Question: Query 1. Modify data. Replace the text. Your First Name, Your Last Name with your first name and your last name in the DML


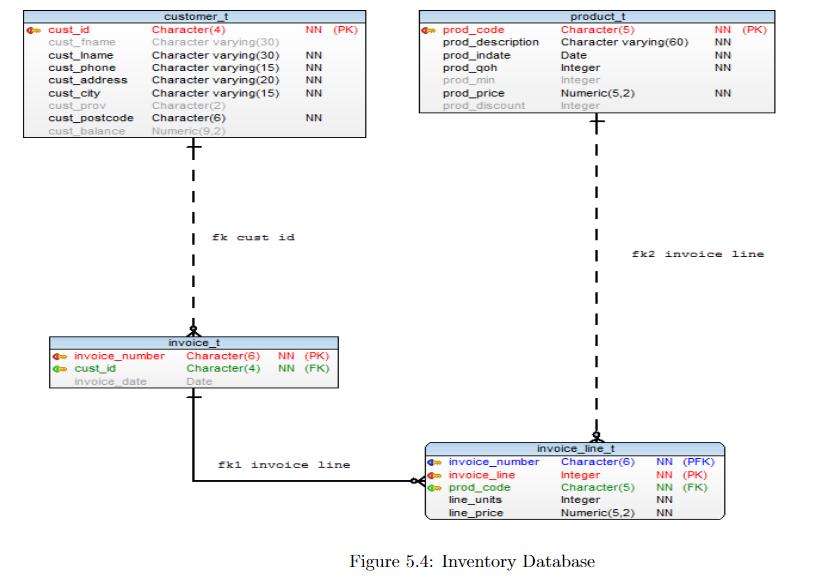

Query 1. Modify data. Replace the text. Your First Name, Your Last Name with your first name and your last name in the DML file. Aside: Last Name is the Family Name or Surname. Replace 0 in Balance field with another number. Replace the other five entries in the Customer_T table with your own data. Write the names of your colleagues sitting besides you in the lab. Do not skip this step. After modifying the script run it. Type and run each of the statements to verify that the tables are created successfully. SELECT FROM Customer_T; SELECT FROM Invoice_T; SELECT FROM Product_T; SELECT * FROM Invoice_Line_T; Query 2. List data in sorted order. List all customers (last name and then first name), sorted by last name. Hint: Use the clause ORDER BY. Query 3. List year of invoice number. List only invoice numbers and invoice dates (4-digit year) from the Invoice T table. Tip: Use the EXTRACT function. Query 4. List Data, identify correct table. List Invoice Number, Product. Code, and Line Price. Identify the table that has these columns? Query 5. List Data. Associate common terms with database field ames. List all product code and product description. Choose the appropriate table to complete the query. Query 6. Filter rows. List customer names (last and first name) and city for those customers who do not live in Ottawa. Hint: Use WHERE clause. Query 7. Use String functions. The city name is stored as Ottawa. Modify the query to list the same number of rows when the condition is written as OTTAWA. Tip: Use the appropriate string function shown in figure 2.2 on page 23, Query 8. Reverse Engineer the database. Reverse Engineer the Inventory database using a data modeling tool. Rearrange the entities and relationships. Insert a text box with your name, section number, student number, course code, and course name. Query 8. Reverse Engineer the database. Reverse Engineer the Inventory database using a data modeling tool. Rearrange the entities and relationships. Insert a text box with your name, section number, student number, course code, and course name. Query 9. Determine identifying and non-identifying entities. Determine the identifying and non-identifying relationships. Note your answers, you will need them for the quiz. Refer to the documentation on identifying and non-identifying relationships. Query 10. Determine the associative entity. Which one of the four entities is an associative entity? Give a reason. 5. SQL CONSTRAINTS Notes on Relationships An identifying relationship is represented by a solid line; a row in a child table can be uniquely identified only if an entry exists in the parent table. For example, in table Invoice_Line_T an entry can be identified only if an Invoice_Number exists in the Invoice_T table. Aside: The prime key Invoice_Number in the Invoice T Table is part of the prime key in the Invoice_Line_T table. A non-identifying relationship is represented by a broken (dashed) line. In a non-identifying relationship, an entry in a child table can be uniquely identified without a corresponding entry in the parent table. For example, an entry in the Invoice T table can be uniquely identified by Invoice_Number alone, it does not need an entry from the customer table. Similarly an entry in the Invoice_Line_T table can be uniquely identified by a combination of Invoice_Number and Invoice_Line it does not depend on an entry in the Product T table. 66 4 cust_id cust_fname cust_Iname cust_phone cust_address cust_city cust prov cust_postcode customer t Character(4) Character varying(30) Character varying (30) Character varying (15) Character varying (20) Character varying(15) Character(2) Character(6) cust_balance Numeric(9,2) + invoice_number cust_id invoice date I I I fk cust id invoice_t NN (PK) NN NN Date NN NN NN Character(6) NN (PK) Character(4) NN (FK) fkl invoice line prod_code prod_description prod_indate prod_qoh prod_min prod_price prod discount product_t Character(5) Character varying(60) Date Integer Integer Numeric(5,2) Integer invoice_line_t 4 invoice_number Character(6) invoice_line prod_code line_units line_price NN (PK) NN Figure 5.4: Inventory Database NN NN NN fk2 invoice line NN (PFK) Integer NN (PK) Character(5) NN (FK) Integer NN Numeric(5,2) NN Requirements Create a database called Inventory in postgres. First load and run Inventory-DDL, the DDL script will create tables. Load the Inventory-DML script. Locate the following line, INSERT INTO Customer_T VALUES ( C002 , Your First Name , Your Last Name , 613-727-4723 , 1385 Woodroffe Ave , Ottawa , ON , K2G1V8,0); A note on CONSTRAINTS. You can run the DML.sql file only once, the constraints will prevent you from running it again. If you need to run the DML the second time, first run the DDL. This will drop all existing tables and recreate them. Now you will be able to run your modified DML.sql.
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Answer Query1 UPDATE custmert SET custfnameJohn custlnameSmith custphone9856321548 custaddressKottar... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


