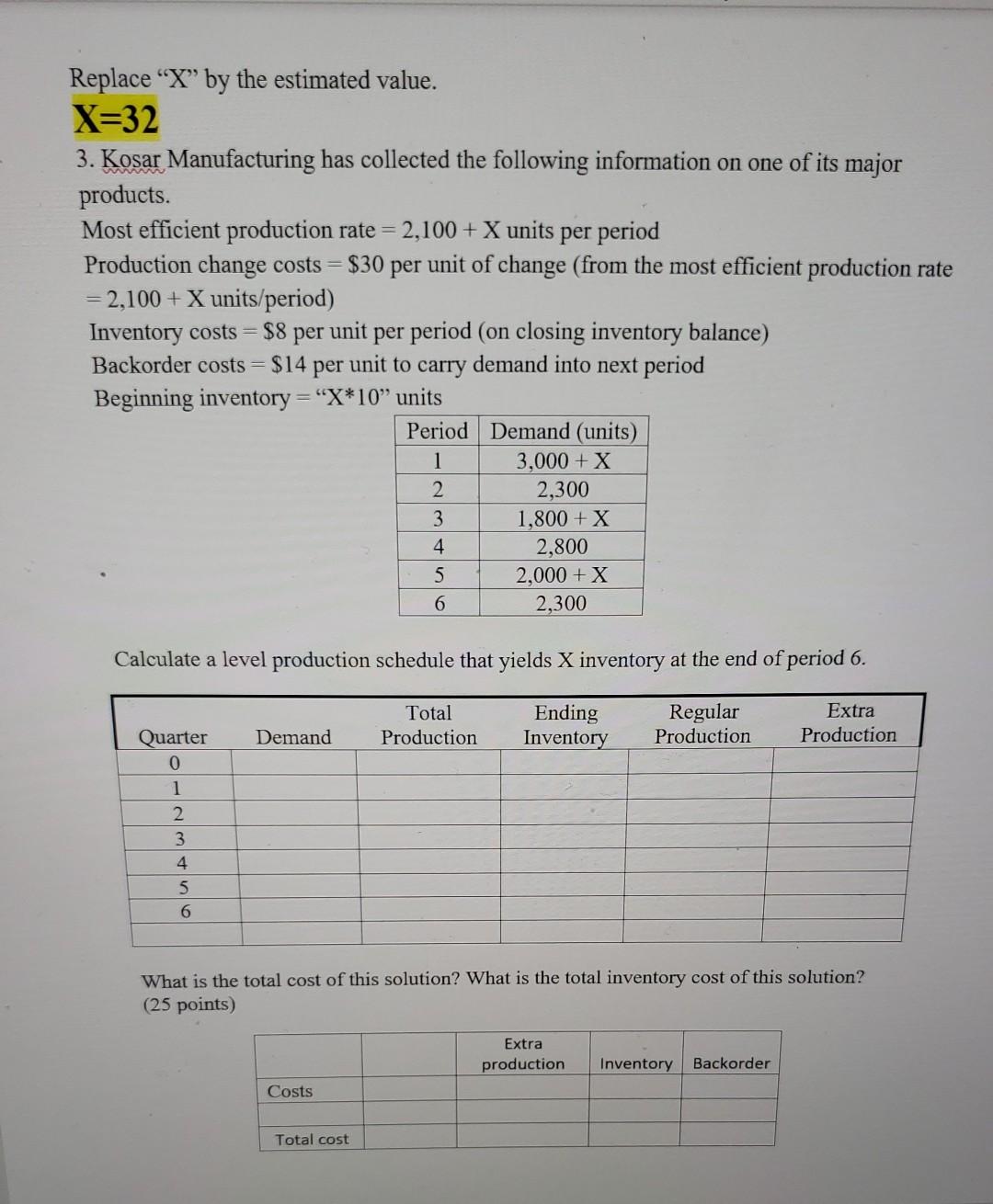
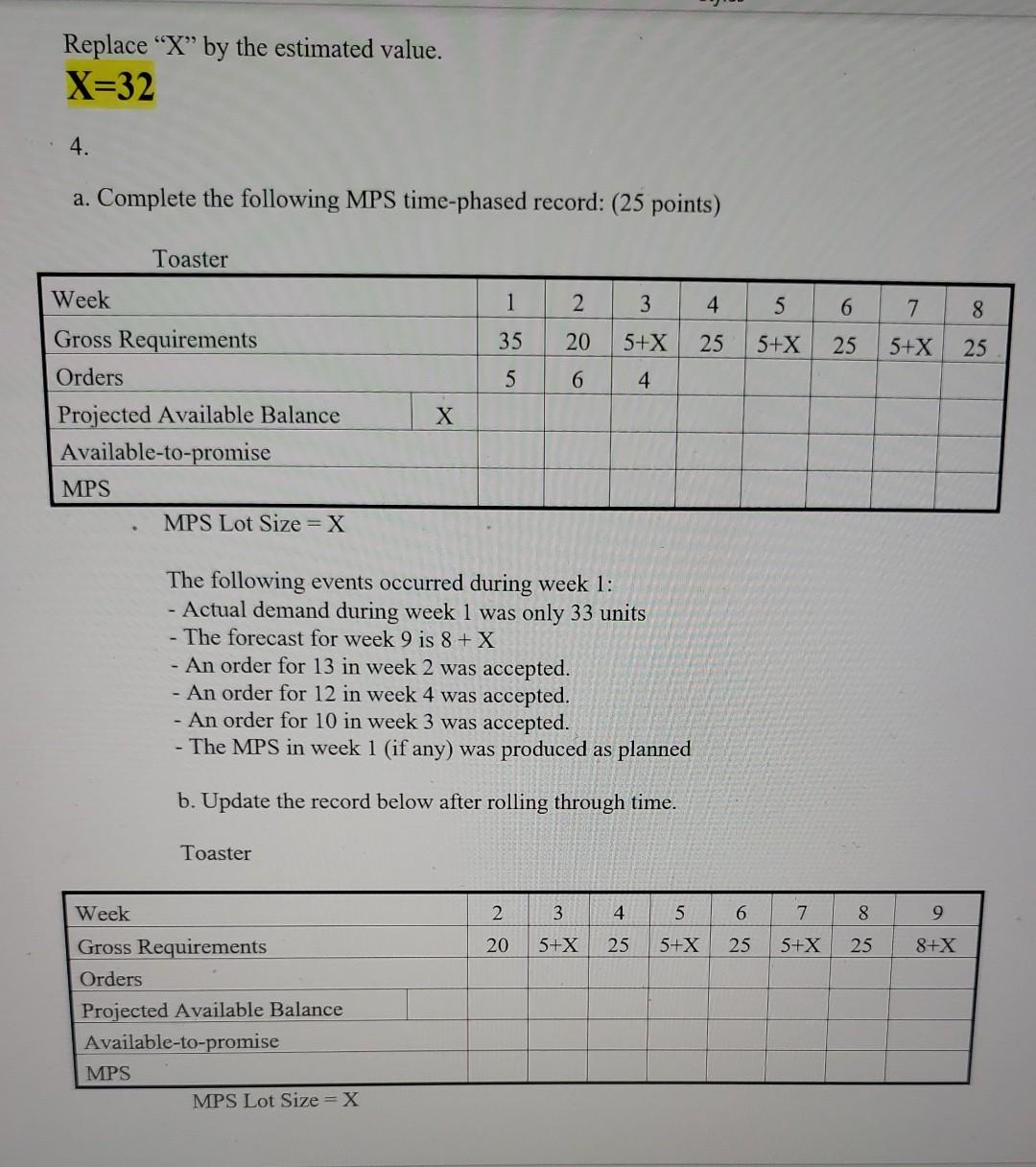
Replace X by the estimated value. X=32 1. The demand manager of Maverick Jeans is responsible for ensuring sufficient warehouse space for the finished jeans that come from the production plants. It has occasionally been necessary to rent pubic warehouse space, something that Maverick would like to avoid. In order to determine the space requirements, the demand manager is evaluating a few forecasts. The demand (in 1,000 case units) for the last fiscal year is shown below. Month 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 Demand X X-1 X+2 X+3 X+4 X+5 X+5 X+9 X+12 X+10 X+14 X+16 X+15 X+18 a. Use a 4-month moving average to estimate the month-in-advance forecast of demand for months 5-14 and generate a forecast for the fifteenth month. b. Repeat part a, use a 4-month weighted moving average with the following weights First weight (most recent month): X/110 Second weight: [1-X/110]*0.4 Third weight: [1-X/110]*0.35 Fourth weight (least recent month): [1-X/110]*0.25 Use all decimal places for the weights. c. Use X as the forecast for month 1. Use a smoothing model with a=X/110 to estimate the month-in-advance forecast of demand for months 2-14 and generate a forecast for the fifteenth month. d. Use X as the forecast for month 1. Use a smoothing model with a = [1-X/110] to estimate the month-in-advance forecast of demand for months 2-14 and generate