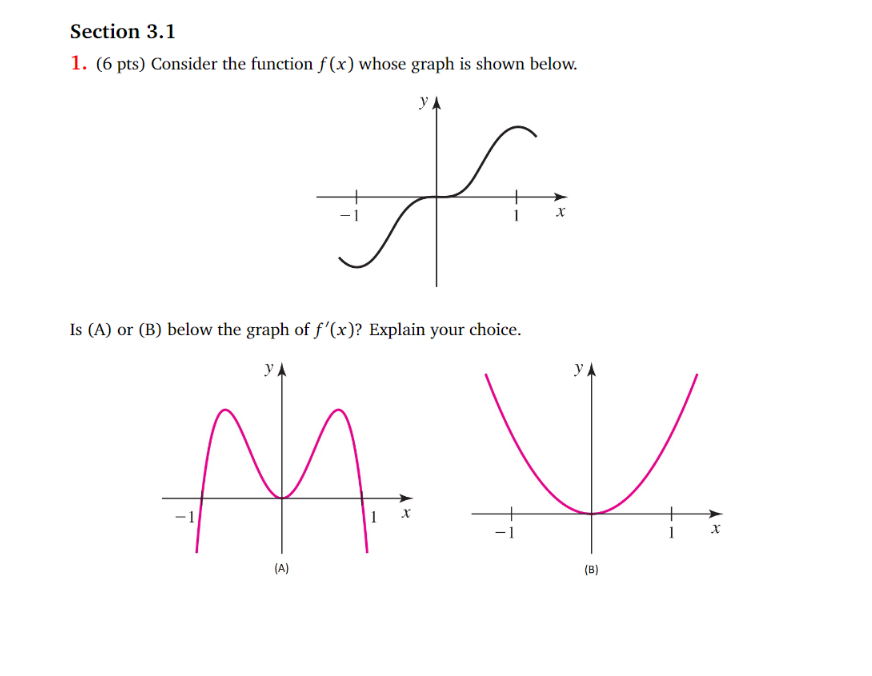
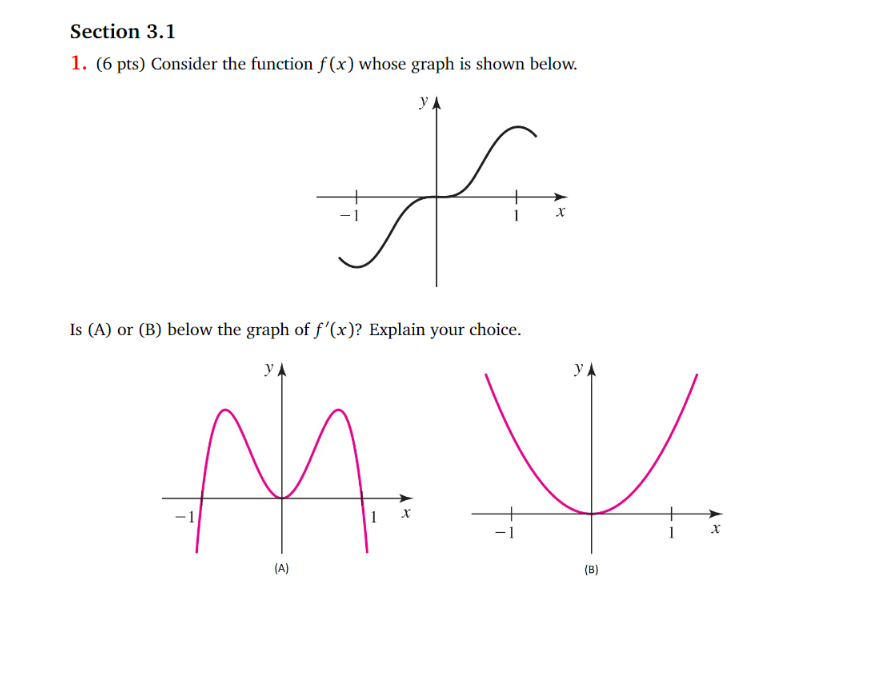
Question: Section 3.1 1. (6 pts) Consider the function f (x) whose graph is shown below. X Is (A) or (B) below the graph of f'(x)?





