Question: Section 1: The Stack class (20 points) This class represents the stack data structure discussed in this module. Use the implementation of the Node class
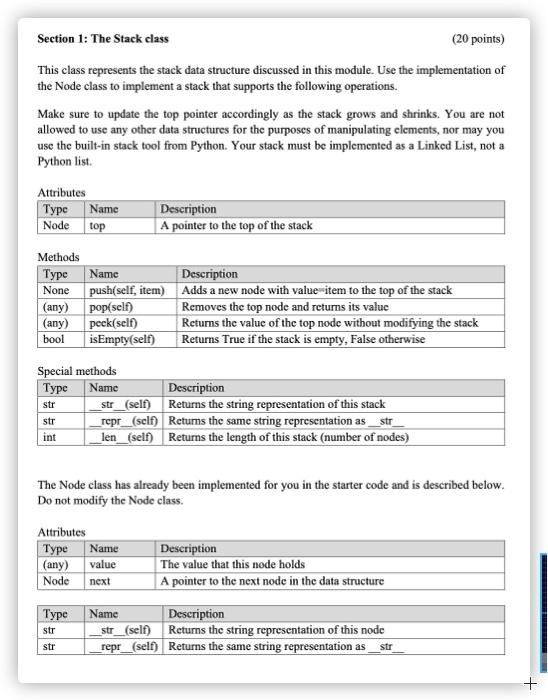

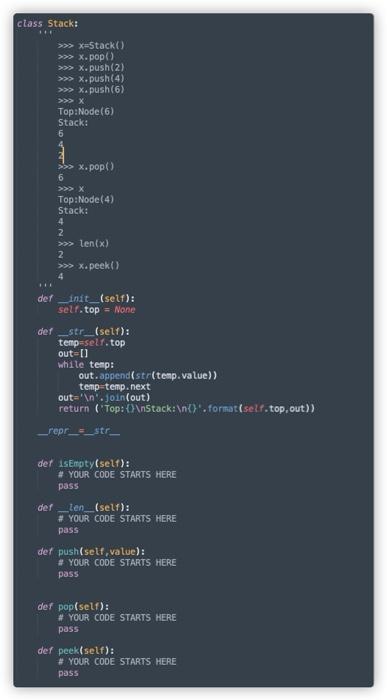
Section 1: The Stack class (20 points) This class represents the stack data structure discussed in this module. Use the implementation of the Node class to implement a stack that supports the following operations. Make sure to update the top pointer accordingly as the stack grows and shrinks. You are not allowed to use any other data structures for the purposes of manipulating elements, nor may you use the built-in stack tool from Python. Your stack must be implemented as a Linked List, not a Python list. Attributes Type Name Node top Description A pointer to the top of the stack Methods Type Name Description None push(self, item) Adds a new node with value-item to the top of the stack (any) pop(self) Removes the top node and returns its value (any) peek(self) Returns the value of the top node without modifying the stack bool isEmpty(self) Returns True if the stack is empty, False otherwise Special methods Type Name Description str_(self) Returns the string representation of this stack str _repr_(self) Returns the same string representation as int _len_(self) Returns the length of this stack (number of nodes) str str The Node class has already been implemented for you in the starter code and is described below. Do not modify the Node class. Attributes Type Name (any) value Node next Description The value that this node holds A pointer to the next node in the data structure Type str Name Description _str_(self) Returns the string representation of this node repr_(self) Returns the same string representation as str str + push(self, item) Adds a new node with value=item to the top of the stack. Nothing is returned by this method. Input (excluding self) (any) item The value to store in a node pop(self) Removes the top node from the stack and returns that node's value (not the Node object). Output (any) Value held in the topmost node of the stack None Nothing is returned if the stack is empty peek(self) Returns the value (not the Node object) of the topmost node of the stack, but it is not removed. Output (any) Value held in the topmost node of the stack None Nothing is returned if the stack is empty isEmpty(self) Tests to see whether this stack is empty or not. Output bool True if this stack is empty, False otherwise _len_(self) Returns the number of elements in this stack. Output int The number of elements in this stack _str_(self), _repr_(self) Returns the string representation of this stack. This has already been implemented for you, so do not modify it. If the class is implemented correctly, _str_ and _repr_display the contents of the stack in the format shown in the doctest. Output The string representation of this stack str class Stack: >>> X Stack >>> X.pop() >>> X.push(2) >>> X.push(4) >>> X.push(6) >>> X Top:Node (6) Stack: 6 >> X.pop() 6 Top:Node(4) Stack: 4 2 >>> Len(x) 2 >>> X.peek() 4 def __init__(self): sell.top = None def_str_(self): temp=self.top out-0) while temp: out.append(str(temp.value)) tempatemp. next out=' '.join(out) return (Top: OnStack: t.format(self.top,out) repr_=_str_ der isEmpty(self): # YOUR CODE STARTS HERE pass def_len_(self): # YOUR CODE STARTS HERE pass det push(self, value): # YOUR CODE STARTS HERE pass def pop(self): # YOUR CODE STARTS HERE pass def peek(self): # YOUR CODE STARTS HERE pass
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


