Question: See the question below (iii) An option value V satisfies the Black-Scholes equation av 022321/ av 5+388824TSTV0, where a is the volatility, and r(t) is
See the question below
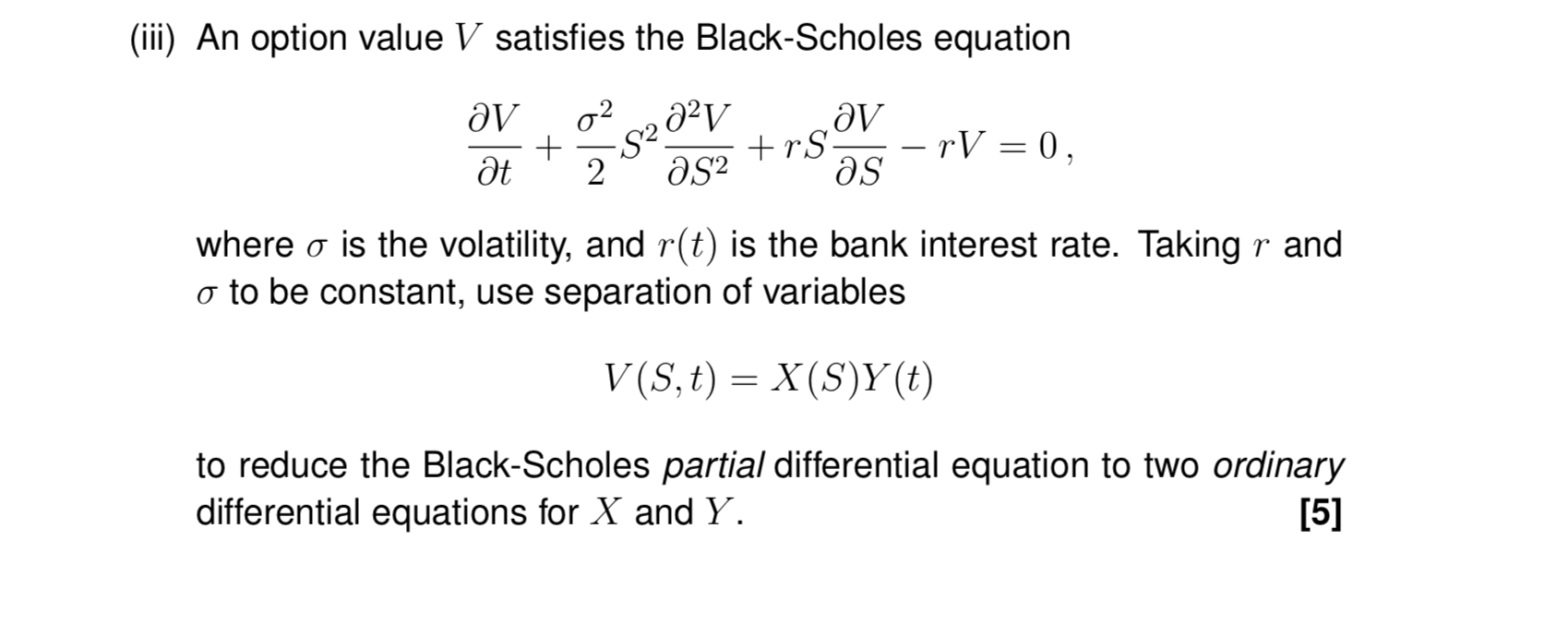
(iii) An option value V satisfies the Black-Scholes equation av 022321/ av 5+388824TSTV0, where a is the volatility, and r(t) is the bank interest rate. Taking r and a to be constant, use separation of variables V(S, t) = X(S)Y(t) to reduce the Black-Scholes partial differential equation to two ordinary differential equations for X and Y. [5]
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


