Question: REVISE STUDENT ASSIGNMENT FOR ERRORS OR INSUFFICIENT EXPLANATIONS, ANSWER QUESTIONS 1-4 (NUMBER THE ANSWERS) ASSIGNMENT: STUDENT WORK: One way consumers can evaluate alternatives is to
REVISE STUDENT ASSIGNMENT FOR ERRORS OR INSUFFICIENT EXPLANATIONS, ANSWER QUESTIONS 1-4 (NUMBER THE ANSWERS)
ASSIGNMENT:

STUDENT WORK:


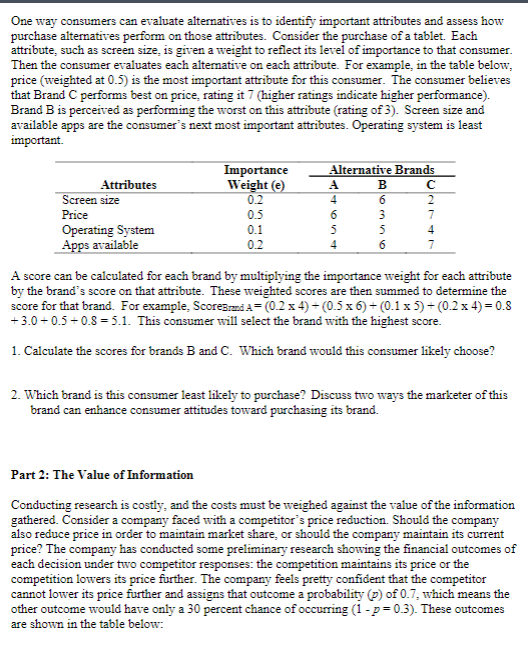
One way consumers can evaluate alternatives is to identify important attributes and assess how purchase alternatives perform on those attributes. Consider the purchase of a tablet. Each attribute, such as screen size, is given a weight to reflect its level of importance to that consumer. Then the consumer evaluates each alternative on each attribute. For example, in the table below, price (weighted at 0.5 ) is the most important attribute for this consumer. The consumer believes that Brand C performs best on price, rating it 7 (higher ratings indicate higher performance). Brand B is perceived as performing the worst on this attribute (rating of 3). Screen size and available apps are the consumer's next most important attributes. Operating system is least important. A score can be calculated for each brand by multiplying the importance weight for each attribute by the brand's score on that attribute. These weighted scores are then summed to determine the score for that brand. For example, ScoreBrnd A =(0.24)+(0.56)+(0.15)+(0.24)=0.8 +3.0+0.5+0.8=5.1. This consumer will select the brand with the highest score. 1. Calculate the scores for brands B and C. Which brand would this consumer likely choose? 2. Which brand is this consumer least likely to purchase? Discuss two ways the marketer of this brand can enhance consumer attitudes toward purchasing its brand. Part 2: The Value of Information Conducting research is costly, and the costs must be weighed against the value of the information gathered. Consider a company faced with a competitor's price reduction. Should the company also reduce price in order to maintain market share, or should the company maintain its current price? The company has conducted some preliminary research showing the financial outcomes of each decision under two competitor responses: the competition maintains its price or the competition lowers its price further. The company feels pretty confident that the competitor cannot lower its price further and assigns that outcome a probability (p) of 0.7 , which means the other outcome would have only a 30 percent chance of occurring (1p=0.3). These outcomes are shown in the table below: For example, if the company reduces its price and the competitor maintains its price, the company would realize $160,000, and so on. From this information, the expected monetary value (EMV) of each company action (reduce price or maintain price) can be determined using the following equation: EMV(p)(financialoutcomep)+(1p)(financialoutcome(1p)) The company would select the action expected to deliver the greatest EMV. More information might be desirable, but is it worth the cost of acquiring it? One way to assess the value of additional information is to determine the expected value of perfect information (EMV PLP ), calculated using the following equation: EMVpt=EMVcertaintyEMVbetthemaive If the value of perfect information is more than the cost of conducting the research, then the research should be undertaken (that is, EMVP!7 cost of research). However, if the value of the additional information is less than the cost of obtaining more information, the research should not be conducted. Please answer and show your work 3. Calculate the expected monetary value (EMV) of both company actions. Which action should the company take? 4. What is the expected value of perfect information (EMVPI) ? Should the research be conducted? Whether or not the company should conduct market research to obtain perfect information depends on the cost of the research. If the cost of the research is less than $32,000, then the company should conduct the research, as it would be expected to generate a positive return on investment. However, if the cost of the research is greater than $32,000, then the company should not conduct the research, as it would be expected to generate a negative return on investment. In this analysis, the company calculated the expected monetary value (EV) of two potential actions: reducing the price and maintaining the price of their product. Reducing the price was found to have a higher expected monetary value ($148,000) compared to maintaining the price ($138,000), suggesting that the company should opt to lower its price. The expected value of perfect information (EVPI) was then determined to be $32,000, representing the maximum amount the company would be willing to invest in obtaining perfect information about the competitor's pricing strategy. The decision to conduct market research to acquire this perfect information should depend on whether the cost of the research is less than the EVPI, ensuring a positive return on investment, or greater than the EVPI, which would imply a negative return on investment. 1. Brand A: Score =4.(0.54)+(0.256)+(0.253)=4 Brand C: Score =7.(0.54)+(0.256)+(0.253)=4 Since both brands A and C have the same score, it is difficult to say for certain which brand the customer would choose. However, the customer may choose brand A because it has a higher score on the most important attribute (price). 2. The customer is least likely to purchase brand B, as it has the lowest score on the most important attribute (price). In this analysis, we calculated the scores for brands A, B, and C based on various attributes and their respective weights. Both Brand A and Brand C received the same score, indicating an equal overall appeal to the customer. However, given that price is the most crucial attribute, the customer is likely to choose Brand A, as it outperforms Brand C in this key category. On the other hand, Brand B is the least likely choice for the customer, as it received the lowest score in the most important attribute, price. Therefore, the customer's decision hinges on price considerations, making Brand A the preferred option and Brand B the least likely selection. Part 2: 1. Calculate the expected monetary value (EV) of both company actions (reduce price or maintain price). Reduce price: EV=(0.7$160,000)+(0.3$120,000)=$148,000 Maintain price: EV=(0.7$120,000)+(0.3$180,000)=$138,000 2. Which action should the company take? The company should reduce its price, as this has the higher expected monetary value. 3. What is the expected value of perfect information (EVPI)? The EVPI is the amount of money the company would be willing to pay for perfect information about the competitor's pricing decision. This can be calculated as follows: EVPI =( EMV with perfect information ) - (EMV without perfect information) The EMV with perfect information is the maximum financial outcome that the company could achieve, which is $180,000 (if the company reduces its price and the competitor maintains its price). The EMV without perfect information is the EV of the action that the company would take without perfect information, which is $148,000 (reducing price). Therefore, the EVPI is: EVPI = $180,000$148,000=$32,000 4. Should the company conduct market research to obtain perfect information about the competitor's pricing decision
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


