Question: Scientific solutions!!! Apple INC.: MANAGING A GLOBAL SUPPLY CHAIN. Case Study 1. Financial analysis. Conduct a thorough financial analysis. Objectives The objectives of the financial

Scientific solutions!!!
Apple INC.: MANAGING A GLOBAL SUPPLY CHAIN. Case Study
1. Financial analysis. Conduct a thorough financial analysis.
Objectives
The objectives of the financial analysis of a company in the case analysis are:
1. To establish the current financial health of the company using data provided in the case.
2. To use conclusions from the financial analysis as one of the metrics to establish whether the company's strategy has been a success.
3. To draw conclusions from the financial analysis about whether the financials rate a constraint on future strategic growth or whether the financials are a facilitator for enhancing future growth.
Ratio Analysis
Profitability, Liquidity, Leverage, and Activity ratios are important, especially the Current Ratio, and Debt-to-Equity ratio. Different industries have different activity ratios that are important, for example, Retail - inventory turnover, sales/square foot; Airlines - cost/seat mile. Identify the activity ratio for the industry covered by the case. Other ratios that may be important: Dividend payout; P/E Some ratios are more relevant if you have the industry ratios
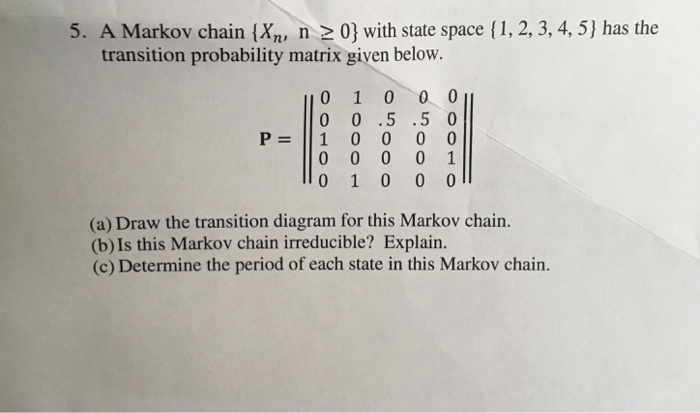
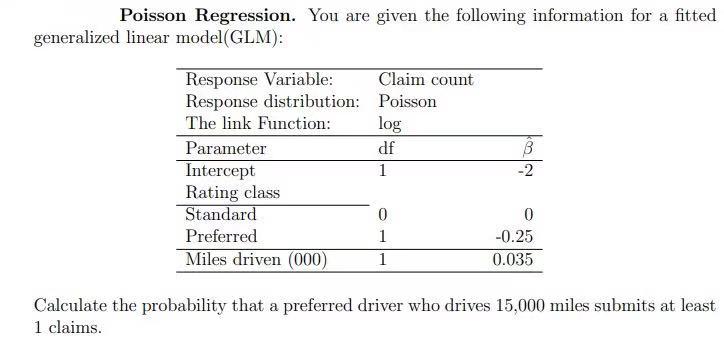

5. A Markov chain {X,, n 2 0} with state space { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 } has the transition probability matrix given below. DO P = Ooouo ooouo OHOOO HOO OOH (a) Draw the transition diagram for this Markov chain. (b) Is this Markov chain irreducible? Explain. (c) Determine the period of each state in this Markov chain.Poisson Regression. You are given the following information for a fitted generalized linear model (GLM): Response Variable: Claim count Response distribution: Poisson The link Function: log Parameter df B Intercept 1 Rating class Standard O Preferred -0.25 Miles driven (000) 0.035 Calculate the probability that a preferred driver who drives 15,000 miles submits at least 1 claims.SECTION 5.2. The Weak Law of Large Numbers Problem 4. In order to estimate f, the true fraction of smokers in a large population. Alvin selects n people at random. His estimator Mn is obtained by dividing Sn, the number of smokers in his sample, by n, i.e., Mn = Sn. Alvin chooses the sample size n to be the smallest possible number for which the Chebyshev inequality yields a guarantee that P(IMn - 1 Z E) 56, where e and o are some prespecified tolerances. Determine how the value of n recom- mended by the Chebyshev inequality changes in the following cases. (a) The value of e is reduced to half its original value. (b) The probability o is reduced to half its original value
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


