Question: Section-B Answer the following independent questions including computations (if needed) or examples supporting your answers. I. Consider the following three government bonds: Bond Bond Price
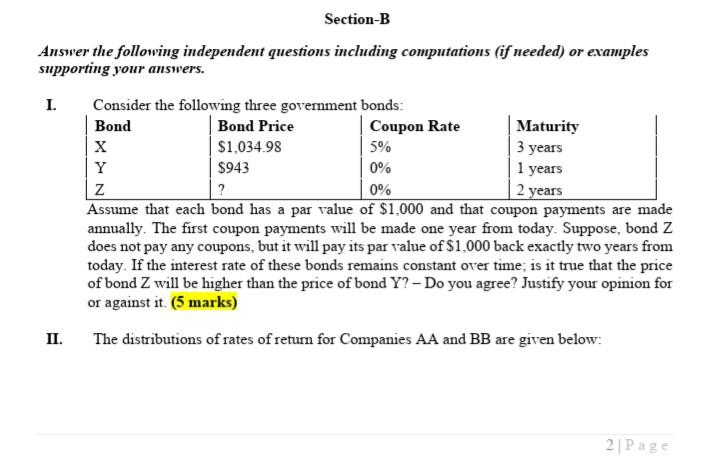
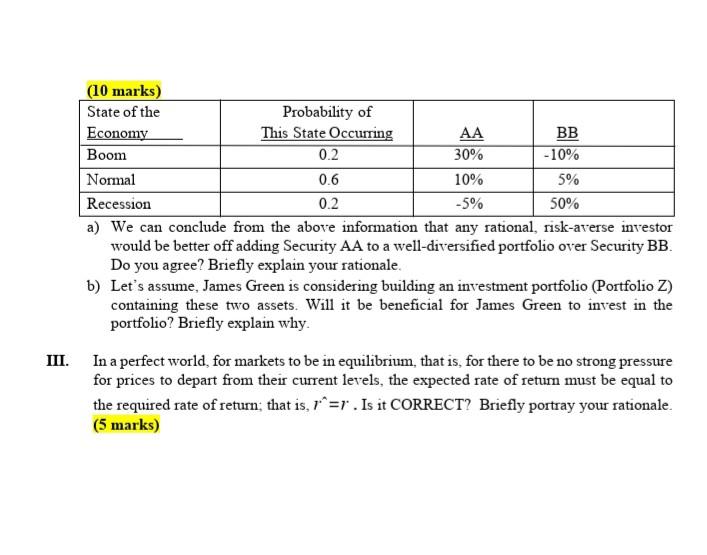
Section-B Answer the following independent questions including computations (if needed) or examples supporting your answers. I. Consider the following three government bonds: Bond Bond Price Coupon Rate Maturity X $1,034.98 5% 3 years Y $943 0% 1 years z ? 0% 2 years Assume that each bond has a par value of $1,000 and that coupon payments are made annually. The first coupon payments will be made one year from today. Suppose, bond Z does not pay any coupons, but it will pay its par value of $1.000 back exactly two years from today. If the interest rate of these bonds remains constant over time is it true that the price of bond Z will be higher than the price of bond Y? - Do you agree? Justify your opinion for or against it. (5 marks) II. The distributions of rates of return for Companies AA and BB are given below: 2 Page (10 marks) State of the Probability of Economy This State Occurring AA BB Boom 0.2 30% -10% Normal 0.6 10% 5% Recession 0.2 -5% 50% a) We can conclude from the above information that any rational, risk-averse investor would be better off adding Security AA to a well-diversified portfolio over Security BB. Do you agree? Briefly explain your rationale. b) Let's assume, James Green is considering building an investment portfolio (Portfolio Z) containing these two assets. Will it be beneficial for James Green to invest in the portfolio? Briefly explain why. III. In a perfect world for markets to be in equilibrium, that is, for there to be no strong pressure for prices to depart from their current levels, the expected rate of return must be equal to the required rate of return; that is, r=r. Is it CORRECT? Briefly portray your rationale
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


