Question: second part is simple question second part only the one with an x on it Good Scent, Inc., produces two colognes: Rose and Violet. Of


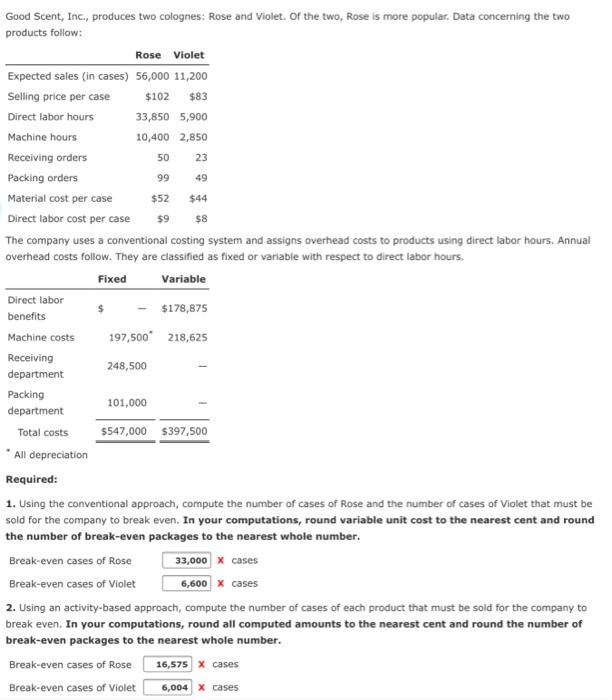
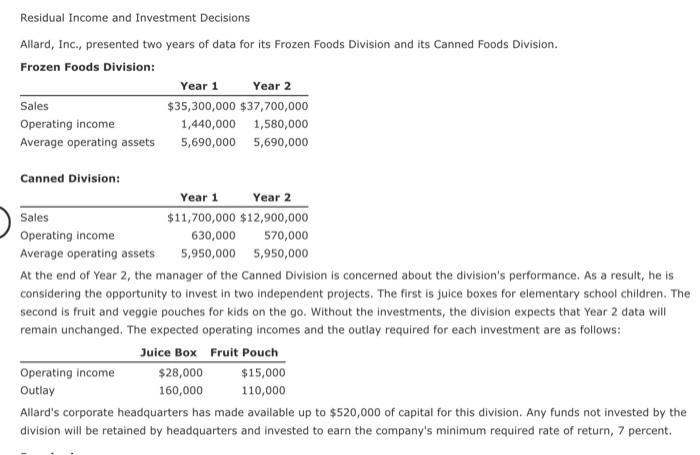
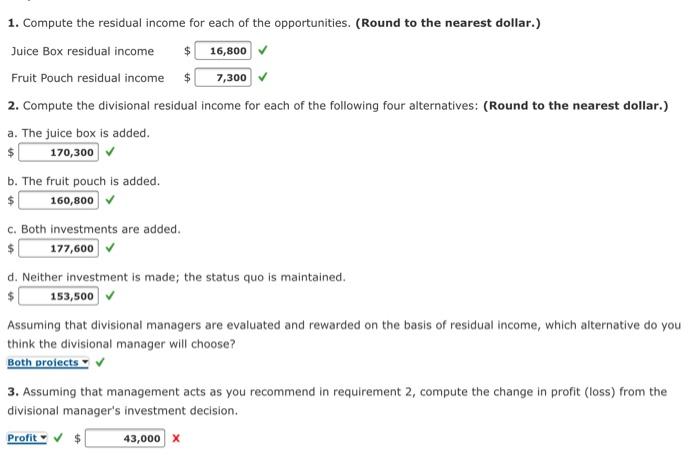
Good Scent, Inc., produces two colognes: Rose and Violet. Of the two, Rose is more popular. Data concerning the two products follow: Rose Violet specte als in $6,000 1,200 Selling proper Direct labor hours 33,850 5.900 Machine bours 10.400 2,850 Heing orders Packing orders Material care Direct labor cost pe care 19 The company uses a conventional costing system and assigns overhead costs to products using direct labor hours. Annual overhead costs follow. They are classified as fixed or variable with respect to direct labor hours. Variable Direct labore Machines 197,500 210.625 Receiving department 24.500 Packing department 101.000 Total costa 507,900 1997.500 All depreciation Required: 1. Using the conventional approach, compute the number of cases of Rose and the number of cases of Violet that must be sold for the company to break even. In your computations, round variable unit cost to the nearest cent and round the number of break-even packages to the nearest whole number. Break-even cases of Rose 33.000 revence of 6.600 X 2. Using an activity-based approach, compute the number of cases of each product that must be sold for the company to break even. In your computations, round all computed amounts to the nearest cent and round the number of break-even packages to the nearest whole number. Break even cases of rose 16,575 x Break even cases of Viet 4,004 X 1. Remember to calculate package contribution margin per unit. 2. Benefits and Machine costs are unit based variable costs. The CVP formula will utilize three costs that utilize X1 (number of packages), X2 (receiving orders), and X3 (packing orders). Sa Operating income Auera peting Year 1 Year 2 $11.700,000 $12,000,000 630,000 570,000 S.950,000 950.000 At the end of Year 2, the manager of the Canned Division is concerned about the division's performance. As a result, he is considering the opportunity to invest in two independent projects. The first is juice boxes for elementary school children. The second is fruit and veggie pouches for kids on the go. Without the investments, the division expects that Year 2 data will remain unchanged. The expected operating Incomes and the outlay required for each investment are as follows: Operating income Outly Juice Berruit Pouch 0.000 125,000 100.000 110,000 Allard's corporate headquarters has made available up to $520,000 of capital for this division. Any funds not invested by the division will be retained by headquarters and invested to earn the company's minimum required rate of return, 7 percent. Required: 1. Compute the residual income for each of the opportunities. (Round to the nearest dollar.) Juce or reduce nie u restrual income 2. Compute the divisional residual income for each of the following four alternatives (Round to the nearest dollar.) a. The juice box is added. 16,000 7.300 1.70,300 b. The fruit pouch is added $ 160.000 c. Both investments are added. 177.600 d. Neither investment is made the status quo is maintained. $ 151.500 Assuming that divisional managers are evaluated and rewarded on the basis of residual income, which alternative do you think the divisional manager will choose? 