Question: Required information Problem 5-1A Perpetual: Alternative cost flows LO P1 The following information applies to the questions displayed below. Warnerwoods Company uses a perpetual inventory
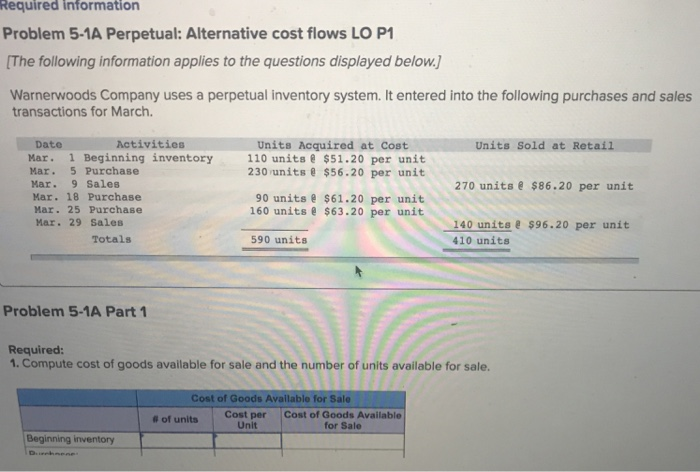
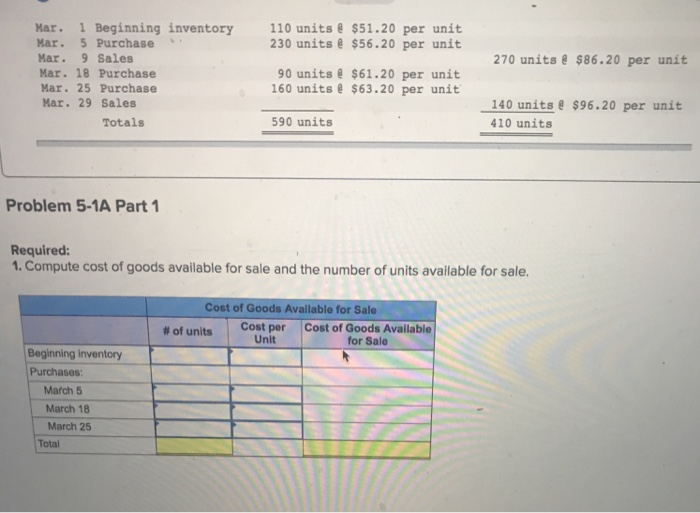
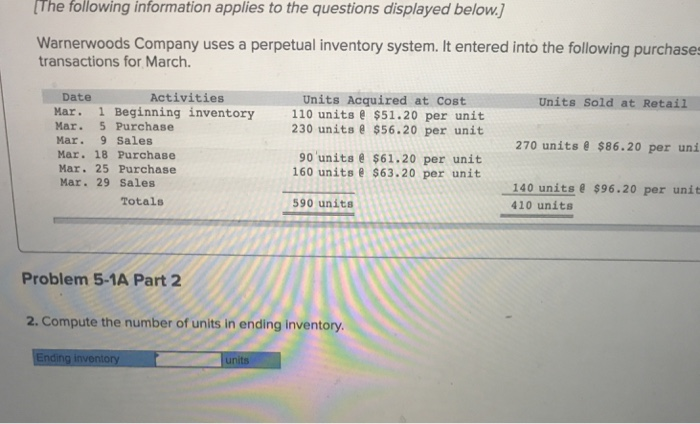
Required information Problem 5-1A Perpetual: Alternative cost flows LO P1 The following information applies to the questions displayed below. Warnerwoods Company uses a perpetual inventory system. It entered into the following purchases and sales transactions for March. Activities Units Sold at Retail 270 units $86.20 per unit 140 units e $96.20 per unit Date Units Acquired at Cost Mar. 1 Beginning inventory 110 units $51.20 per unit 230 units $56.20 per unit Mar. 5 Purchase Mar. 9 Sales Mar. 18 Purchase Mar. 25 Purchase Mar. 29 Sales 90 units $61.20 per unit 160 units $63.20 per unit Totals 590 units 410 units Problem 5-1A Part 1 Required 1. Compute cost of goods available for sale and the number of units available for sale. Cost of Goods Available for Sale #Of units Cost per Unit Cost of Goods Available for Sale Beginning inventory Mar. 1 Beginning inventory110 units $51.20 per unit Mar. 5 Purchase Mar. 9 Sales Mar. 18 Purchase Mar. 25 Purchase Mar. 29 Sales 230 units $56.20 per unit 270 units $86.20 per unit 90 units $61.20 per unit 160 units $63.20 per unit 140 units&$96.20 per unit 410 units Totals 590 units Problem 5-1A Part 1 Required: 1. Compute cost of goods available for sale and the number of units available for sale. Cost of Goods Available for Sale | Cost per Unit Cost of Goods Available for Sale # of units Purchases March 5 March 18 March 25 Total The following information applies to the questions displayed below. Warnerwoods Company uses a perpetual inventory system. It entered into the following purchases transactions for March. DateActivities Mar. 1 Beginning inventory Mar. 5 Purchase Mar. 9 Sales Mar. 18 Purchase Mar. 25 Purchase Mar. 29 Sales Units Acquired at Cost Units Sold at Retail 110 unitse $51.20 per unit 230 units $56.20 per unit 90 unitse $61.20 per unit 160 units $63.20 per unit 270 units $86.20 per uni 140 unitse $96.20 per unit 410 units Totals 590 units Problem 5-1A Part 2 2. Compute the number of units in ending inventory nding inventory
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


