Question: ri R$ 7:) Here, each V represents a change in voltage (in volts) at a battery, each R represents a resistance (in ohms) at a
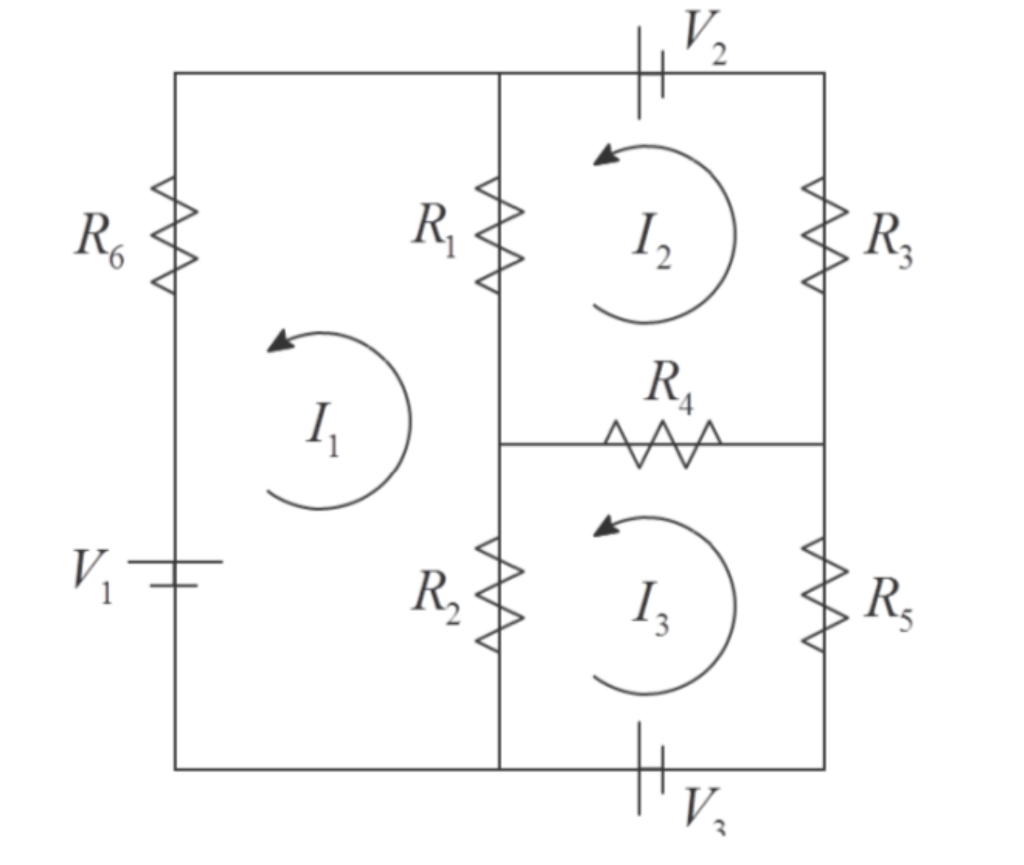

ri R$ 7:) Here, each V represents a change in voltage (in volts) at a battery, each R represents a resistance (in ohms) at a resistor and each I represents a current (in amps) through a wire. These quantities obey two simple laws: 1. Ohm's law: The voltage drop across a resistor is V = IR. 2. Kirchhoff's second law: The sum of all the voltage changes in a closed loop is zero. Using these two laws, we can construct the following system of equations: Roli +R 1-12) +R (1, -13) = R312 +R (12-13) +R (12-1) = R513 +R (13 - 12) + R2(13 - 11) = V, V2, V3. Suppose that the resistances are given by Ri = 15, R2 = 20, R3 = 6, R4 = 18, R5 = 25 and Ro = 30 (all in ohms) and that we are trying to calculate the currents 11, 12 and 13. 1. Write these equations in the matrix form Ax = b, where x is a 3x1 vector of unknown currents. You need to do this by hand, not in Matlab. (Note that the equations above are not fully simplified. You can use the pretest to make sure you simplified correctly.) Using the lu command in Matlab, find the matrices L, U and P such that LU = PA. Calculate the product UPL and save the resulting matrix in a variable named ans1. (There is no mathematical reason to calculate this matrix
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


