Question: Section 11.3 I Question 1 B on pt '0 2 8 98 G) Details Migraine and Acupuncture: A migraine is a particularly painful type of
Section 11.3
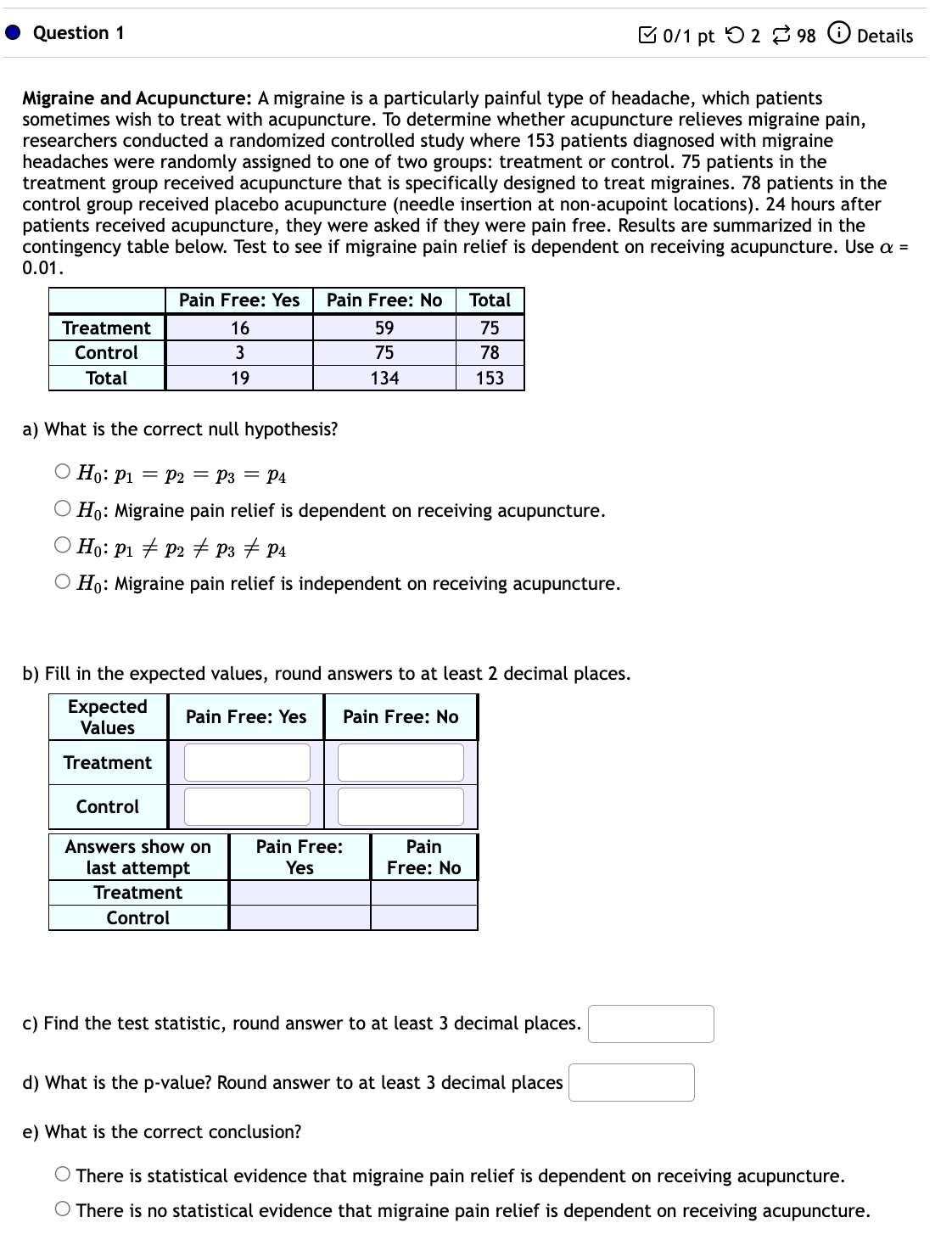
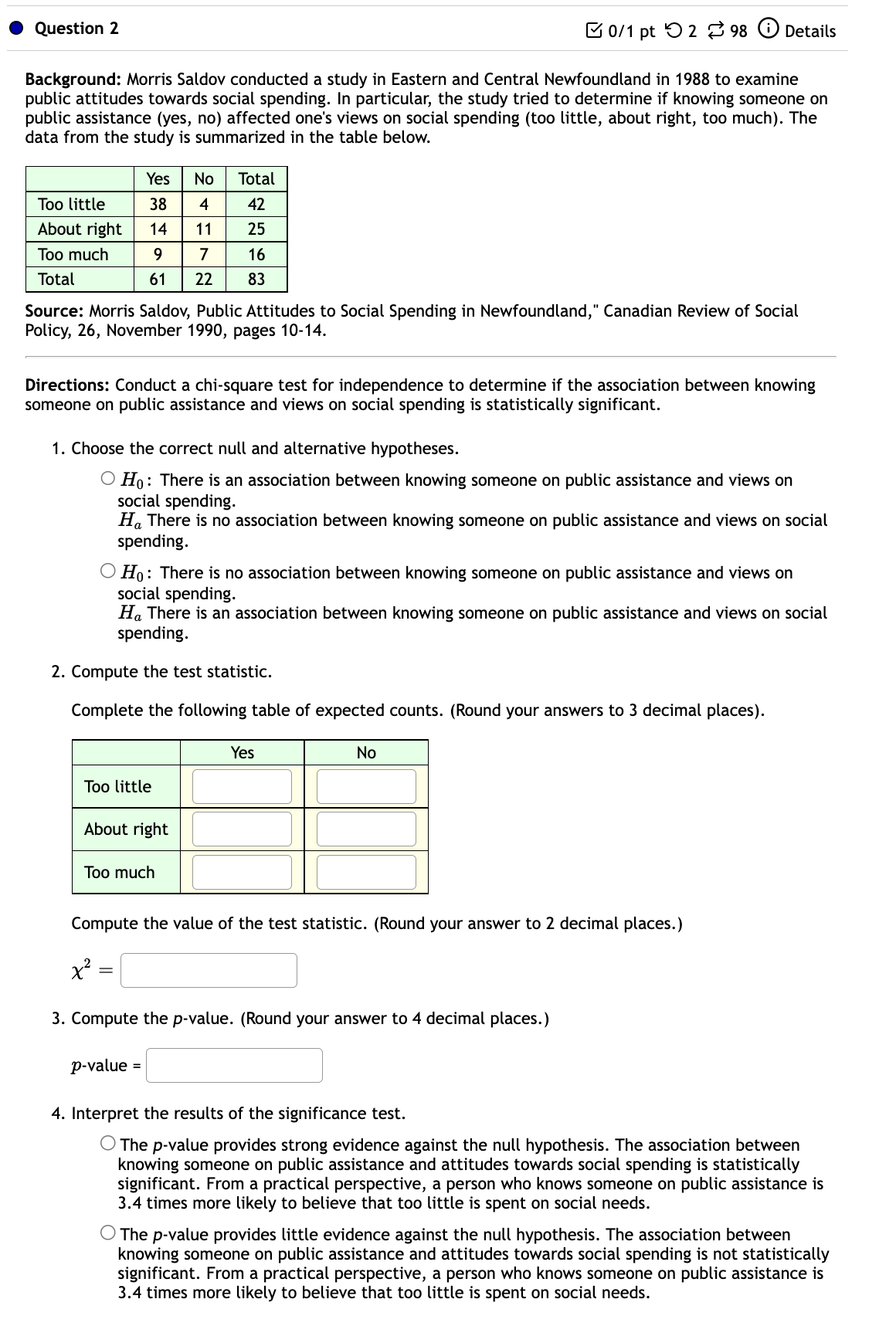
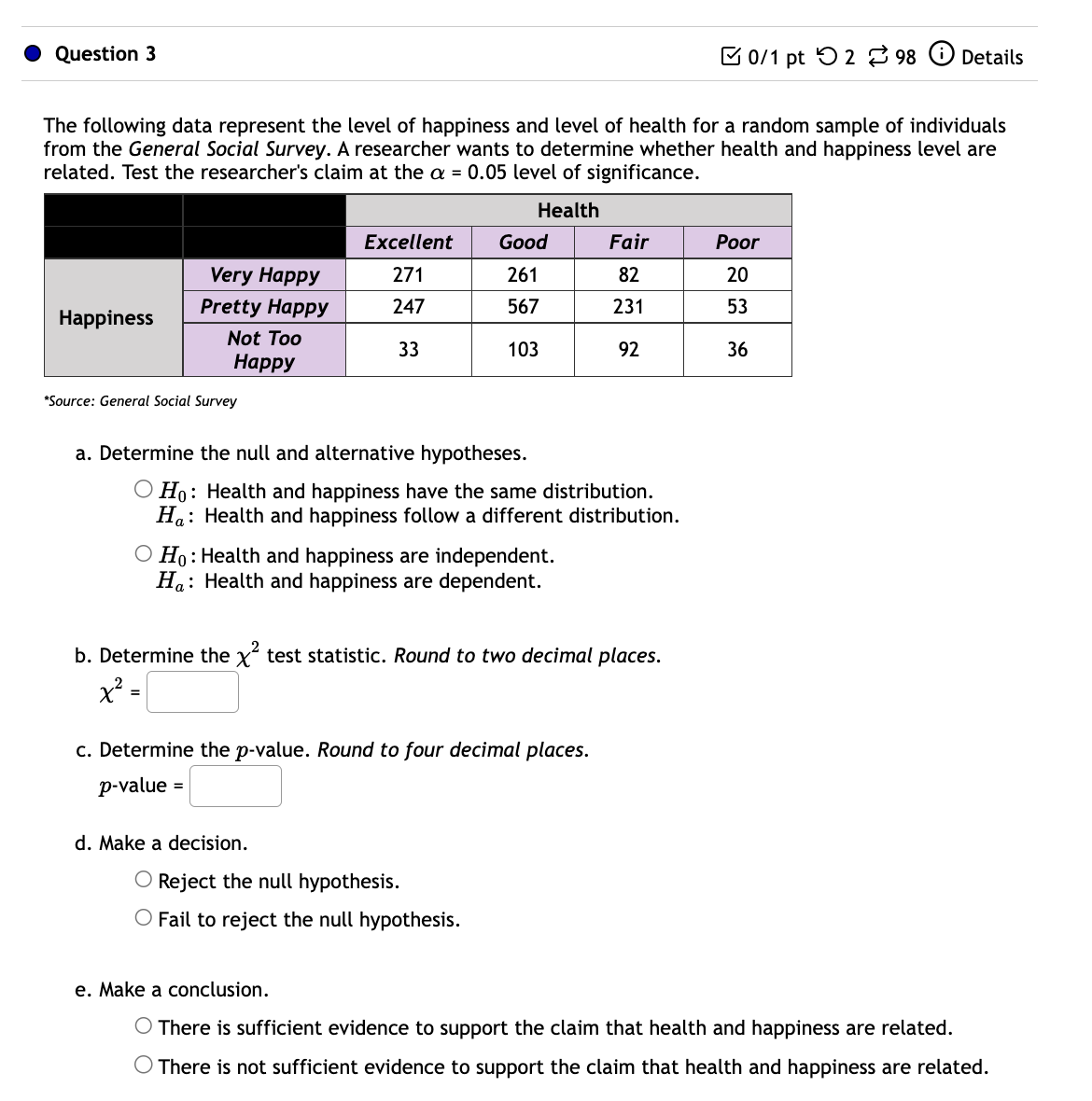

I Question 1 B on pt '0 2 8 98 G) Details Migraine and Acupuncture: A migraine is a particularly painful type of headache, which patients sometimes wish to treat with acupuncture. To determine whether acupuncture relieves migraine pain, researchers conducted a randomized controlled study where 153 patients diagnosed with migraine headaches were randomly assigned to one of two groups: treatment or control. 75 patients in the treatment group received acupuncture that is specifically designed to treat migraines. 78 patients in the control group received placebo acupuncture (needle insertion at non-acupoint locations). 24 hours after patients received acupuncture, they were asked if they were pain free. Results are summarized in the contingency table below. Test to see if migraine pain relief is dependent on receiving acupuncture. Use a = 0.01. _ Pain Free: Yes Pain Free: No _\"- Control 3 75 78 Total 19 134 153 a) What is the correct null hypothesis? OHo=p1 =P2=P3=P4 O HO: Migraine pain relief is dependent on receiving acupuncture. OHo=p1 #102 #93 a 104 O Ho: Migraine pain relief is independent on receiving acupuncture. b) Fill in the expected values, round answers to at least 2 decimal places. Expected Pain Free: Yes Pain Free: No Values Treatment Control Answers show on Pain Free: Pain last attempt Yes Free: No Treatment Control c) Find the test statistic, round answer to at least 3 decimal places. C] d) What is the p-value? Round answer to at least 3 decimal places C] e) What is the correct conclusion? 