Question: Required information Exercise 7-21B Complete the accounting cycle using long-term asset transactions (L07-4, 7-7) [The following information applies to the questions displayed below.) On January
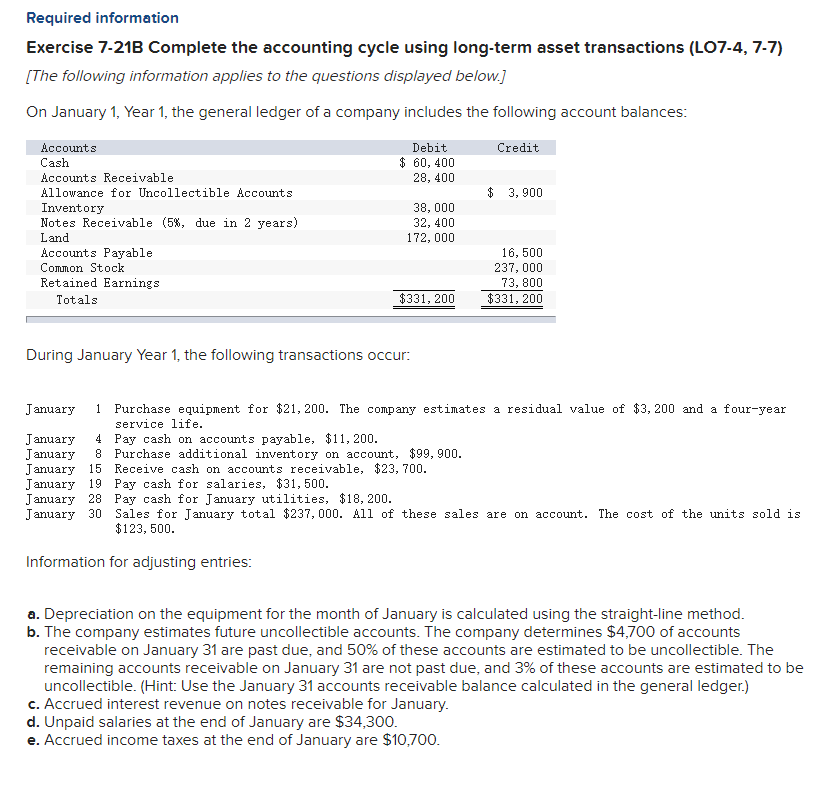
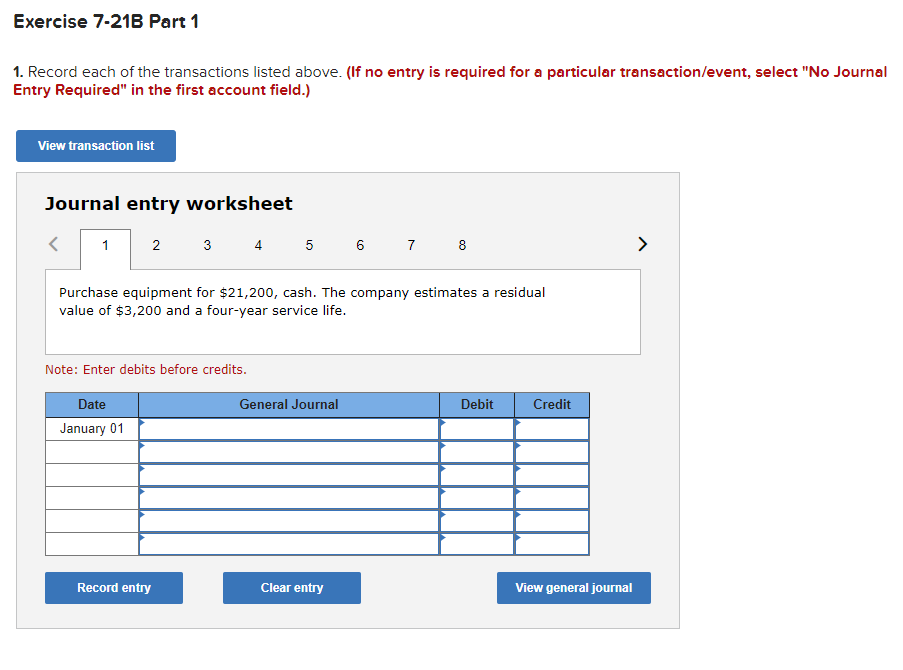
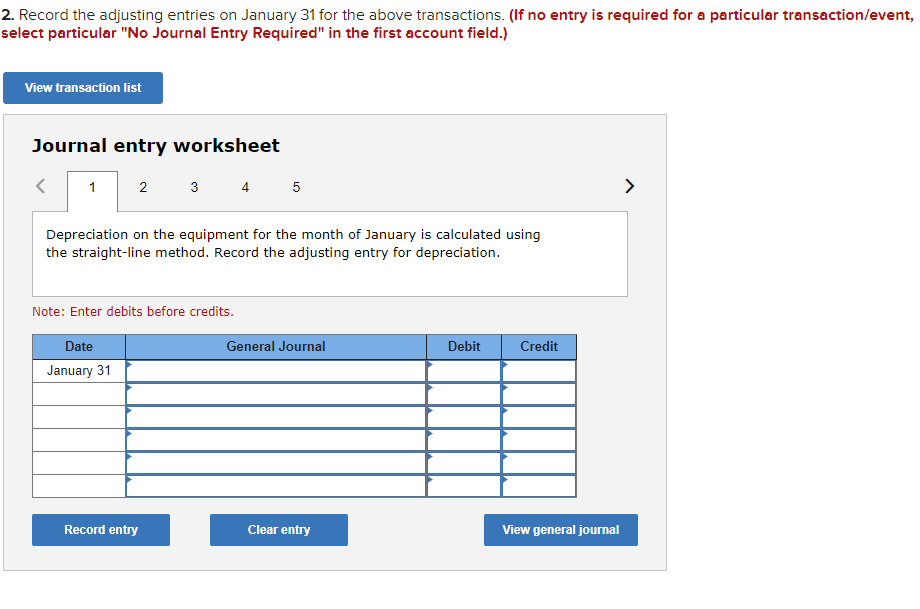
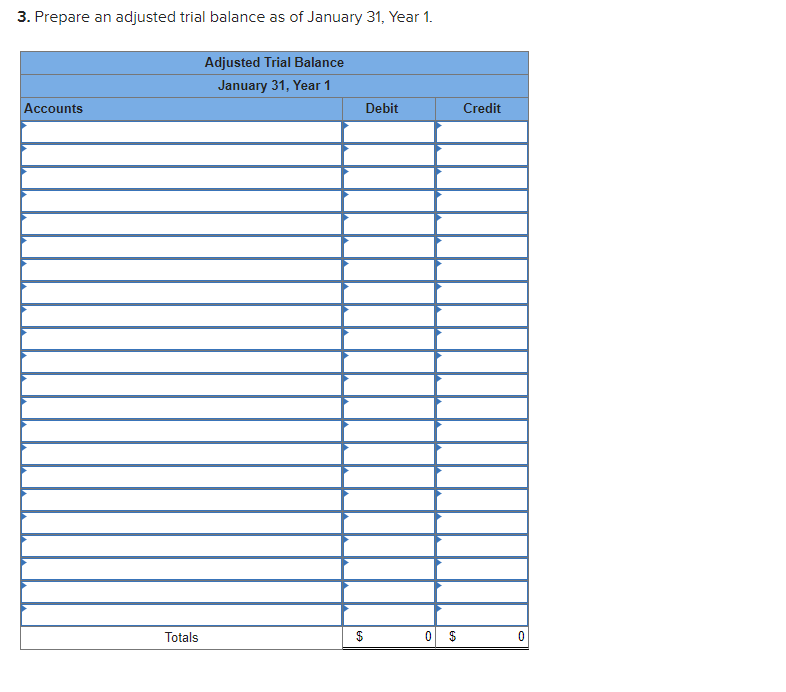
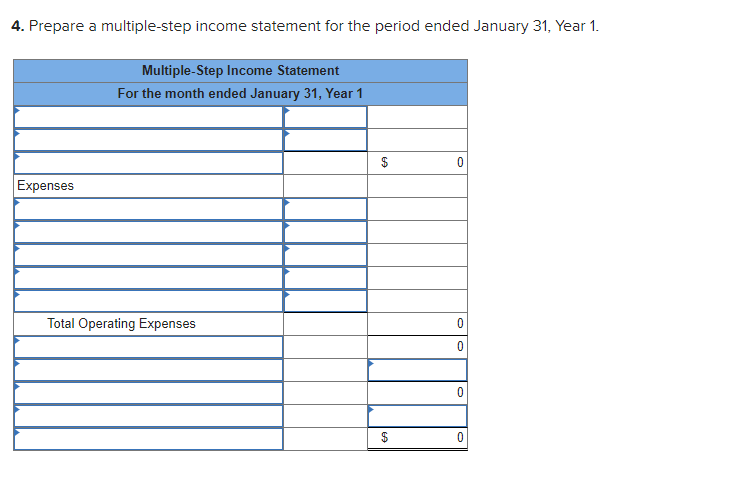
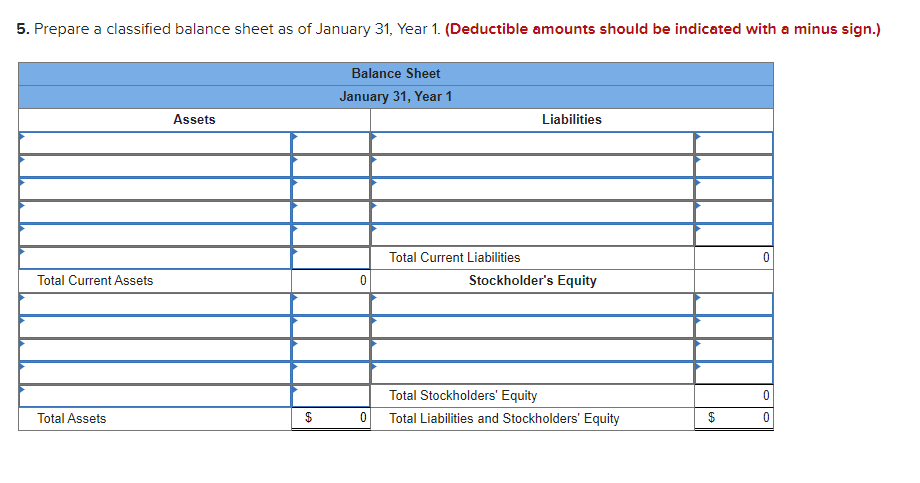
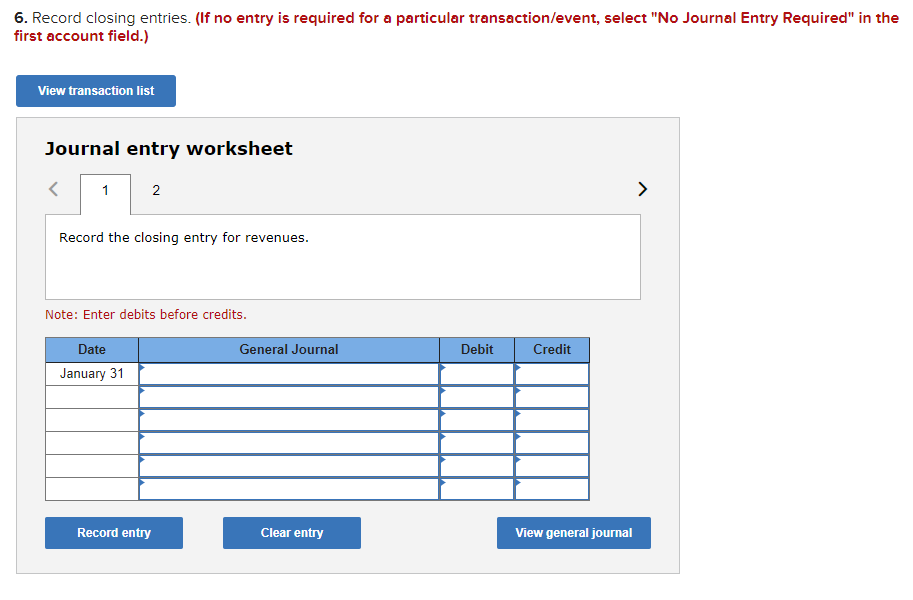
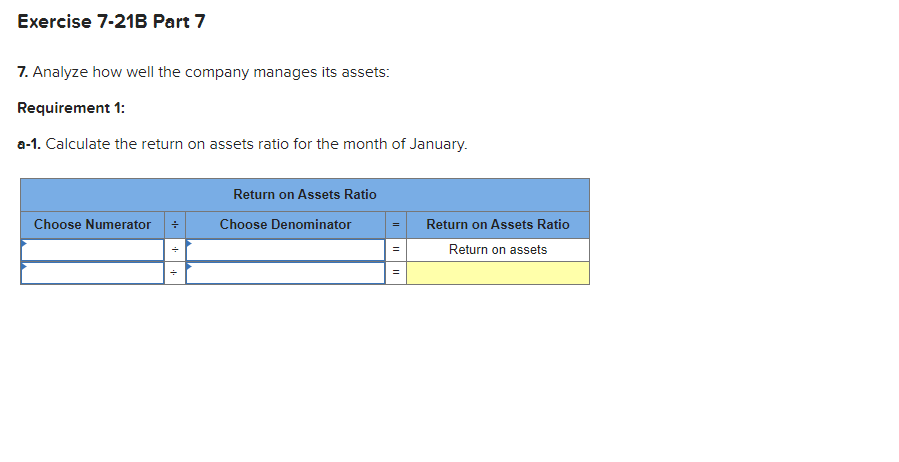
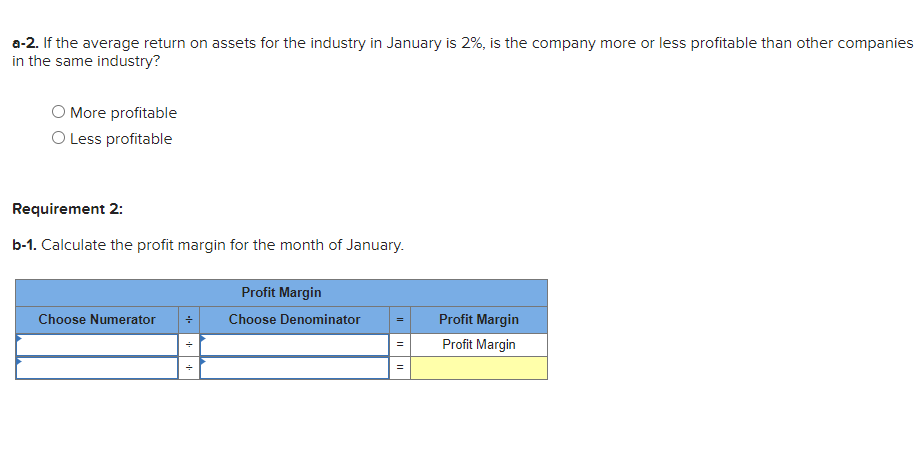
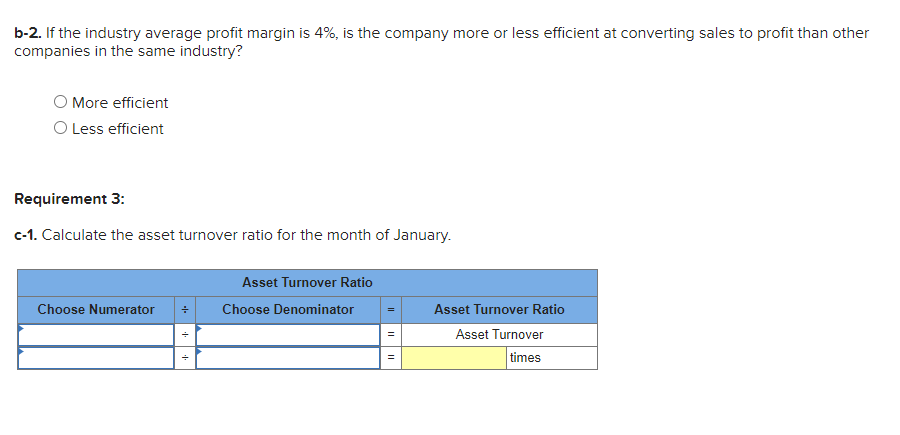
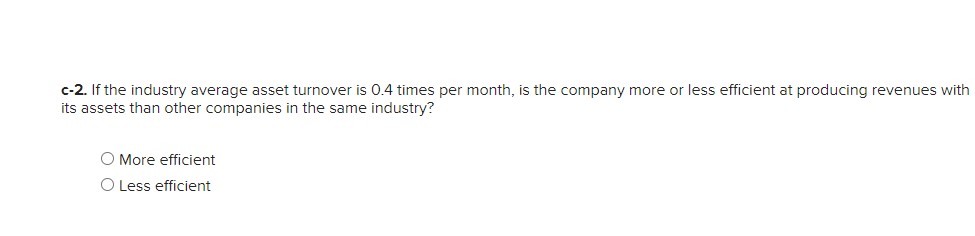
Required information Exercise 7-21B Complete the accounting cycle using long-term asset transactions (L07-4, 7-7) [The following information applies to the questions displayed below.) On January 1, Year 1, the general ledger of a company includes the following account balances: Credit Debit $ 60,400 28, 400 $ 3,900 Accounts Cash Accounts Receivable Allowance for Uncollectible Accounts Inventory Notes Receivable (5%, due in 2 years) Land Accounts Payable Common Stock Retained Earnings Totals 38,000 32, 400 172,000 16,500 237,000 73, 800 $331, 200 $331, 200 During January Year 1, the following transactions occur: January 1 Purchase equipment for $21,200. The company estimates a residual value of $3,200 and a four-year service life. January 4 Pay cash on accounts payable, $11,200. January 8 Purchase additional inventory on account, $99, 900. January 15 Receive cash on accounts receivable, $23, 700. January 19 Pay cash for salaries, $31,500. January 28 Pay cash for January utilities, $18, 200. January 30 Sales for January total $237, 000. All of these sales are on account. The cost of the units sold is $123,500. Information for adjusting entries: a. Depreciation on the equipment for the month of January is calculated using the straight-line method. b. The company estimates future uncollectible accounts. The company determines $4,700 of accounts receivable on January 31 are past due, and 50% of these accounts are estimated to be uncollectible. The remaining accounts receivable on January 31 are not past due, and 3% of these accounts are estimated to be uncollectible. (Hint: Use the January 31 accounts receivable balance calculated in the general ledger.) c. Accrued interest revenue on notes receivable for January. d. Unpaid salaries at the end of January are $34,300. e. Accrued income taxes at the end of January are $10,700. Exercise 7-21B Part 1 1. Record each of the transactions listed above. (If no entry is required for a particular transaction/event, select "No Journal Entry Required" in the first account field.) View transaction list Journal entry worksheet 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Purchase equipment for $21,200, cash. The company estimates a residual value of $3,200 and a four-year service life. Note: Enter debits before credits. General Journal Debit Credit Date January 01 Record entry Clear entry View general journal 2. Record the adjusting entries on January 31 for the above transactions. (If no entry is required for a particular transaction/event, select particular "No Journal Entry Required" in the first account field.) View transaction list Journal entry worksheet Depreciation on the equipment for the month of January is calculated using the straight-line method. Record the adjusting entry for depreciation. Note: Enter debits before credits. General Journal Debit Credit Date January 31 Record entry Clear entry View general journal 2. Record the adjusting entries on January 31 for the above transactions. (If no entry is required for a particular transaction/event, select particular "No Journal Entry Required" in the first account field.) View transaction list Journal entry worksheet Depreciation on the equipment for the month of January is calculated using the straight-line