3. Assuming that management acts as you recommend in requirement 2, compute the change in profit (loss) from the divisional manager's investment decision. Profit 43.000 50 23 99 49 $8 Good Scent, Inc., produces two colognes: Rose and Violet. Of the two, Rose is more popular. Data concerning the two products follow: Rose Violet Expected sales (in cases) 56,000 11,200 Selling price per case $102 $83 Direct labor hours 33,850 5,900 Machine hours 10,400 2,850 Receiving orders Packing orders Material cost per case $52 $44 Direct labor cost per case $9 The company uses a conventional costing system and assigns overhead costs to products using direct labor hours. Annual overhead costs follow. They are classified as fixed or variable with respect to direct labor hours. Fixed Variable Direct labor $178,875 benefits Machine costs 197,500*218,625 Receiving 248,500 department Packing 101,000 department Total costs $547,000 $397,500 * All depreciation Required: 1. Using the conventional approach, compute the number of cases of Rose and the number of cases of Violet that must be sold for the company to break even. In your computations, round variable unit cost to the nearest cent and round the number of break-even packages to the nearest whole number. Break-even cases of Rose 33,000 cases Break-even cases of Violet 6,600 X cases 2. Using an activity-based approach, compute the number of cases of each product that must be sold for the company to break even. In your computations, round all computed amounts to the nearest cent and round the number of break-even packages to the nearest whole number. Break-even cases of Rose 16,575 X cases Break-even cases of Violet 6,004 X cases Residual Income and Investment Decisions Allard, Inc., presented two years of data for its Frozen Foods Division and its Canned Foods Division. Frozen Foods Division: Year 1 Year 2 Sales $35,300,000 $37,700,000 Operating income 1,440,000 1,580,000 Average operating assets 5,690,000 5,690,000 Canned Division: Year 1 Year 2 Sales $11,700,000 $12,900,000 Operating income 630,000 570,000 Average operating assets 5,950,000 5,950,000 At the end of Year 2, the manager of the Canned Division is concerned about the division's performance. As a result, he is considering the opportunity to invest in two independent projects. The first is juice boxes for elementary school children. The second is fruit and veggie pouches for kids on the go. Without the investments, the division expects that year 2 data will remain unchanged. The expected operating incomes and the outlay required for each investment are as follows: Juice Box Fruit Pouch Operating income $28,000 $15,000 Outlay 160,000 110,000 Allard's corporate headquarters has made available up to $520,000 of capital for this division. Any funds not invested by the division will be retained by headquarters and invested to earn the company's minimum required rate of return, 7 percent. $ $ 1. Compute the residual income for each of the opportunities. (Round to the nearest dollar.) Juice Box residual income 16,800 Fruit Pouch residual income 7,300 2. Compute the divisional residual income for each of the following four alternatives: (Round to the nearest dollar.) a. The juice box is added. $ 170,300 b. The fruit pouch is added. $ 160,800 c. Both investments are added. 177,600 d. Neither investment is made; the status quo is maintained. 153,500 Assuming that divisional managers are evaluated and rewarded on the basis of residual income, which alternative do you think the divisional manager will choose? Both projects 3. Assuming that management acts as you recommend in requirement 2, compute the change in profit (loss) from the divisional manager's investment decision. Profit $ 43,000 x
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


