Question: Requirement 1. Compute the overhead variances for the year variable overhead cost variance, variable overhead efficiency variance, fixed overhead cost variance, and fixed overhead volume
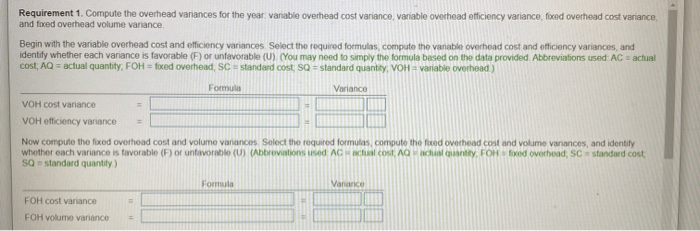
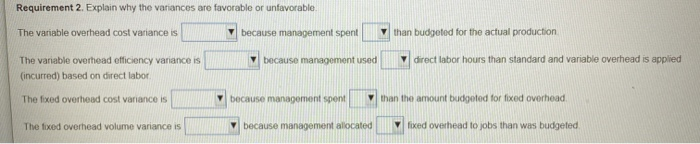
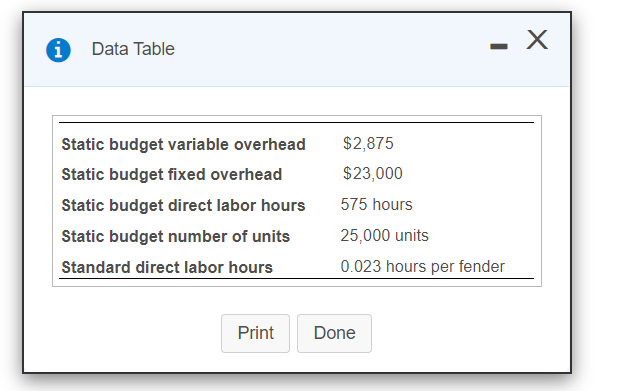
Requirement 1. Compute the overhead variances for the year variable overhead cost variance, variable overhead efficiency variance, fixed overhead cost variance, and fixed overhead volume variance Begin with the variable overhead cost and efficiency variances Select the required formulas, compute the variable overhead cost and officiency variances, and identify whether each variance is favorable (F) or unfavorable (U). (You may need to simply the formula based on the data provided Abbreviations used AC = actual cost; AQ = actual quantity, FOH = foxed overhead, SC standard cost SQ = standard quantity, VOH : variable overhead) Formula Variance VOH cost variance VOH efficiency variance Now compute the fixed overhead cost and volume vanances Select the required formulas, compute the food overhead cost and volume variances, and identify whother each variance is favorable (F) or unfavorable (U) (Abbreviations used AC actual cosachant quantity, FOH food overhead, SC standard cost SO standard quantity) Formula Vanance FOH cost variance FOH volume variance Requirement 2. Explain why the variances are favorable or unfavorable. The variable overhead cost variance is because management spent than budgeted for the actual production w because management used direct labor hours than standard and variable overhead is applied The variable overhead efficiency variance is (incurred) based on direct labor The fixed overhead cost variance is because management spent than the amount budgeted for fixed overhead The fixed overhead volume variance is because management allocated fixed overhead to jobs than was budgeted i x Data Table Static budget variable overhead Static budget fixed overhead Static budget direct labor hours Static budget number of units Standard direct labor hours $2,875 $23,000 575 hours 25,000 units 0.023 hours per fender Print Done Requirement 1. Compute the overhead variances for the year variable overhead cost variance, variable overhead efficiency variance, fixed overhead cost variance, and fixed overhead volume variance Begin with the variable overhead cost and efficiency variances Select the required formulas, compute the variable overhead cost and officiency variances, and identify whether each variance is favorable (F) or unfavorable (U). (You may need to simply the formula based on the data provided Abbreviations used AC = actual cost; AQ = actual quantity, FOH = foxed overhead, SC standard cost SQ = standard quantity, VOH : variable overhead) Formula Variance VOH cost variance VOH efficiency variance Now compute the fixed overhead cost and volume vanances Select the required formulas, compute the food overhead cost and volume variances, and identify whother each variance is favorable (F) or unfavorable (U) (Abbreviations used AC actual cosachant quantity, FOH food overhead, SC standard cost SO standard quantity) Formula Vanance FOH cost variance FOH volume variance Requirement 2. Explain why the variances are favorable or unfavorable. The variable overhead cost variance is because management spent than budgeted for the actual production w because management used direct labor hours than standard and variable overhead is applied The variable overhead efficiency variance is (incurred) based on direct labor The fixed overhead cost variance is because management spent than the amount budgeted for fixed overhead The fixed overhead volume variance is because management allocated fixed overhead to jobs than was budgeted i x Data Table Static budget variable overhead Static budget fixed overhead Static budget direct labor hours Static budget number of units Standard direct labor hours $2,875 $23,000 575 hours 25,000 units 0.023 hours per fender Print Done
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


