Question: Sample Input : c ( a ( null e ( null null ) ) d ( null null ) ) =================================================================================== /** A binary tree


Sample Input : c ( a ( null e ( null null ) ) d ( null null ) )
===================================================================================
/** A binary tree in which each node has two children. */ public class BinaryTree { private Node root;
/** Constructs an empty tree. */ public BinaryTree() { root = null; }
/** Constructs a tree with one node and no children. @param rootData the data for the root */ public BinaryTree(Comparable rootData) { root = new Node(); root.data = rootData; root.left = null; root.right = null; }
/** Constructs a binary tree. @param rootData the data for the root @param left the left subtree @param right the right subtree */ public BinaryTree(Comparable rootData, BinaryTree left, BinaryTree right) { root = new Node(); root.data = rootData; root.left = null; root.right = null; if (left != null) { root.left = left.root; } if (right != null){ root.right = right.root; } }
class Node { public Comparable data; public Node left; public Node right; }
/** Checks whether this tree is empty. @return true if this tree is empty */ public boolean isEmpty() { return root == null; }
/** Gets the data at the root of this tree. @return the root data */ public Comparable data() { return root.data; }
/** Gets the left subtree of this tree. @return the left child of the root */ public BinaryTree left() { BinaryTree result = new BinaryTree(); result.root = root.left; return result; }
/** Gets the right subtree of this tree. @return the right child of the root */ public BinaryTree right() { BinaryTree result = new BinaryTree(); result.root = root.right; return result; } }
============================================================================
import java.util.*;
public class PoD {
//=============================================================================
/** * Returns true if the binary tree is a binary search tree (BST) * * @param Tree BinaryTree of interest * @return boolean (true if BST) */
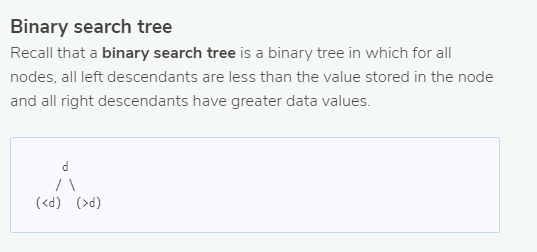
public static boolean isBST(BinaryTree tree) { /* Check if the binary tree is a BST: For all nodes, all left descendants are less than the value stored in the node and all right descendants have greater data values. d / \ (
boolean meetsCriteria; return meetsCriteria;
}
//=============================================================================
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
//int i = in.nextInt(); //int j = in.nextInt();
BinaryTree newTree = buildTree(in);
boolean isBinarySearchTree = isBST(newTree);
in.close();
if (isBinarySearchTree) { System.out.println("This is a binary search tree"); } else { System.out.println("NOT a binary search tree"); }
System.out.print("END OF OUTPUT"); }
/** * Reads in data to form a binary tree: * N ( L R ) * N = node data * L = Left binary tree data (possibly of same form) * R = Right binary tree data (possibly of same form) * expects all nodes until reaching null * * e.g. input: a ( b ( null null ) c ( null null ) ) * creates tree: * a * / \ * b c */
public static BinaryTree buildTree(Scanner in) { String data = in.next(); BinaryTree left = null; BinaryTree right = null;
if (data.equals("null")) { return null;}
if (!in.next().equals("(")) { System.out.println("BAD INPUT: (L"); }
left = buildTree(in); right = buildTree(in);
if (!in.next().equals(")")) { System.out.println("BAD INPUT: R)"); }
return new BinaryTree(data, left, right); } }
Binary search tree Recall that a binary search tree is a binary tree in which for all nodes, all left descendants are less than the value stored in the node and all right descendants have greater data values
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