0 There is statistical evidence that migraine pain relief is dependent on receiving acupuncture. C) There is no statistical evidence that migraine pain relief is dependent on receiving acupuncture. 0 Question 2 E 0/1 pt '0 2 3 98 6) Details Background: Morris Saldov conducted a study in Eastern and Central Newfoundland in 1988 to examine public attitudes towards social spending. In particular, the study tried to determine if knowing someone on public assistance (yes, no) affected one's views on social spending (too little, about right, too much). The data from the study is summarized in the table below. Yes No Total Too little About right Too much Total Source: Morris Saldov, Public Attitudes to Social Spending in Newfoundland," Canadian Review of Social Policy, 26, November 1990, pages 10-14. Directions: Conduct a chi-square test for independence to determine if the association between knowing someone on public assistance and views on social spending is statistically significant. 1. Choose the correct null and alternative hypotheses. O Ho: There is an association between knowing someone on public assistance and views on social spending. Ha There is no association between knowing someone on public assistance and views on social spending. 0 Ho: There is no association between knowing someone on public assistance and views on social spending. Ha There is an association between knowing someone on public assistance and views on social spending. 2. Compute the test statistic. Complete the following table of expected counts. (Round your answers to 3 decimal places). Yes No Too little l ' About right l l Too much ' ' Compute the value of the test statistic. (Round your answer to 2 decimal places.) 3. Compute the p-value. {Round your answer to 4 decimal places.) 4. Interpret the results of the significance test. 0 The p-value provides strong evidence against the null hypothesis. The association between knowing someone on public assistance and attitudes towards social spending is statistically significant. From a practical perspective, a person who knows someone on public assistance is 3.4 times more likely to believe that too little is spent on social needs. 0 The p-value provides little evidence against the null hypothesis. The association between knowing someone on public assistance and attitudes towards social spending is not statistically significant. From a practical perspective, a person who knows someone on public assistance is 3.4 times more likely to believe that too little is spent on social needs. 0 Question 3 B 0/1 pt '0 2 8 98 6) Details The following data represent the level of happiness and level of health for a random sample of individuals from the General Social Survey. A researcher wants to determine whether health and happiness level are related. Test the researcher's claim at the a = 0.05 level of significance. Excellent Very Happy Pretty Happy Happiness 'Source: General Social Surveyr a. Determine the null and alternative hypotheses. O HO: Health and happiness have the same distribution. Ha: Health and happiness follow a different distribution. 