Question: Section 1, Compulsory (a) The table below shows the potential-determining equilibrium (PDE) and standard electrode potential for each of the left-hand side (LHS) and right-hand
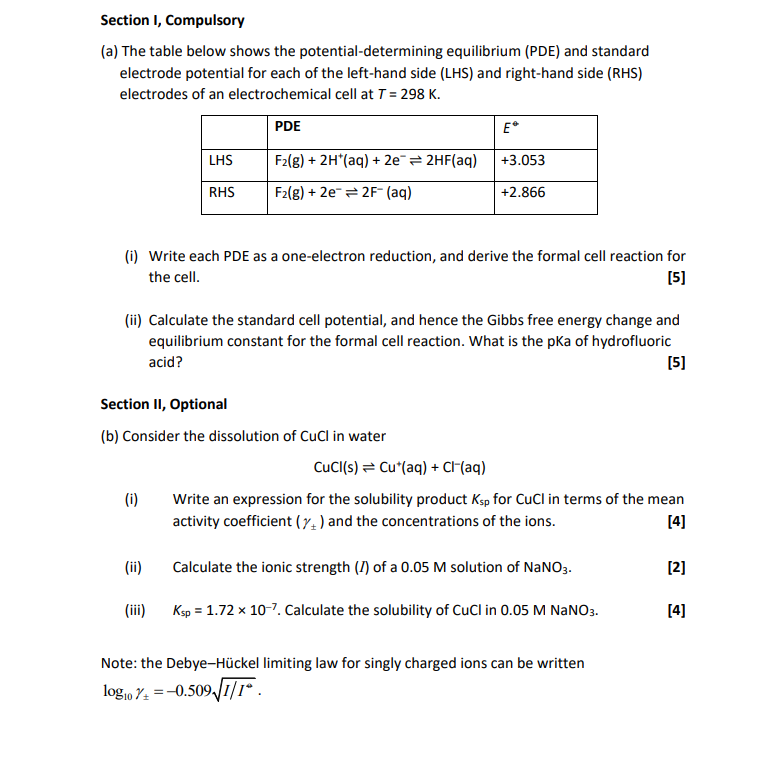
Section 1, Compulsory (a) The table below shows the potential-determining equilibrium (PDE) and standard electrode potential for each of the left-hand side (LHS) and right-hand side (RHS) electrodes of an electrochemical cell at T = 298 K. PDE E* LHS F2(g) + 2H+ (aq) + 2e = 2HF(aq) +3.053 RHS F2(g) + 2e = 2F- (aq) + +2.866 (i) Write each PDE as a one-electron reduction, and derive the formal cell reaction for the cell. [5] (ii) Calculate the standard cell potential, and hence the Gibbs free energy change and equilibrium constant for the formal cell reaction. What is the pka of hydrofluoric acid? [5] Section II, Optional (b) Consider the dissolution of Cucl in water CuCl(s) = Cu*(aq) + CI+(aq) (i) Write an expression for the solubility product Ksp for CuCl in terms of the mean activity coefficient (Y) and the concentrations of the ions. [4] (ii) Calculate the ionic strength (I) of a 0.05 M solution of NaNO3. 121 (iii) Ksp = 1.72 x 10-7. Calculate the solubility of CuCl in 0.05 M NaNO3. [4] Note: the Debye-Hckel limiting law for singly charged ions can be written logio 7: = -0.509/I/I
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