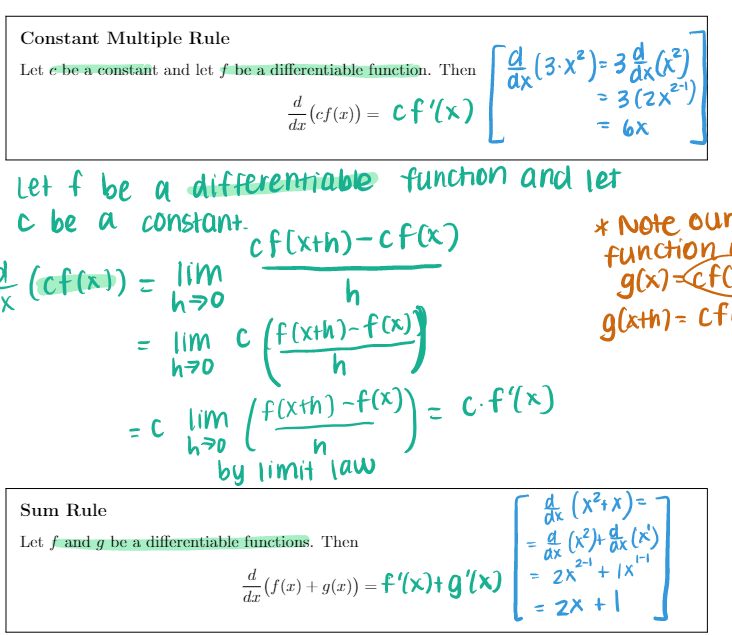
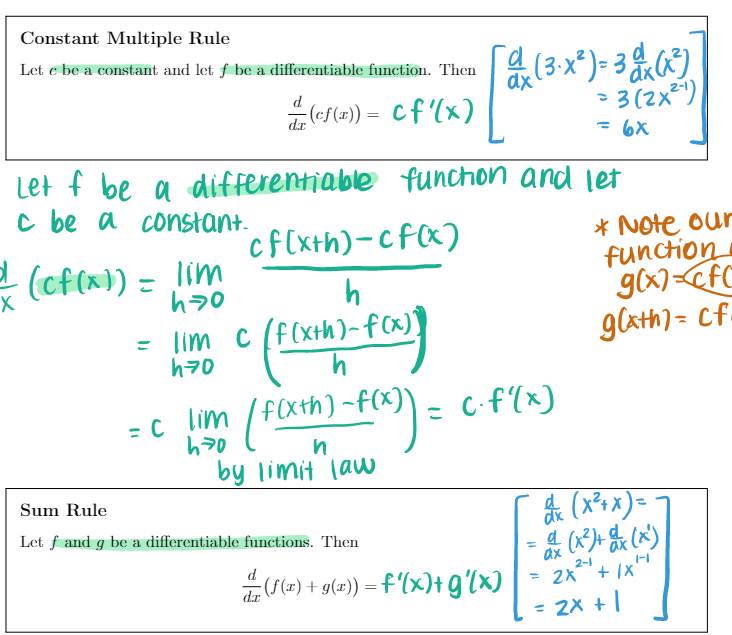
![c ( f (xth)-f ( x)] g lath ) = cf h70](https://s3.amazonaws.com/si.experts.images/answers/2024/06/6667d34b7f8c2_3316667d34b6dd8f.jpg)
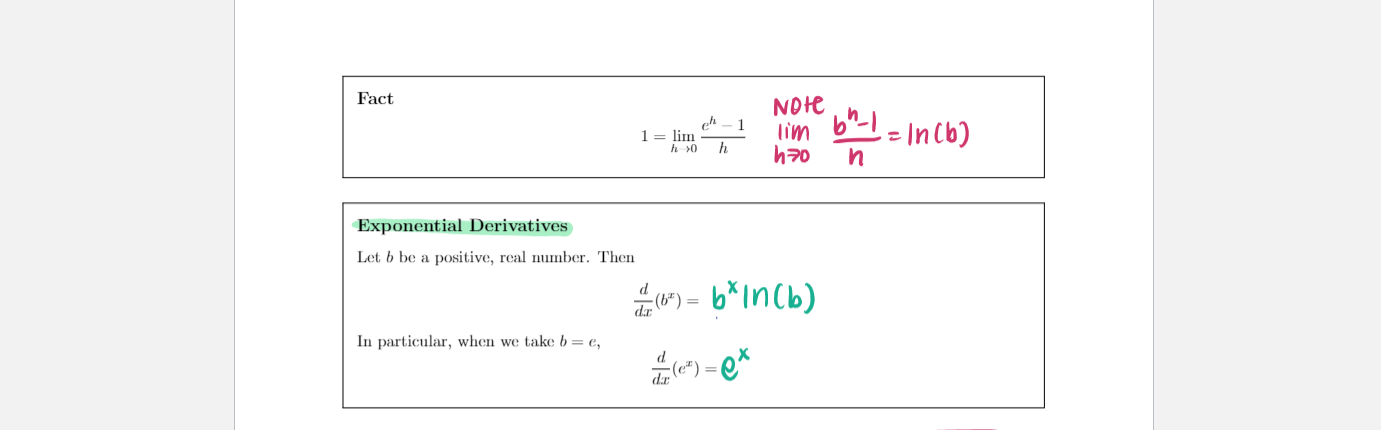
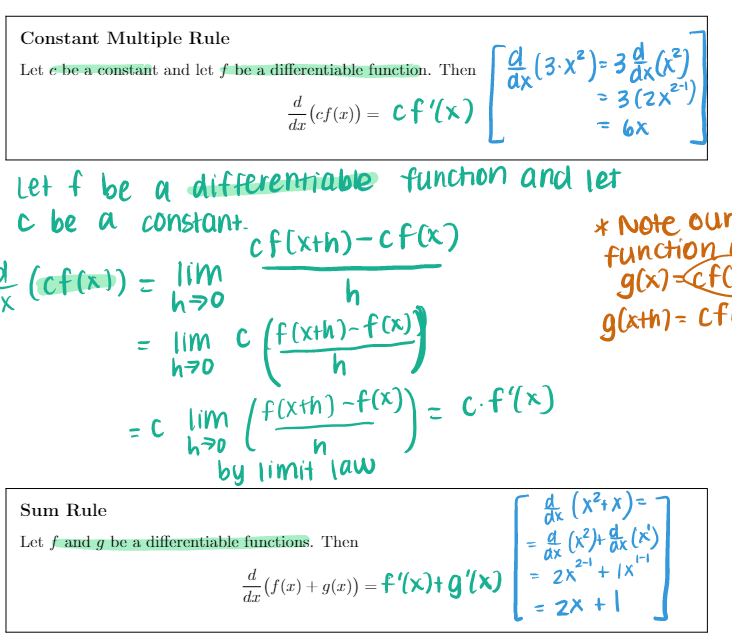
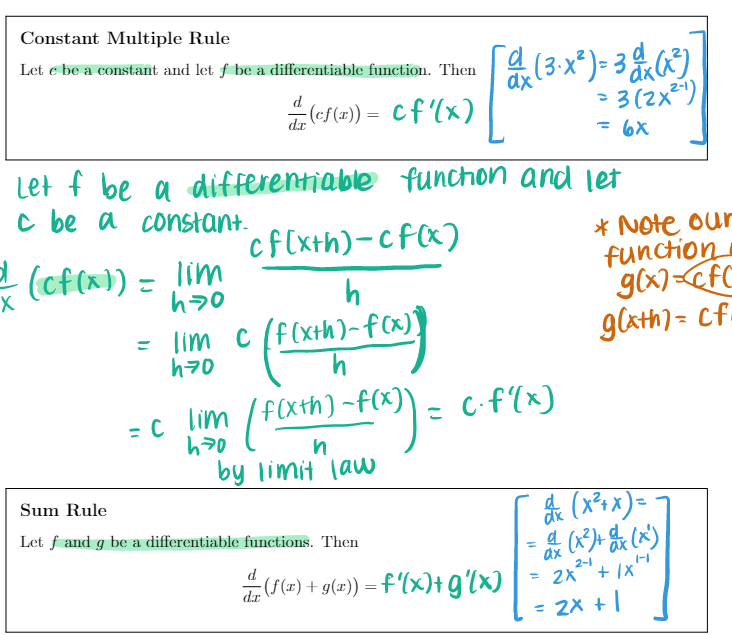
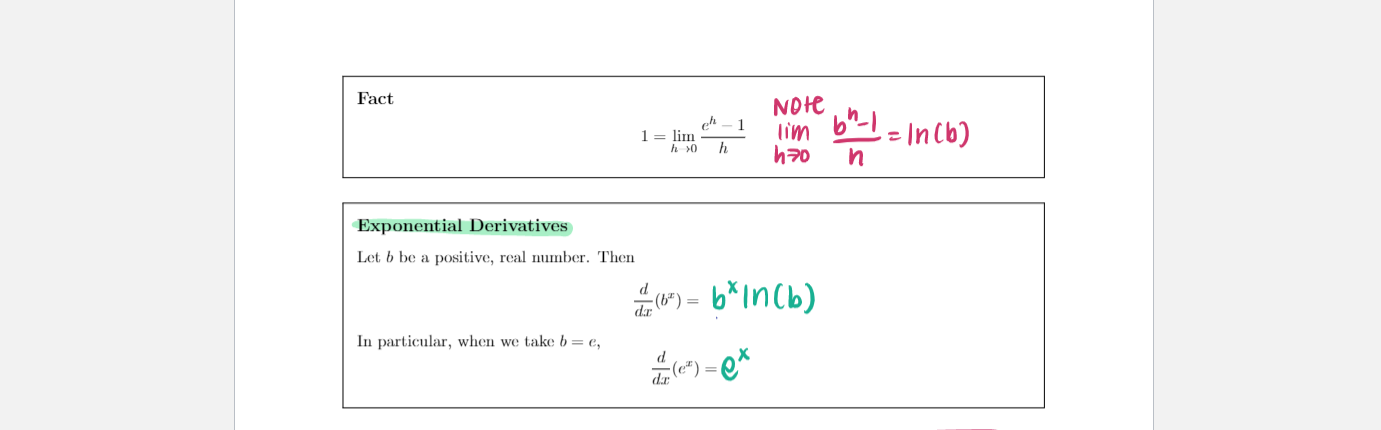
Section 3.1 1. (6 pts) Consider the function f (x) whose graph is shown below. X Is (A) or (B) below the graph of f'(x)? Explain your choice. VA Y x (A) (B)\fTheorem Let n be a real number. d n-1 That Is , dar (1" ) = n x ax ( X5 ) = 5X = 5x*Constant Multiple