0 H0 : Health and happiness are independent. Ha: Health and happiness are dependent. b. Determine the x2 test statistic. Round to two decimal places. 2 x = C] c. Determine the p-value. Round to four decimal places. d. Make a decision. 0 Reject the null hypothesis. 0 Fail to reject the null hypothesis. e. Make a conclusion. 0 There is sufficient evidence to support the claim that health and happiness are related. 0 There is not sufficient evidence to support the claim that health and happiness are related. 0 Question 4 8 0:1 pt '0 2 8 98 G) Details The following data represent a sample of people's smoking habits and their usage of seat belts while in a car. A researcher wants to determine whether smoking habits and seat belt usage are related. Test the researchers claim at the a = 0.05 level of significance. No Seat Belt Seat Belt Smoke 67 448 Do not Smoke 327 2,187 'Source: Harris Poll a. Determine the null and alternative hypotheses. O HO: Smoking habits and seat belt usage have the same distribution. Ha: Smoking habits and seat belt usage follow a different distribution. 0 H0 : Smoking habits and seat belt usage are independent. Ha: Smoking habits and seat belt usage are dependent. b. Determine the test Statistic. Round to two decimal places. 2 x = C] c. Determine the p-value. Round to four decimal places. d. Make a decision. 0 Fail to reject the null hypothesis. 0 Reject the null hypothesis. e. Make a conclusion. 0 There is sufficient evidence to support the claim that smoking habits and seat belt usage are related. 0 There is not sufficient evidence to support the claim that smoking habits and seat belt usage are related
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


