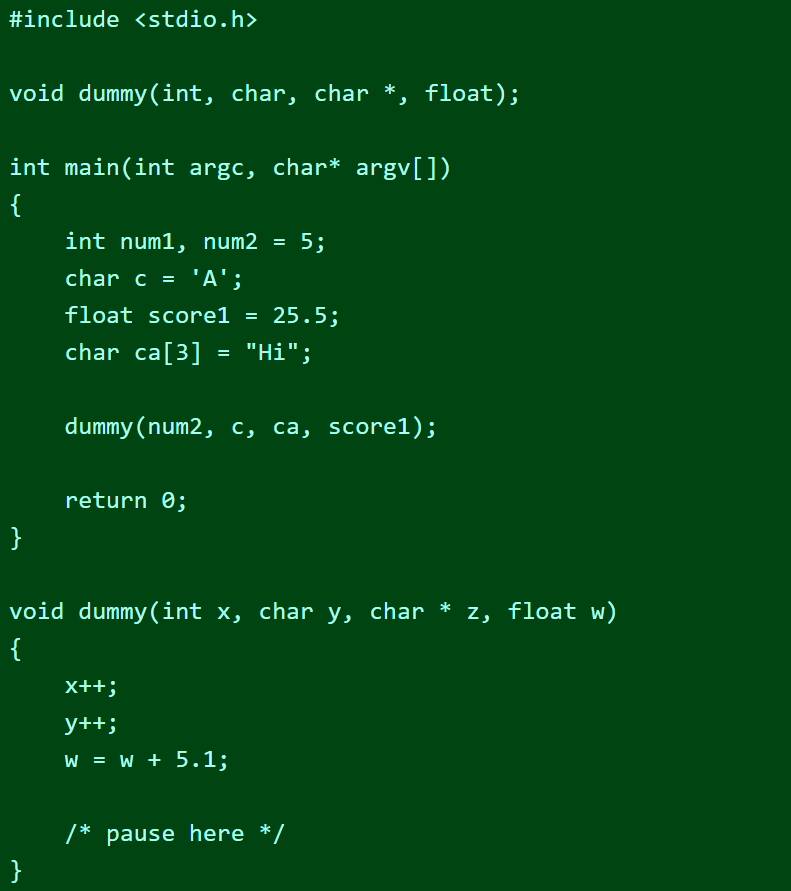
Question: Run the following C program and complete the table showing all the variables. You may add printf function calls to obtain the addresses and values
Run the following C program and complete the table showing all the variables. You may add printf function calls to obtain the addresses and values of all 13 variables. (Count the array ca as 3 variable/values and also include argc and argv in the table).
Note: When you compile this source code, the compiler will warn about some "unused" variables. For this part, you can disregard this warning message.
Tracing Table
In the file, you can see a template table whose columns represent Address, Name, Datatype, Scope, and Value.
| Address | Name | Datatype | Scope | Value |
| argc | ||||
| argv | ||||
| num1 | ||||
| num2 | ||||
| c | ||||
| score1 | ||||
| ca[0] | ||||
| ca[1] | ||||
| ca[2] | ||||
| x | ||||
| y | ||||
| z | ||||
| w |
By using this table, trace the code BUT you also need to investigate the code and show the actual values and addresses of the variables. Use printf function and insert function calls to the code so you can print actual values and addresses. Check how those variables are allocated on the actual memory. (You may also want to use the sizeof function to see the size of a variable type.)
-
Address
Address values are positive numbers. For this assignment, you must show addresses in hexadecimal (not like 60000. Check the specification of printf. There is a way to print it as an address which is in hexadecimal).
-
Name
It is already filled.
-
Datatype
Write the datatype of the variable.
-
Scope
Write the name of the function in which the variable exists.
-
Value
Check the actual value stored in the variable and fill in this column. So your table will never have "?".
You need to show all the values the variable got. For example, if the code had an integer variable named a and its value changes as follows, you would need to fill like "-10498, 0, 10" (note the first one is an uninitialized value).
-

If the datatype of a variable is a pointer, you must show the address value stored in it. For example, if its datatype is char*, you must show the address stored in the variable, not the characters stored at the address.
#include
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