Rule Let c be a constant and let f be a differentiable function. Then ax ( 3 . x 2 ) = 3 x ( x 3) " ( cf ( I ) ) = cf' (x ) = 3 (2 x2-1 ) = 6X Let f be a differentiable function and let c be a constant. cf [ xth) - cf ( x ) * Note our X (cf ( x) ) = lim function h g ( x ) =cf = lim c ( f (xth)-f ( x)] g lath ) = cf h70 h = c lim ( f(xth) - f ( x ) ) _ c.f(x ) h70 n by limit law Sum Rule ax ( x2 + x ) Let f and g be a differentiable functions. Then a ( * 3 )+ dx ( x ) + (f(x) + g(2)) =f'(x)+g'(x) = 2X + 1X = 2X + 1Constant Multiple Rule Let c be a constant and let f be a differentiable function. Then ax ( 3 . x 2 ) = 3 x ( x 3) " ( cf ( I ) ) = cf' (x ) = 3 (2 x2-1 ) = 6X Let f be a differentiable function and let c be a constant. cf [ xth) - cf ( x ) * Note our X (cf ( x) ) = lim function h g ( x ) =cf = lim c ( f (xth)-f ( x)] g lath ) = cf h70 h = c lim ( f(xth) - f ( x ) ) _ c.f(x ) h70 n by limit law Sum Rule ax ( x2 + x ) Let f and g be a differentiable functions. Then a ( * 3 )+ dx ( x ) + (f(x) + g(2)) =f'(x)+g'(x) = 2X + 1X = 2X + 1\fFact Note 1 = lim lim 6" - 1 h >0 h = In (b) h7o n Exponential Derivatives Let b be a positive, real number. Then 1- (6* ) = 6* in (b) In particular, when we take b = e, do (*) = ex
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