method. Record the adjusting entry for depreciation. Note: Enter debits before credits. General Journal Debit Credit Date January 31 Record entry Clear entry View general journal 3. Prepare an adjusted trial balance as of January 31, Year 1. Adjusted Trial Balance January 31, Year 1 Accounts Debit Credit Totals $ 0 $ 0 4. Prepare a multiple-step income statement for the period ended January 31, Year 1. Multiple-Step Income Statement For the month ended January 31, Year 1 $ 0 Expenses Total Operating Expenses 0 0 $ 0 5. Prepare a classified balance sheet as of January 31, Year 1. (Deductible amounts should be indicated with a minus sign.) Balance Sheet January 31, Year 1 Assets Liabilities 0 Total Current Liabilities Stockholder's Equity Total Current Assets 0 0 Total Stockholders' Equity Total Liabilities and Stockholders' Equity Total Assets $ 0 $ 0 6. Record closing entries. (If no entry is required for a particular transaction/event, select "No Journal Entry Required" in the first account field.) View transaction list Journal entry worksheet Record the closing entry for revenues. Note: Enter debits before credits. General Journal Debit Credit Date January 31 Record entry Clear entry View general journal Exercise 7-21B Part 7 7. Analyze how well the company manages its assets: Requirement 1: a-1. Calculate the return on assets ratio for the month of January. Return on Assets Ratio Choose Denominator Choose Numerator : Return on Assets Ratio Return on assets a-2. If the average return on assets for the industry in January is 2%, is the company more or less profitable than other companies in the same industry? More profitable O Less profitable Requirement 2: b-1. Calculate the profit margin for the month of January. Profit Margin Choose Denominator Choose Numerator Profit Margin Profit Margin b-2. If the industry average profit margin is 4%, is the company more or less efficient at converting sales to profit than other companies in the same industry? O More efficient O Less efficient Requirement 3: C-1. Calculate the asset turnover ratio for the month of January Asset Turnover Ratio Choose Denominator Choose Numerator : 11 Asset Turnover Ratio Asset Turnover times . c-2. If the industry average asset turnover is 0.4 times per month, is the company more or less efficient at producing revenues with its assets than other companies in the same industry? O More efficient O Less efficient If you are interested in get paid for answer some Financial accounting question, please contact this email: zj8308543@gmail.com
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