a forecast for the fifteenth month. e. Compare the average forecast error and MAD for the forecasting methods in parts a., b., c., and d. Based on these error calculations, which of the four forecast methods would you recommend? Why? (25 points) Replace X by the estimated value. X=32 2. An operations planner, Lovell Bradley, is developing a sales and operations plan that involves backorders. The company's demand and production rates for the next eight periods are as follows Period 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Demand 8,200 + (X*100) 10,500 - (X*100) 7,500 + (X*100) 6,600 + (X*100) 9,200 - (X*100) 8,000 + (X*100) 6,500+ (X*100) 8,000 (X*100) Production 8,000 8,100 8,200 8,400 8,600 7,600 8,100 7,700 Beginning inventory at the start of period 1 is X*180 units. Calculate beginning inventory, ending inventory, average inventory, and the backorder amount, if any, for each of the next eight periods. (25 points) 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Period: Beginning Inventory Production Demand Ending Inventory Average Inventory Backorders Replace X by the estimated value. X=32 3. Kosar Manufacturing has collected the following information on one of its major products. Most efficient production rate = 2,100 +X units per period Production change costs = $30 per unit of change (from the most efficient production rate = 2,100 + X units/period) Inventory costs = $8 per unit per period (on closing inventory balance) Backorder costs = $14 per unit to carry demand into next period Beginning inventory = "X*10 units Period Demand (units) 1 3,000 + X 2 2,300 1,800 + X 2,800 2,000 + X 2,300 3 4 5 6 Calculate a level production schedule that yields X inventory at the end of period 6. Total Production Ending Inventory Regular Production Extra Production Demand Quarter 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 What is the total cost of this solution? What is the total inventory cost of this solution? (25 points) Extra production Inventory Backorder Costs Total cost Replace "X" by the estimated value. X=32 4. a. Complete the following MPS time-phased record: (25 points) Toaster 1 2 4 5 6 8 7 5+X 35 20 5+X 25 5+X 25 25 5 6 4 Week Gross Requirements Orders Projected Available Balance Available-to-promise MPS MPS Lot Size = X X The following events occurred during week 1: - Actual demand during week 1 was only 33 units - The forecast for week 9 is 8 + X - An order for 13 in week 2 was accepted. - An order for 12 in week 4 was accepted. - An order for 10 in week 3 was accepted. - The MPS in week 1 (if any) was produced as planned b. Update the record below after rolling through time. Toaster 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 20 5+X 25 5+X 25 5+X 25 8+X Week Gross Requirements Orders Projected Available Balance Available-to-promise MPS MPS Lot Size = X
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


